글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Exp Mol Med.] 방사선에 의한 미토콘드리아SOD2에 의한 암의 전이연구Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase 2 mediates γ-irradiation-induced cancer cell invasion.
KIRAMS / 정찬헌, 엄홍덕*
- 출처
- Exp Mol Med.
- 등재일
- 2019 Feb 12
- 저널이슈번호
- 51(2):14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0207-5.
- 내용
Abstract
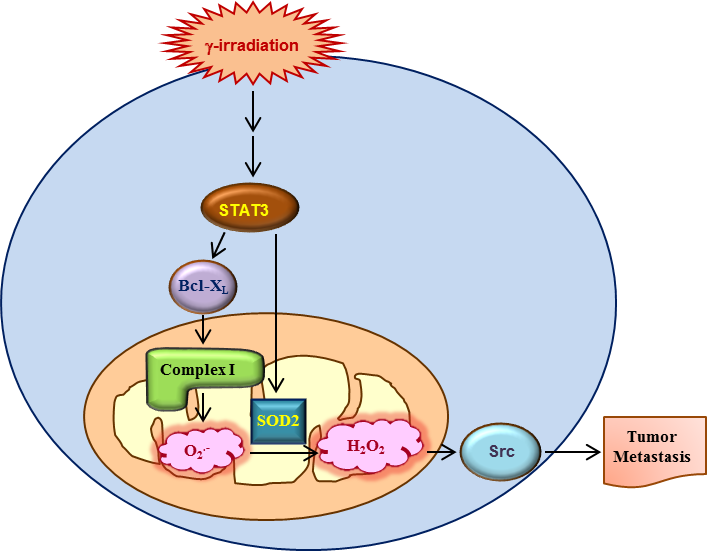
Sublethal doses of γ-rays promote cancer cell invasion by stimulating a signaling pathway that sequentially involves p53, sulfatase 2 (SULF2), β-catenin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and Bcl-XL. Given that Bcl-XL can increase O2•- production by stimulating respiratory complex I, the possible role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in γ-irradiation-induced cell invasion was investigated. Indeed, γ-irradiation promoted cell invasion by increasing mitochondrial ROS levels, which was prevented by metformin, an inhibitor of complex I. γ-Irradiation-stimulated STAT3 increased the expression of superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of O2•- to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). In contrast to O2•-, H2O2 functions as a signaling molecule. γ-Irradiation consistently stimulated the Src-dependent invasion pathway in a manner dependent on both complex I and SOD2. SOD2 was also essential for the invasion of un-irradiated cancer cells induced by upregulation of Bcl-XL, an intracellular oncogene, or extracellular factors, such as SULF2 and IL-6. Overall, these data suggested that SOD2 is critical for the malignant effects of radiotherapy and tumor progression through diverse endogenous factors.
Author informationJung CH1,2, Kim EM1, Song JY1, Park JK1, Um HD3.
1
Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Korea.
2
Jaseng Spine and Joint Research Institute, Jaseng Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
3
Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Korea. hdum@kirams.re.kr.
- 연구소개
- 방사선치료에서 살아남은 암세포는 더욱 악성화 되어 전이력이 상승할 수도 있습니다. 그 기전 규명을 위하여, 본 연구진은 미트콘드리아의 complex I이 암 전이의 핵심 추진체임을 규명한 바 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 방사선치료에서 생존한 암세포에는 Bcl-XL과 미트콘드리아에만 존재하는 superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2)의 양이 증가되어 있음을 발견하였습니다. 이들의 작용을 분석한 결과, Bcl-XL은 complex I을 활성화하여 O2.- 발생을 증가시키고 SOD2는 O2.-를 신호전달인자인 H2O2로 변환시켜 암 전이를 촉진함을 확인하였습니다. 본 연구진은 또한 미트콘드리아에 존재하지 않는 SOD1은 전이와 무관함을 확인하여, 미트콘드리아가 암 전이에 중추적인 역할을 하고 방사선치료에서 생존한 암세포들은 미트콘드리아 활성이 증가되어 악성화가 더욱 상승한다고 생각됩니다.
- 덧글달기









