글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- 2023년 04월호
[Sustainability] Analysis of Activated Materials of Disposed Medical Linear Accelerators according to Clearance Level for Self-Disposal성균관대, KIRAMS / 장영재, 권나혜, 방석호*, 최상현*
- 출처
- Sustainability
- 등재일
- 2023
- 저널이슈번호
- 15(5), 4100
- 내용
Abstract
In Korea, when replacing or discarding parts of a medical linear accelerator (linac), self-disposal is required in the consideration of the activity, but there is no standard regulation to manage radioactive waste. The aim of this study is to check the activity of each part to determine the disposal time according to the clearance level for self-disposal. The results of measuring the components of the linac head parts of the disposed Varian, Elekta, and Siemens equipment were reflected in the Monte Carlo simulation to confirm the radionuclide change according to the presence or absence of impurities. To confirm the degree of activation of the linac, the main radionuclides according to the time after the linac shutdown, considering the workloads of 40/80 Gy/day of 10/15 MV linac irradiated with beams for 10 years in the results of the simulation of the linac parts, and the radionuclide concentration was confirmed. As a result of applying the clearance level for self-disposal in the notice of the Korean Nuclear Safety (KINS) to each linac head part, most parts of the 10 MV linac could be dismantled after 1 month, and 15 MV target and primary collimators were stored after a long period of time before being dismantled. Although additional radionuclides were identified according to the presence or absence of impurities, the disposal timing for each part did not change significantly. In this study, the clearance level for self-disposal for each radionuclide was applied to activated parts by three manufacturers to confirm the self-disposal timing and predict the timing at which workers are not exposed to radiation during dismantling/disposal.
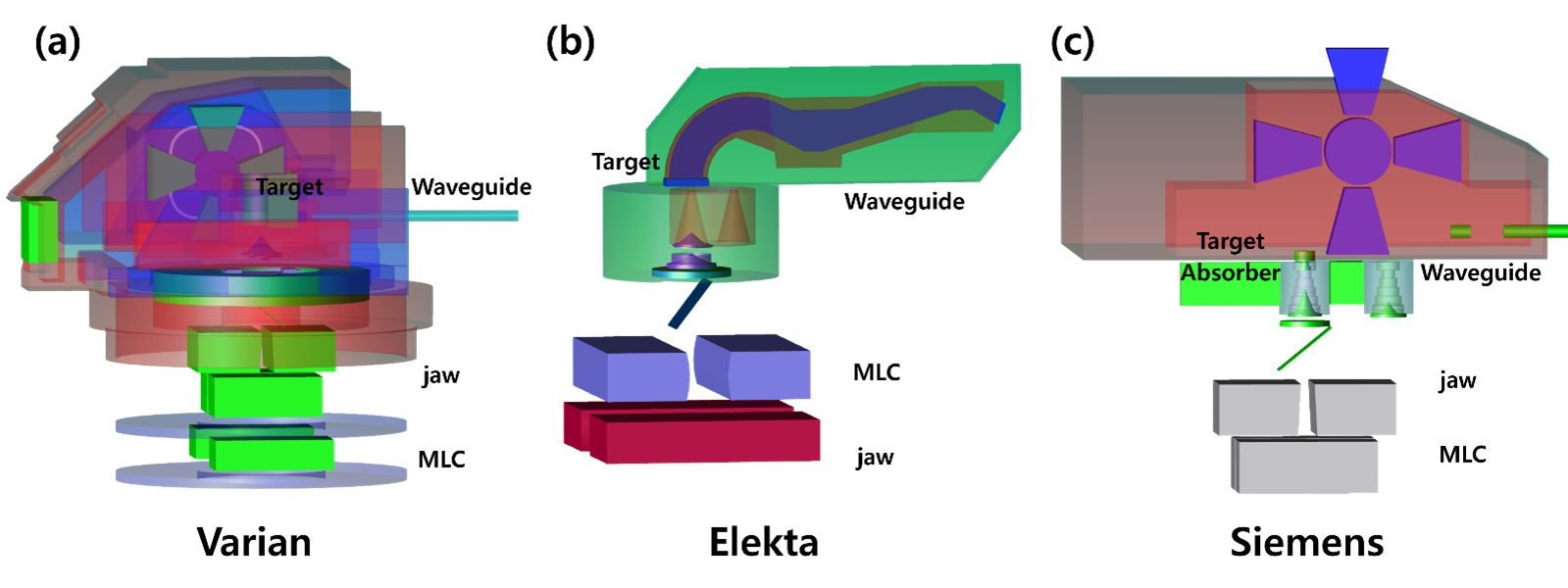 대표그림1. 각 제조사별 치료용 선형가속기 모델링 결과 (a) Varian (b) Elekta (c) Siemens
대표그림1. 각 제조사별 치료용 선형가속기 모델링 결과 (a) Varian (b) Elekta (c) Siemens 
대표그림2. 80 Gy/day 가동하중을 고려한 제조사별 15 MV / 10 MV 에너지 선형가속기의 부품별 허용 농도 (그림 내 빨간색 선은 허용농도 1 기준 선이며, 1 미만이 되는 시점에서 자체처분이 가능하다.) (a) Varian 15 MV (b) Varian 10 MV (c) Elekta 15 MV (d) Elekta 10 MV (e) Siemens 15 MV (f) Siemens 10 MV
Affiliations
Young Jae Jang1,2,† , Na Hye Kwon3,4,† , Seong Hee Park2, Yona Choi2 , Kum Bae Kim1 , Dong Wook Kim3,4 , Suk Ho Bhang5,* and Sang Hyoun Choi1,*
1
Research Team of Radiological Physics & Engineering, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Republic of Korea
2
Department of Accelerator Science, Korea University, Sejong 30015, Republic of Korea
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea
4
Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering Lab (MPBEL), Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea
5
School of Chemical Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea
*
Authors to whom correspondence should be addressed.
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
- 키워드
- radioactive waste; medical linear accelerator; clearance level; radionuclide; Monte Carlo simulation
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 해체 및 폐기한 치료용 선형가속기 부품의 시간에 따른 방사성핵종 및 방사성핵종 농도를 평가 및 분석한 논문입니다. 방사화된 주요 부품은 핵종별 허용농도에 따라 자체처분 허용기준을 적용해야하고, 자체처분 허용기준 이상인 부품들은 폐기가 어렵습니다. 하지만 선형가속기에서 생성되는 방사성 핵종의 정보가 불확실하고 가동하중에 따른 변수로 인해 이를 판단하기 어렵습니다. 몬테칼로 시뮬레이션을 통해 20, 40, 80 Gy/day 의 가동하중 및 10, 15 MV 에너지를 10년동안 조사한 베리안, 엘렉타, 지멘스사 장비의 헤드부품에 대해 자체처분 가능시점을 표기하였습니다. 이와 같은 결과를 바탕으로 방사화폐기물을 관리한다면 작업종사자가 방사화 피폭에 노출되지 않고 작업 할 수 있는 부품 및 기간을 미리 예측할 수 있을 것입니다.
- 덧글달기







