글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2023년 03월호
[Cancers (Basel) .] Prediction of Radiotherapy Compliance in Elderly Cancer Patients Using an Internally Validated Decision Tree
가천의대 / Biche Osong, 이석호*
- 출처
- Cancers (Basel) .
- 등재일
- 2022 Dec 12
- 저널이슈번호
- 14(24):6116. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246116.
- 내용
Abstract
This study aims to analyze the relationship between the available variables and treatment compliance in elderly cancer patients treated with radiotherapy and to establish a decision tree model to guide caregivers in their decision-making process. For this purpose, 456 patients over 74 years of age who received radiotherapy between 2005 and 2017 were included in this retrospective analysis. The outcome of interest was radiotherapy compliance, determined by whether patients completed their scheduled radiotherapy treatment (compliance means they completed their treatment and noncompliance means they did not). A bootstrap (B = 400) technique was implemented to select the best tuning parameters to establish the decision tree. The developed decision tree uses patient status, the Charlson comorbidity index, the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance scale, age, sex, cancer type, health insurance status, radiotherapy aim, and fractionation type (conventional fractionation versus hypofractionation) to distinguish between compliant and noncompliant patients. The decision tree's mean area under the curve and 95% confidence interval was 0.71 (0.66-0.77). Although external validation is needed to determine the decision tree's clinical usefulness, its discriminating ability was moderate and it could serve as an aid for caregivers to select the optimal treatment for elderly cancer patients.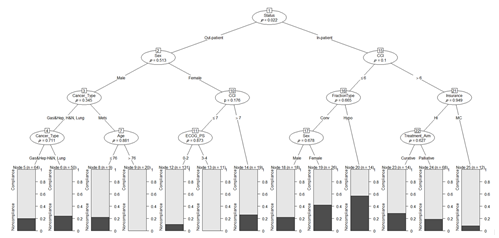
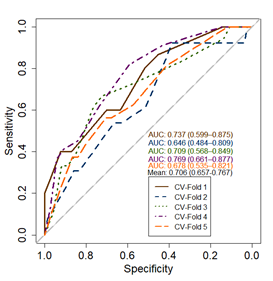
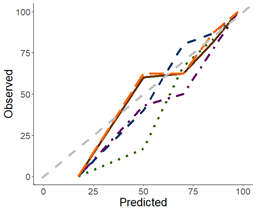
Figure 2. Decision tree for predicting radiotherapy compliance in elderly cancer patients. The oval
structures represent the variables that branch out to form the tree. The branches connect the variables
and hold the condition for the splits. The rectangle structures that do not branch any further on the
tree are the leaf or decision node from which the probability of compliance (white) and noncompliance
(black) is read. The values at the top of the leaf nodes indicate the number of patients in that node,
and the p-values in the oval structures indicate the significance level of the variab Figure 3. Decision tree performance in terms of discrimination (AUC) and calibration.
Affiliations
Biche Osong 1, Inigo Bermejo 1, Kyu Chan Lee 2, Seok Ho Lee 2, Andre Dekker 1, Johan van Soest 1
1Department of Radiation Oncology (Maastro), GROW School for Oncology, Maastricht University Medical Centre+, 6229 ET Maastricht, The Netherlands.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon 21565, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- compliance; decision tree; elderly cancer patients; radiotherapy.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [J Pers Med.] Evaluation of Pretreatment Albumin-Bilirubin Grade as a Better Prognostic Factor Compared to Child-Pugh Classification in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Radiotherapy
- 다음글 [Cancer Res Treat.] Analysis of Once-Daily Thoracic Radiotherapy Dose According to the Underlying Lung Disease in Patients with Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy







