글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- 2019년 12월호
[Biomaterials.] Biodegradable micro-sized discoidal polymeric particles for lung-targeted delivery system.연세의대 / 박준영, 박상효, 강원준*, 기재홍*
- 출처
- Biomaterials.
- 등재일
- 2019 Oct
- 저널이슈번호
- 218:119331. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119331. Epub 2019 Jul 5.
- 내용
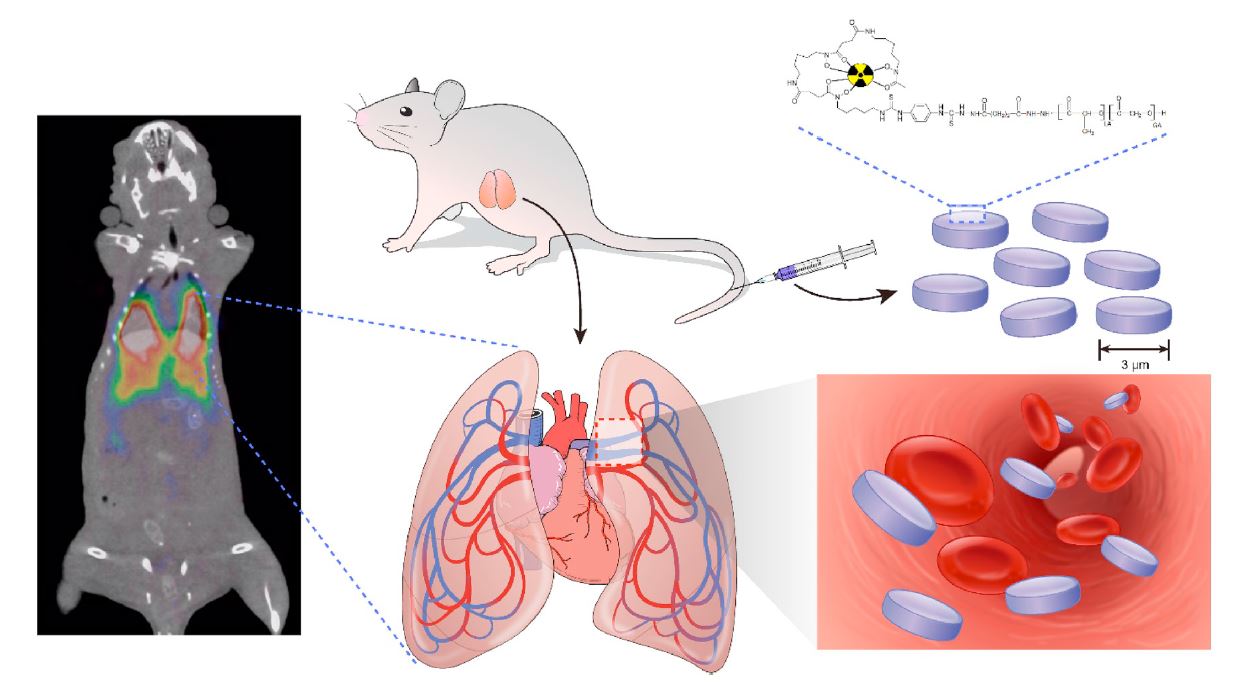
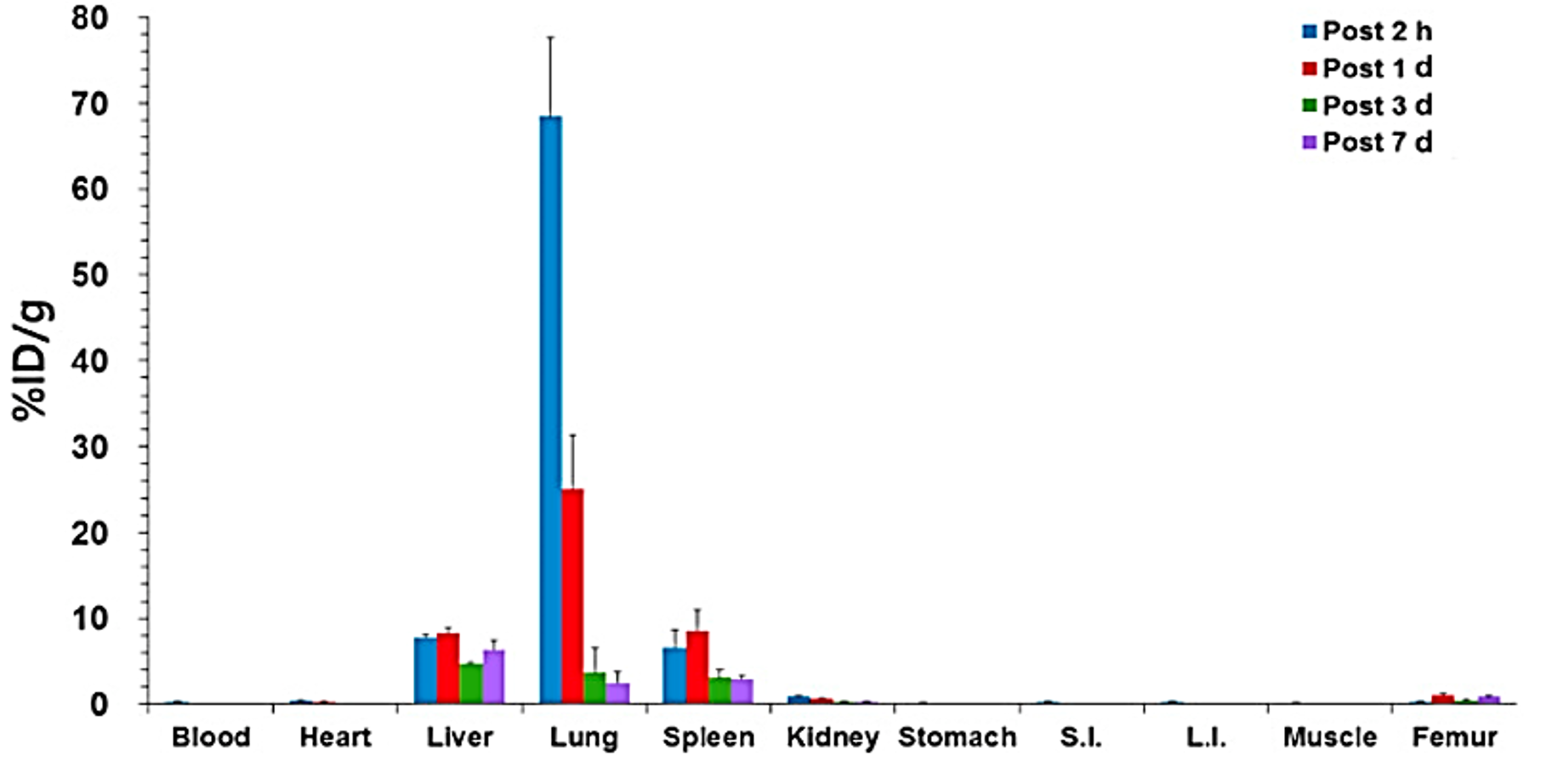
Abstract
Various types of particle-based drug delivery systems have been explored for the treatment of pulmonary diseases; however, bio-distribution and elimination of the particles should be monitored for better understanding of their therapeutic efficacy and safety. This study aimed to characterize the biological properties of micro-sized discoidal polymeric particles (DPPs) as lung-targeted drug delivery carriers. DPPs were prepared using a top-down fabrication approach and characterized by assessing size and zeta potential. They were labeled with zirconium-89 (89Zr), and bio-distribution studies and PET imaging were performed for 7 days after intravenous administration. Their hydrodynamic size was 2.8 ± 6.1 μm and average zeta potential was -39.9 ± 5.39 mV. At doses of 5, 12.5, and 25 mg/kg, they showed no acute toxicity in nude mice. Desferrioxamine (DFO)-functionalized 89Zr-labeled DPPs gave a decay-corrected radiochemical yield of 82.1 ± 0.2%. Furthermore, 89Zr-DPPs, from chelate-free labeling methods, showed a yield of 48.5 ± 0.9%. Bio-distribution studies and PET imaging showed 89Zr-DFO-DPPs to be mainly accumulated in the lungs and degraded within 3 d of injection. However, 89Zr-DFO-DPPs showed significantly low uptake in the bone. Overall, our results suggested micro-sized DPPs as promising drug delivery carriers for the targeted treatment of various pulmonary diseases.
