글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2023년 07월호
[Ann Surg Oncol .] Survival After Breast-Conserving Surgery Compared with that After Mastectomy in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
울산의대 / 곽성찬, 이새별*
- 출처
- Ann Surg Oncol .
- 등재일
- 2023 May
- 저널이슈번호
- 30(5):2845-2853. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-12993-0. Epub 2022 Dec 28.
- 내용
Abstract
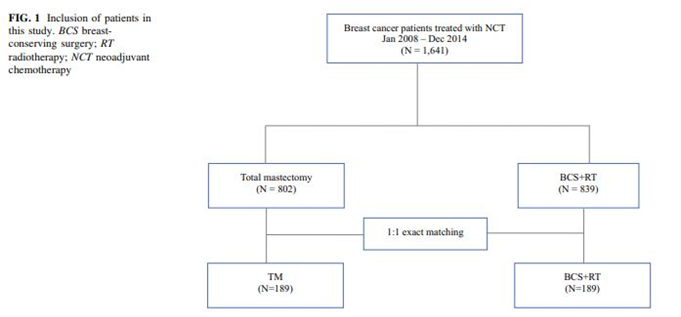
Background: Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) plus radiotherapy (BCS + RT) has been shown to improve survival compared with mastectomy in patients with early breast cancer; however, whether this superiority is maintained in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT) is unclear. We evaluated and compared the survival outcomes after BCS + RT and mastectomy in Korean women with breast cancer treated with NCT.Methods: We evaluated 1641 patients who received NCT before surgery (BCS or mastectomy). We performed propensity score matching to minimize potential bias due to factors other than the surgical method and compared the 5-year, disease-free survival (DFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and overall survival (OS) rates before and after exact matching.
Results: Among the 1641 patients, 839 (51.1%) underwent BCS + RT and 802 (48.9%) underwent mastectomy. Patients who underwent mastectomy had larger tumors and more frequently had positive nodes. For BCS+RT and mastectomy, the unadjusted 5-year DFS, 5-year DMFS, and 5-year OS rates were 87.0% and 73.1%, 89.5% and 77.0%, and 91.8% and 81.0%, respectively (all p < 0.05 = 0.000). After PSM, 5-year DFS, 5-year DMFS, and 5-year OS rates for BCS + RT and mastectomy were 87.6% and 69.1%, 89.7% and 76.0%, and 89.1% and 75.7%, respectively (all p < 0.05). In both unadjusted and adjusted analyses accounting for various confounding factors, BCS + RT was significantly associated with improved DFS (p < 0.05), DMFS (p < 0.05), and OS (p < 0.05) rates compared with mastectomy.
Conclusions: BCS + RT does not impair DFS and OS in patients treated with NCT. Tumor biology and treatment response are significant prognostic indicators. Our results suggest that BCS + RT may be preferred in most breast cancer patients when both BCS and mastectomy are suitable.
Affiliations
Sungchan Gwark 1, Hwa Jung Kim 2, Jisun Kim 3, Il Yong Chung 3, Hee Jeong Kim 3, Beom Seok Ko 3, Jong Won Lee 3, Byung Ho Son 3, Sei Hyun Ahn 1, Sae Byul Lee 4
1Department of Surgery, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, South Korea.
2Department of Biostatistics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
3Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. newstar153@hanmail.net.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Int Wound J .] Early outcomes of complete excision followed by immediate postoperative single fractional 10 Gy for anterior chest keloids: A preliminary results
- 다음글 [Neoplasia .] Neural network based ensemble model to predict radiation induced lymphopenia after concurrent chemo-radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer from two institutions








편집위원
유방암에서 선행항암화학요법 후 유방보존술 및 방사선치료를 받은 환자와 유방전절제술을 시행받은 환자를 단일기관의 자료를 이용하여 후향적으로 비교하였고, 성향점수매칭을 하여 비교했을 때에도 유방보존수술 및 방사선치료를 받은 환자군의 무병생존율과 전체생존율이 우월함을 보여줌
덧글달기닫기2023-07-04 15:13:44
등록