글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- 2024년 01월호
[Chemosphere .] Bioaccumulation and in vivo fate of toxic benzylalkyldimethylammonium chloride in rats via the radiotracer analysis방사성 추적자 분석을 통한 쥐의 독성 벤질 알킬 디메틸 암모늄 클로라이드의 생체 축적 및 생체 내 운명경북대 / 박정은, 류승헌, 전종호*
- 출처
- Chemosphere .
- 등재일
- 2023 Oct:338:139460. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.20
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
-
Abstract
Benzylalkyldimethylammonium chloride (BAC), a quaternary ammonium compound (QAC), is utilized in industrial and biomedical applications for antimicrobial purposes. Since the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, various types of BAC-containing household chemicals have been produced. BACs have several adverse effects; however, their biological uptake, translocation, and excretion in animal models (essential for better understanding in vivo behavior and toxicological impact) remain unclear. In this study, we performed the first biodistribution and whole-body imaging studies of BAC in male Sprague Dawley rats, using two different administration routes. Quantitative whole-body autoradiography (QWBA) data obtained for intranasal 14C-labeled BAC ([14C]C12-BAC) exposure showed substantial uptake values for the respiratory organs (e.g. 346 ng g-1 of lung at 3 h post administration) and the radiotracer was transported to other internal organs. The amount of radiotracer in the heart, adrenal gland, and pancreas were 198, 1410, and 186 ng g-1 tissue respectively at 168 h following exposure. Autoradiograms obtained after intravenous injection also showed high accumulation and slow excretion in these organs. The cumulative excretion analysis revealed that approximately 6.4% of the administered radioactivity remained in rats after a week. The results indicated that continuous inhalation exposure to BAC leads to potential toxic effects in extrapulmonary organs and the respiratory tract. Thus, the radiolabeling method utilized may help assess various synthetic QACs in living subjects.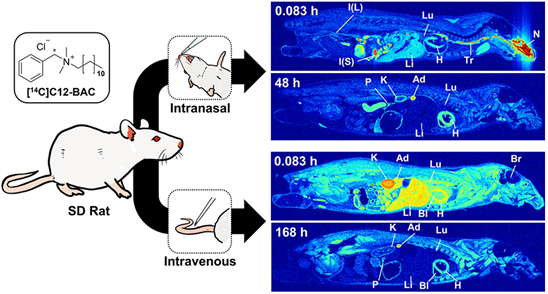
- BAC benzylic 위치에 14C가 도입된 방사성추적자([14C]BAC)를 합성함
- 동물 모델(rat)에 [14C]BAC를 비강 및 정맥을 통해 노출함
- QWBA를 활용하여 BAC의 체내 분자 영상 연구를 수행함
Affiliations
Jung Eun Park 1, Seung-Hun Ryu 2, Satoshi Ito 3, Mi-Kyung Song 4, Eun Ji Gu 1, Hyunil Shin 5, Young-Hee Kim 2, Jongho Jeon 6
1Department of Applied Chemistry, College of Engineering, Kyungpook National University, 80 Daehak-ro, Buk-gu, Daegu, 41566, Republic of Korea.
2Humidifier Disinfectant Health Center, Environmental Health Research Department, National Institute of Environmental Research, 42 Hwangyong-ro, Seo-gu, Incheon, 22689, Republic of Korea.
3Drug Development Solutions Center, Sekisui Medical Co., Ltd., 2117 Muramatsu, Tokai, Ibaraki, 319-1182, Japan.
4Inhalation Toxicology Center for Airborne Risk Factor, Korea Institute of Toxicology, 30 Baehak1-gil, Jeongeup, Jeollabuk-do, 56212, Republic of Korea.
5KRCC Co., Ltd, 193 Chenggyesan-ro, Seocho-gu, Seoul, 06802, Republic of Korea.
6Department of Applied Chemistry, College of Engineering, Kyungpook National University, 80 Daehak-ro, Buk-gu, Daegu, 41566, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: jeonj@knu.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Benzylalkyldimethylammonium chloride; Biological uptake; In vivo assessment; Quantitative whole-body autoradiography; Radiotracer.
- 연구소개
- 코로나-19 시대를 거쳐오면서 전 세계적으로 방역용 4급 암모늄 화합물(QACs)에 대한 생산과 사용이 크게 증가하였습니다. 이에 따라 QACs의 체내 독성에 우려가 커지고 있습니다. 본 논문은 방역에 많이 활용된 QAC 계열 살균제인 benzylalkyldimethylammonium chloride (BAC)의 체내 거동, 대사 및 배출에 대한 연구입니다. 이를 위하여 방사성동위원소(14C)가 표지된 BAC([14C]BAC)를 합성하였고, 동물의 비강과 정맥에 각각 노출하여 정량 전신 자가방사영상분석(QWBA)을 수행하였습니다. 연구 결과 BAC는 심근, 부신, 췌장에서 다른 장기에 비해 상대적으로 높은 분포와 느린 배출 속도를 보였습니다. 이를 통해 BAC의 타겟 장기를 확인하고 잠재적 체내 독성 영향을 예측할 수 있었습니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
살균항균제로 널리 이용되는 Quaternary ammonium compounds에 대한 독성평가를 위해서는 우선 생체분포를 통해 흡입 또는 흡수 후 이동경로, 축적장기 등을 장기적으로 파악하는 것이 선행되어야 합니다. 이를 위해 본 연구에서는 방사성동위원소 C-14으로 표지한 [14C]C12-BAC 를 이용하여 QWBA를 수행함으로써, 시험약물 및 그 대사체의 분포와 축적과 관련된 정보를 효과적으로 보여주었습니다. 이러한 핵의학적 연구방법은 독성물질에 대한 노출에 대하여 그 위험성을 평가하는데 매우 유용하게 이용될 것으로 기대합니다.
덧글달기닫기2024-01-08 14:39:56
등록