글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Cancer Res Treat.] Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Uterine Cervical Cancer: Therapeutic Monitoring and Prognostic Values after Radical Radiotherapy
자궁경부암에서 혈장 세포유리 DNA: 방사선치료 후 치료반응 모니터링 및 예후 인자서울의대 / 김재식, 양선아, 강현철*
- 출처
- Cancer Res Treat.
- 등재일
- 2023 Apr
- 저널이슈번호
- 55(2):659-670.
- 내용
-
Abstract
Purpose: In the present study, we aimed to establish a liquid biopsy-based monitoring method using peripheral blood cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for patients with cervical cancer who underwent radical radiotherapy (RT).Materials and methods: Twenty-five patients with cervical cancer were prospectively recruited and treated with external beam RT and brachytherapy. In all patients, except one, chemotherapy was administered concurrently during RT. Whole peripheral blood samples were obtained at least twice from each patient. We performed next-generation sequencing (NGS) for the target-captured libraries (67 oncogenes and human papillomavirus [HPV] type 16/18) using 64 plasma cfDNA samples from the 25 participants. The ratio of HPV cfDNA and the variant allele frequency (VAF) in cfDNA was calculated, and their dynamic changes were monitored. The median follow-up duration was 25.4 months.
Results: In total, we identified 21,866 cfDNA variants. ARID1A and frameshift variants occupied the largest portion of altered genes and HIGH-grade variant types, respectively. In most cases, tumor shrinkage was followed by a decrease in the HPV ratio; however, an increase in HPV ratio indicated distant metastasis, despite the reduced tumor size. The initial HPV ratio reflecting the tumor burden was likely associated with treatment outcomes (p = 0.16). We did not determine a role for serial changes in the VAF in cfDNA.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the HPV cfDNA ratio, calculated after targeted NGS, may be valuable for monitoring and predicting treatment responses. Accordingly, further validation of these findings is warranted.
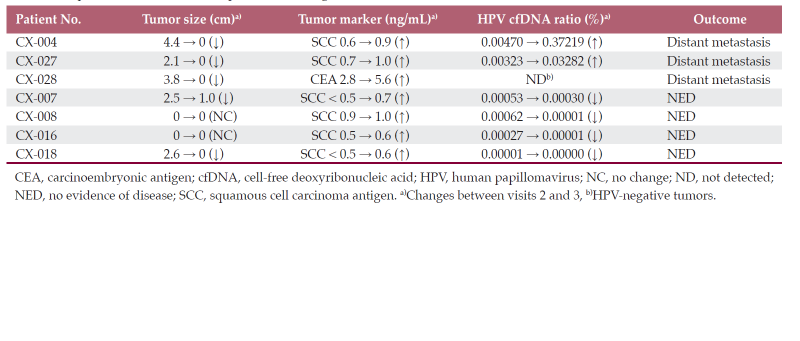
기존의 MRI 또는 암표지자의 반응과는 다른 세포유리 DNA의 반응이 환자의 예후를 보다 정확하게 예측하는 표. 만약 이를 임상에 적용한다면 최소 침습적인 검사 (혈액)로 방사선치료를 받은 여러 환자에게 큰 도움을 줄 수 있다.
Affiliations
Jae Sik Kim 1 2, Sunah Yang 3, Kyeonghun Jeong 4, Dong-Yun Kim 1 5, Kwangsoo Kim 3, Hyun-Cheol Kang 1 6
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
3Transdisciplinary Department of Medicine and Advanced Technology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
4Interdisciplinary Program in Bioengineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
5Department of Radiation Oncology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
6Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 키워드
- Cell-free DNA; Human papillomavirus viruses; Uterine cervical neoplasms; Variant allele frequency.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 항암방사선치료를 받은 자궁경부암의 치료 반응에 대한 판단의 어려움을 극복하기 위해 혈액 안의 세포유리 DNA (cell-free DNA) 검사의 유용성을 검증한 전향적 연구이다. 비록 적은 수의 환자 (25명)을 대상으로 짧은 기간 동안 수집된 검체를 분석하였지만 의미 있는 결과를 얻을 수 있었다. 기존의 자궁경부암의 원인으로 알려진 HPV 바이러스의 표적 NGS를 통해 혈액안의 극소수의 바이러스를 모니터링한다면 MRI와 같은 영상 검사 또는 기존의 알려진 암표지자 보다 훨씬 빠르고 정확한 예후 예측이 가능하다. 다만 암 유전자의 variant allele frequency (VAF)의 표적 NGS의 유의성은 확인하지 못하였기 때문에서 추가 연구 과제가 남겨져 있다고 하겠다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cancers (Basel) .] Clinical Outcomes of Thymic Carcinoma: The Role of Radiotherapy Combined with Multimodal Treatments
- 다음글 [Clin Transl Radiat Oncol .] Incorporating axillary-lateral thoracic vessel juncture dosimetric variables improves model for predicting lymphedema in patients with breast cancer: A validation analysis