Author informationPark JY1, Park S2, Lee TS3, Hwang YH3, Kim JY3, Kang WJ4, Key J5.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, Wonju, Gangwon-do, 26493, Republic of Korea.
3
Division of RI Application, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), Seoul, 01812, Republic of Korea.
4
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: mdkwj@yuhs.ac.
5
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, Wonju, Gangwon-do, 26493, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: jkey@yonsei.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Discoidal polymeric particle; Drug delivery system; PET imaging; Pulmonary disease; Zr-89
- 연구소개
- 본 연구의 목적은 폐에 효과적으로 약물을 전달하는 입자를 개발하는 것입니다. 폐에 약물을 효과적으로 전달하기 위해서는 입자의 크기, 모양, 표면 특성들을 나노단위에서 정밀하게 조절하는 것이 필요합니다. 100 nm 이하의 작은 입자나 분자 단위의 약물의 경우, 폐를 빠르게 지나가기 때문에 약물전달 효과가 낮고, 수십 마이크로 사이즈의 입자의 경우, 폐에 장기적으로 축적되어 추가적인 폐질환을 일으킬 수 있습니다. 본 연구에서 보고한 입자는 top-down fabrication 방법으로 준비되었으며, 적혈구와 유사한 모양을 가지고 있습니다. 입자의 표면을 89Zr으로 표지하여 체내 움직임을 정맥 투여 후 7일 동안 PET 영상으로 관찰하였습니다. 전달체의 크기는 지름이 약 3μm입니다. 생분해 및 생체 적합성을 나타내는 PLGA 폴리머를 이용하여 입자를 제작하였고, 5, 12.5, 25mg/kg의 용량에서 통계적으로 유의한 생체독성을 나타내지 않았습니다. 생체분포 분석 결과, 입자 주입량의 약 70% 이상이 주로 폐에 축적이 되었고, 주입 후 3일 이내에 완전히 폐에서 제거되는 것을 확인하였습니다. 또한 89Zr의 일반적 특징과 달리 뼈로의 흡수가 현저히 낮았습니다. 따라서 이번 연구를 통해 개발된 입자는 다양한 폐질환의 표적 치료를 위한 약물 전달체로 활용될 수 있을 것이라 기대됩니다.
- 덧글달기







