글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Cell Death Dis.] LXA 4-FPR2 signaling regulates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis via crosstalk with TGF-β/Smad signaling
연세의대, 서울대 / 김현중, 조재호*, 김진모*
- 출처
- Cell Death Dis.
- 등재일
- 2020 Aug 8
- 저널이슈번호
- 11(8):653. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02846-7.
- 내용
Abstract
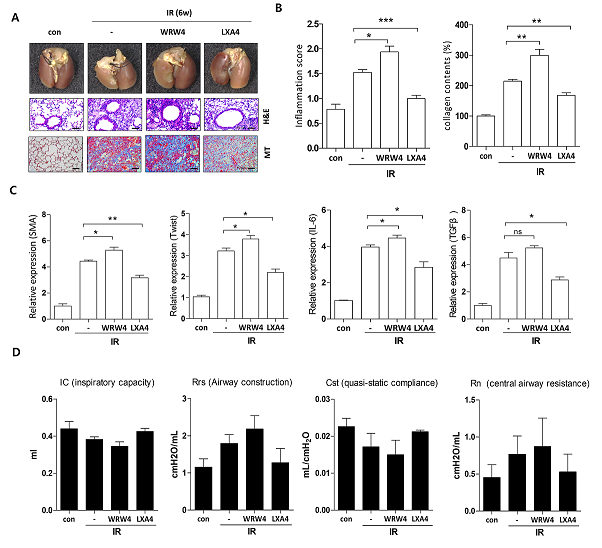
Radiation therapy is an important modality in the treatment of lung cancer, but it can lead to radiation pneumonitis, and eventually radiation fibrosis. To date, only few available drugs can effectively manage radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Lipoxins are endogenous molecules exhibit anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving effects. These molecules play a vital role in reducing excessive tissue injury and chronic inflammation; however, their effects on radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) are unknown. In this study, we investigated the effects of lipoxin A4 (LXA4) on RILI using our specialized small-animal model of RILI following focal-ablative lung irradiation (IR). LXA4 significantly inhibited immune-cell recruitment and reduced IR-induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and fibrotic proteins in the lung lesion sites. In addition, micro-CT revealed that LXA4 reduced IR-induced increases in lung consolidation volume. The flexiVentTM assays showed that LXA4 significantly reversed IR-induced lung function damage. Moreover, LXA4 downregulated the activities of NF-κB and the Smad-binding element promoters. The expression of FPR2, an LXA4 receptor, increased during the development of IR-induced pulmonary fibrosis, whereas silencing of endogenous LXA4 using an antagonist (WRW4) or FPR2 siRNA resulted in impaired development of pulmonary fibrosis in response to IR. Collectively, these data suggest that LXA4 could serve as a potent therapeutic agent for alleviating RILI.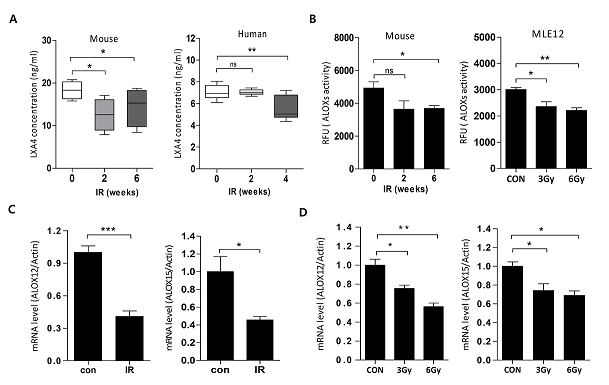
Affiliations
Hyunjung Kim 1 , Sung-Hyo Park 1 , Song Yee Han 1 , Yun-Sil Lee 2 , Jaeho Cho 3 , Jin-Mo Kim 4 5
1 Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
2 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, South Korea.
3 Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea. jjhmd@yuhs.ac.
4 Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea. jmk0831@snu.ac.kr.
5 Department of Manufacturing Pharmacy, Natural Product Research Institute, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea. jmk0831@snu.ac.kr.
- 연구소개
- 본 논문은 임상의 방사선치료 상황을 반영하는 임상유사 방사선폐손상 소동물모델을 기반으로 한 폐섬유화의 기전연구로 아스피린과 같은 (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) NSAIDs 계통에 의해 유도될 수 있고 항염증 효과를 가진다고 알려진 LipoxinA4 (LXA4)의 방사선폐섬유화를 억제효과와 조절기전을 밝히고자 하였다. 대표적인 연구결과로 방사선치료후의 환자혈액샘플 및 방사선폐섬유화 동물모델에서 방사선조사후의 LXA4의 생성이 감소함을 확인하였고 또한 LXA4의 생성에 관련이 있는 효소인 ALOX12/15의 발현이 감소됨을 확인하였다. 이는 방사선폐섬유화 치료에 있어 LXA4가 중요한 타겟이라는 점을 시사할 수 있다. 더불어 LXA4의 처리는 방사선에 의한 염증반응 및 폐섬유화억제됨을 밝혔고 방사선폐섬유화과정인 주요 사이토카인의 발현억제 및 Collagen의 축적을 감소시켰다. 방사선폐섬유화 주요 조절기전인 NF-KappaB와 TGFb-Smad signaling을 억제함을 확인하였다. 본 연구의 결과는 방사선폐섬유화의 새로운 타겟을 통한 신약개발에 필요한 기반기술 및 필요한 기초자료를 제공함으로써 난치성질환의 치료개발의 기반을 제공할 수 있으리라 사료된다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Int J Radiat Biol.] Characterization of sphere cells derived from a patient-derived xenograft model of lung adenocarcinoma treated with ionizing radiation
- 다음글 [Cancer Res Treat.] Sequential Treatment with an Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Followed by a Small-Molecule Targeted Agent Increases Drug-induced Pneumonitis










편집위원
방사선치료는 효과적인 폐암 치료법이지만, 폐섬유증을 유발할 수 있으며, 현재까지 그 치료법은 매우 제한적이다. 본 연구는 specialized animal model을 통해 anti-inflammatory effect를 갖는 lipoxin A4(LXA4)가 radiation-induced lung injury (RILI)에 대한 치료제가 될 수 있음을 제시하였다.
2020-10-05 17:46:12
편집위원2
방사선에 의해 유도되는 폐섬유화에서 LXA 4-FPR2 signaling과 TGF-β/Smad signaling 의 crosstalk을 규명함으로써 방사선에 의한 폐섬유화 기전에 대한 다양한 방향을 제시한 연구라 생각됨.
2020-10-05 17:46:56