(구)글로벌 핫이슈
방사선종양학
- 2019년 03월호
[JAMA Oncol.] 정위방사선수술과 수술적 절제를 받은 뇌전이의 국소 제어율 비교, 무작위 임상연구의 2차 분석Comparison of Local Control of Brain Metastases With Stereotactic Radiosurgery vs Surgical Resection: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial.Fox Chase Cancer Center / Stephanie E. Weiss*
- 출처
- JAMA Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2018 Nov 8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4610. [Epu
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
Importance:
Brain metastases are a common source of morbidity for patients with cancer, and limited data exist to support the local therapeutic choice between surgical resection and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).Objective:
To evaluate local control of brain metastases among patients treated with SRS vs surgical resection within the European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 22952-26001 phase 3 trial.Design, Setting, and Participants:
This unplanned, exploratory analysis of the international, multi-institutional randomized clinical trial EORTC 22952-26001 (conducted from 1996-2007) was performed from February 9, 2017, through July 25, 2018. The EORTC 22952-26001 trial randomized patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases to whole-brain radiotherapy vs observation after complete surgical resection or before SRS. Patients in the present analysis were stratified but not randomized according to local modality (SRS or surgical resection) and treated per protocol with 1 to 2 brain metastases and tumors with a diameter of no greater than 4 cm.Interventions:
Surgical resection or SRS.Main Outcomes and Measures:
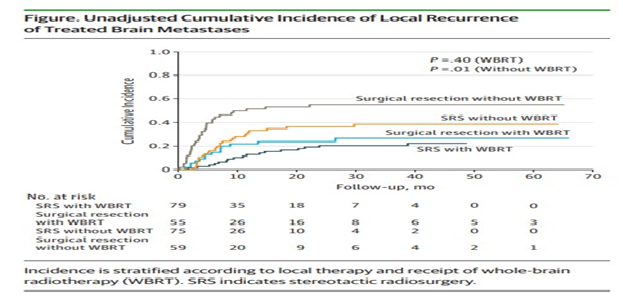
The primary end point was local recurrence of treated lesions. Cumulative incidence of local recurrence was calculated according to modality (surgical resection vs SRS) with competing risk regression to adjust for prognostic factors and competing risk of death.Results:
A total of 268 patients were included in the analysis (66.4% men; median age, 60.7 years [range, 26.9-81.1 years]); 154 (57.5%) underwent SRS and 114 (42.5%) underwent surgical resection. Median follow-up time was 39.9 months (range, 26.0-1982.0 months). Compared with the SRS group, patients undergoing surgical resection had larger metastases (median 28 mm [range, 10-40 mm] vs 20 mm [range, 4-40 mm]; P < .001), more frequently had 1 brain metastasis (112 [98.2%] vs 114 [74.0%]; P < .001), and differed in location (parietal, 21 [18.4%] vs 61 [39.6%]; posterior fossa, 30 [26.3%] vs 12 [7.8%]; P < .001). In adjusted models, local recurrence was similar between the SRS and surgical resection groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1.15; 95% CI, 0.72-1.83). However, when stratified by interval, patients with surgical resection had a much higher risk of early (0-3 months) local recurrence compared with those undergoing SRS (HR, 5.94; 95% CI, 1.72-20.45), but their risk decreased with time (HR for 3-6 months, 1.37 [95% CI, 0.64-2.90]; HR for 6-9 months, 0.75 [95% CI, 0.28-2.00]). At 9 months or longer, the surgical resection group had a lower risk of local recurrence (HR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.14-0.93).Conclusions and Relevance:
In this exploratory analysis, local control of brain metastases was similar between SRS and surgical resection groups. Stereotactic radiosurgery was associated with improved early local control of treated lesions compared with surgical resection, although the relative benefit decreased with time.Trial Registration:
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00002899.
Author informationChurilla TM1, Chowdhury IH2, Handorf E3, Collette L4, Collette S4, Dong Y1, Alexander BM5, Kocher M6, Soffietti R7, Claus EB8,9, Weiss SE1.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
2
Department of Radiation Oncology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts.
3
Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Facility, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
4
EORTC Headquarters, Brussels, Belgium.
5
Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women's Cancer Center, Boston, Massachusetts.
6
Department of Stereotaxy and Functional Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.
7
Department of Neuro-oncology, University of Turin and City of Health and Science Hospital, Torino, Italy.
8
Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut.
9
Department of Neurosurgery, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
Subgroup analysis이기는 하지만, 1-3개의 limited brain metastases에서 수술과 SRS의 국소제어율은 비슷하였지만, 재발양상을 분석하였을 때 3개월 이내에는 수술을 시행한 군에서 재발이 높은 반면, 9개월 이후에는 SRS군에서 재발율이 증가한다는 보고는 임상에서 SRS 후 f/u시 참고할만한 연구결과라 생각됩니다.
덧글달기닫기2019-03-14 13:53:12
등록