글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- [Sci Rep .] Assessing the applicability of PMOD residence times model for PET image-based radiation dosimetry
연세의대, KIRAMS / 오세종, 유영훈*, 최재용*,
- 출처
- Sci Rep .
- 등재일
- 2023 Nov 8
- 저널이슈번호
- 13(1):19387. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46822-5.
- 내용
Abstract
The effective dose represents the overall internal radiation exposure to the whole body when exposed to radiation sources. This study aims to compare conventional and software-aided methods to derive the effective dose. In the present study, 8F-T807 and 18F-Mefway, specific radiotracers for the paired helical tau and serotonin 1A receptor, were administered to healthy subjects (n = 6, each radiotracer), following which whole-body positron emission tomography (PET) images were obtained for 2 h. Subsequently, time-activity curves for major organs were obtained, and the residence times were calculated using the "conventional" and "Residence Times model" tools in PMOD software. The residence times from each method was input into OLINDA/EXM software, and the effective dose was estimated. The differences in the average residence times of the brain, heart, lung, and liver were 18.4, 20.8, 10.4, and 13.3% for 18F-T807, and 17.5, 16.4, 18.1, and 17.5% for 18F-Mefway, respectively. For the mean effective dose, the error rates between the methods were 3.8 and 1.9% for 18F-T807 and 18F-Mefway, respectively. The organs that showed the greatest difference in the absorbed dose were the urinary bladder for 18F-T807 (40.4%) and the liver for 18F-Mefway (14.1%). This method of obtaining the residence time using PMOD can be easily used to derive the effective dose, and is applicable in evaluating the safety of radiotracers for clinical trials.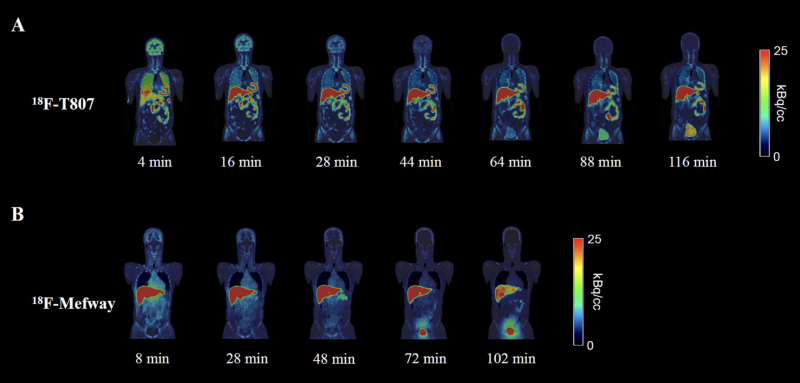
Affiliations
Se Jong Oh 1, Chul Hyoung Lyoo 2, Young Hoon Ryu # 3, Jae Yong Choi # 4 5
1Division of Applied RI, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, 75 Nowon-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Neurology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ryuyh@yuhs.ac.
4Division of Applied RI, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, 75 Nowon-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul, Korea. smhany@kirams.re.kr.
5Radiological and Medico-Oncological Sciences, University of Science and Technology (UST), Seoul, Korea. smhany@kirams.re.kr.
#Contributed equally.
- 연구소개
- 개발 단계의 방사성화합물을 임상시험에 적용하기 위해서는 방사능 피폭에 대한 체내 안전성을 평가해야합니다. 이를 위해서 사용하는 것이 내부피폭선량을 평가하는 것인데, 기존의 방법으로는 복잡한 단계와 계산을 필요로 한다는 제한점이 있습니다. 이를 극복하기 위해서 영상분석 소프트웨어인 PMOD에서는 장기별 머무름 시간을 손쉽게 평가할 수 있는 ‘residence time model’을 개발하였습니다. 본 연구에서는 PMOD를 활용한 진단용 방사성의약품의 내부 선량평가가 기존 방법 대비 5% 이하의 편차를 가지는 것을 확인하여 유효성을 확인하였습니다. 이러한 방법은 향후 개발되는 방사성화합물에 대한 안정성을 손쉽게 평가하는데 활용할 수 있을 것이라고 기대합니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
임상에서 방사성의약품의 사용 시 환자에 대한 피폭의 우려는 항상 염두에 두어야 할 문제로, 선량평가는 매우 중요하게 다루어져야 한다. 영상기반 선량평가(Imaging-based dosimetry)는 복잡한 계산에 기반하여 이루어지는데, 본 연구에서는 18F-T807와 18F-Mefway를 대상으로 PET, MR 등의 영상분석에 널리 이용되고 있는 PMOD 소프트웨어와 최근 개발된 Residence Times model 기법을 이용하여 개선된 선량평가기법을 소개하였다.
2023-12-05 17:38:11