글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2023년 04월호
[J Pers Med.] Evaluation of Pretreatment Albumin-Bilirubin Grade as a Better Prognostic Factor Compared to Child-Pugh Classification in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Radiotherapy
성균관의대 / 이준복, 박준수, 이혜빈*, 남희림*
- 출처
- J Pers Med.
- 등재일
- 2023 Feb 17
- 저널이슈번호
- 13(2):354. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020354.
- 내용
Abstract
This study assessed the use of pretreatment albumin--bilirubin (ALBI) grade as a prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) receiving combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiotherapy (RT). Patients who underwent RT following TACE between January 2011 and December 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. The survival outcomes of patients in regard to the ALBI grade and Child-Pugh (C-P) classification were evaluated. A total of 73 patients with a median follow-up of 16.3 months were included. Thirty-three (45.2%) and forty patients (54.8%) were categorized into ALBI grades 1 and 2-3, respectively, while sixty-four (87.7%) and nine (12.3%) were C-P classes A and B, respectively (p = 0.003). The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for ALBI grade 1 vs. 2-3 were 8.6 months vs. 5.0 months (p = 0.016) and 27.0 months vs. 15.9 months (p = 0.006), respectively. The median PFS and OS for C-P class A vs. B were 6.3 months vs. 6.1 months (p = 0.265) and 24.8 months vs. 19.0 months (p = 0.630), respectively. A multivariate analysis showed that ALBI grades 2-3 were significantly associated with worse PFS (p = 0.035) and OS (p = 0.021). In conclusion, the ALBI grade could be a good prognosticator in HCC patients who were treated with combined TACE-RT.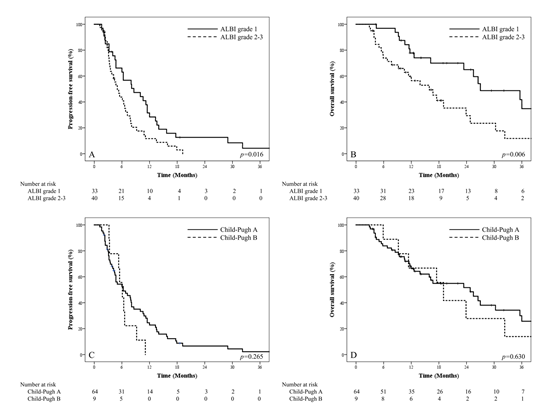
Affiliations
Jason Joon Bock Lee 1, Jun Su Park 2, Hyun Pyo Hong 3, Myung Sub Kim 3, Dong-Hoe Koo 4, Hyebin Lee 1, Heerim Nam 1
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 03181, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Sejong 30099, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Radiology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 03181, Republic of Korea.
4Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 03181, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- Child–Pugh classification; albumin–bilirubin grade; hepatocellular carcinoma; radiotherapy; transarterial chemoembolization.
- 연구소개
- 간암 환자의 치료를 고려할 때 치료 전 간 기능 평가는 필수적입니다. 간 기능 평가에 가장 널리 사용되는 지표는 Child-Pugh (C-P) classification이지만, 이 지표는 복수나 뇌병증의 평가에 있어서 평가자의 주관이 개입될 여지가 있고 albumin과 복수처럼 상호 연관성이 있는 항목이 중복으로 포함되어 있습니다. 이러한 단점을 극복하기 위해 새로운 대안으로 제시되는 지표가 Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) grade입니다. 본 논문에서는 간동맥 화학 색전술과 방사선치료를 함께 받는 환자에서 ALBI grade가 C-P class에 비해 무진행 생존률 및 전체 생존률과 연관성이 높음을 보였습니다. 수술을 비롯한 여러 간암 치료법에서 ALBI grade가 C-P class보다 예후와의 연관성이 높다는 기존의 연구 결과들이 있었으나 간동맥 화학 색전술과 방사선치료의 병용에 있어서 이러한 분석은 본 논문이 최초입니다. 간암의 용적이 크거나 혈관 침범이 있을 경우 간동맥 화학 색전술과 방사선치료를 병용하는 경우가 많은데, 본 연구의 결과가 이러한 임상적 상황에서 치료 방침 결정을 내리는 데 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 기대합니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
간암으로 TACE와 방사선치료를 받은 환자에서 Child-Pugh class보다 ALBI grade가 무병생존율과 생존율을 예측하는 데에 있어 더 좋은 예후인자임을 보임.
덧글달기닫기2023-04-04 17:03:44
등록