글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2023년 07월호
[Neoplasia .] Neural network based ensemble model to predict radiation induced lymphopenia after concurrent chemo-radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer from two institutions연세의대, KAIST / 김예진, 윤홍인*, 조승룡*
- 출처
- Neoplasia .
- 등재일
- 2023 May
- 저널이슈번호
- 39:100889. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2023.100889. Epub 2023 Mar 15.
- 내용
Abstract
The use of adjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) after concurrent chemo-radiation therapy (CCRT) has become the standard of care for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (LA-NSCLC). However, prolonged radiotherapy regimens are known to cause radiation-induced lymphopenia (RIL), a long-neglected toxicity that has been shown to correlate with response to ICIs and survival of patients treated with adjuvant ICI after CCRT.In this study, we aim to develop a novel neural network (NN) approach that integrates patient characteristics, treatment related variables, and differential dose volume histograms (dDVH) of lung and heart to predict the incidence of RIL at the end of treatment. Multi-institutional data of 139 LA-NSCLC patients from two hospitals were collected for training and validation of our suggested model. Ensemble learning was combined with a bootstrap strategy to stabilize the model, which was evaluated internally using repeated cross validation.
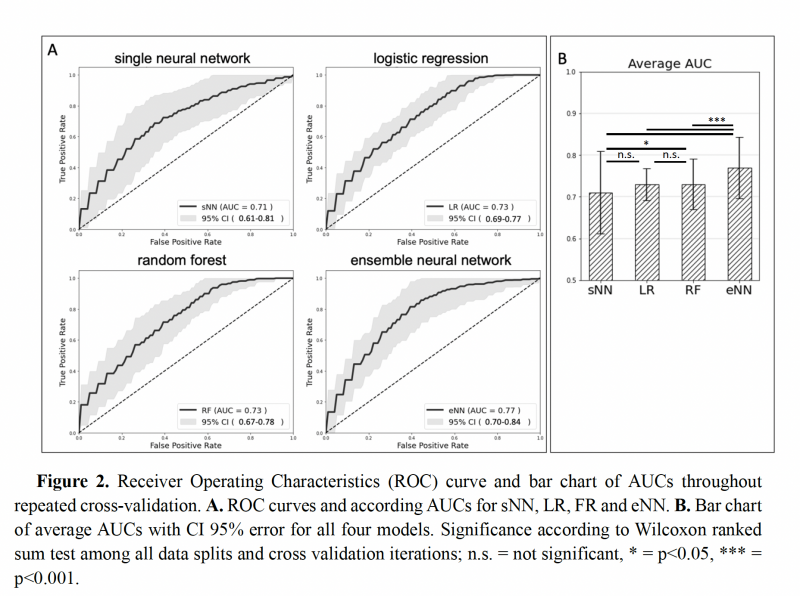
The performance of our proposed model was compared to conventional models using the same input features, such as Logistic Regression (LR) and Random Forests (RF), using the Area Under the Curve (AUC) of Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curves. Our suggested model (AUC=0.77) outperformed the comparison models (AUC=0.72, 0.74) in terms of absolute performance, indicating that the convolutional structure of the network successfully abstracts additional information from the differential DVHs, which we studied using Gradient-weighted Class Activation Map.
This study shows that clinical factors combined with dDVHs can be used to predict the risk of RIL for an individual patient and shows a path toward preventing lymphopenia using patient-specific modifications of the radiotherapy plan.
Affiliations
Yejin Kim 1, Ibrahim Chamseddine 2, Yeona Cho 3, Jin Sung Kim 4, Radhe Mohan 5, Nadya Shusharina 2, Harald Paganetti 2, Steven Lin 5, Hong In Yoon 6, Seungryong Cho 7, Clemens Grassberger 2
1Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea; Department of Radiation Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
4Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University Health System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5Division of Radiation Oncology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA.
6Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University Health System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: yhi0225@yuhs.ac.
7Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea. Electronic address: scho@kaist.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Chemo-radiotherapy; Immunotherapy; Prediction model; Radiation-induced lymphopenia.
- 연구소개
- 미국과 한국에서 화학-방사선치료를 받은 비소세포성폐암 환자에 대하여 치료 후 방사선으로 인한 림프구감소증 (radiation-induced lymphopenia)의 발생 여부를 치료 전에 미리 예측하는 인공지능 알고리즘을 개발하였습니다. 방사선으로 인한 림프구감소증은 치료 후 환자의 생존에도 크게 영향을 미치는 주요 부작용입니다. 이에 본 연구팀은 인공지능을 이용해 치료가 시작되기 전에 환자의 특성과 치료계획등을 종합적으로 분석하여 미리 환자별 부작용 여부를 예측하는 연구를 하였습니다. 이는 미래 의료가 지향하는 정밀치료로 한걸음 더 나아가는 의미있는 연구라 생각됩니다.
- 덧글달기







