글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Med Phys .] Deep learning proton beam range estimation model for quality assurance based on two-dimensional scintillated light distributions in simulations2차원 섬광 분포 기반의 품질관리를 위한 양성자 빔 비정 추정 딥러닝 모델 연구
아산병원 / 이은호, 고영문*
- 출처
- Med Phys .
- 등재일
- 2023 Nov
- 저널이슈번호
- 50(11):7203-7213. doi: 10.1002/mp.16646. Epub 2023 Jul 30.
- 내용
-
Abstract
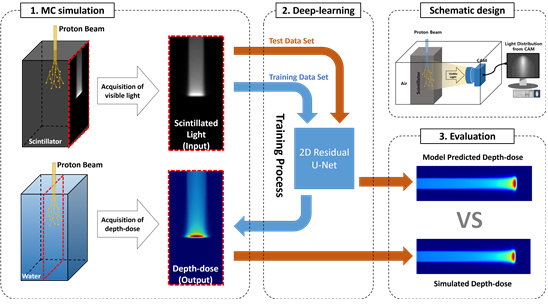
Background: Many studies have utilized optical camera systems with volumetric scintillators for quality assurances (QA) to estimate the proton beam range. However, previous analytically driven range estimation methods have the difficulty to derive the dose distributions from the scintillation images with quenching and optical effects.Purpose: In this study, a deep learning method utilized to QA was used to predict the beam range and spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) for two-dimensional (2D) map conversion from the scintillation light distribution (LD) into the dose distribution in a water phantom.
Methods: The 2D residual U-net modeling for deep learning was used to predict the 2D water dose map from a 2D scintillation LD map. Monte Carlo simulations for dataset preparation were performed with varying monoenergetic proton beam energies, field sizes, and beam axis shifts. The LD was reconstructed using photons backpropagated from the aperture as a virtual lens. The SOBP samples were constructed based on monoenergetic dose distributions. The training set, including the validation set, consisted of 8659 image pairs of LD and water dose maps. After training, dose map prediction was performed using a 300 image pair test set generated under random conditions. The pairs of simulated and predicted dose maps were analyzed by Bragg peak fitting and gamma index maps to evaluate the model prediction.
Result: The estimated beam range and SOBP width resolutions were 0.02 and 0.19 mm respectively for varying beam conditions, and the beam range and SOBP width deviations from the reference simulation result were less than 0.1 and 0.8 mm respectively. The simulated and predicted distributions showed good agreement in the gamma analysis, except for rare cases with failed gamma indices in the proximal and field-marginal regions.
Conclusion: The deep learning conversion method using scintillation LDs in an optical camera system with a scintillator is feasible for estimating proton beam range and SOBP width with high accuracy.
Affiliations
Eunho Lee 1, Byungchul Cho 2 3, Jungwon Kwak 2, Chiyoung Jeong 2, Min-Jae Park 2, Sung-Woo Kim 2, Si Yeol Song 2 3, Youngmoon Goh 2
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- Bragg peak; Monte Carlo simulation; deep learning; residual U-net; scintillation.
- 연구소개
- 이 연구에서는 시뮬레이션 차원에서 광학 카메라 시스템과 형광체에 딥러닝 방법론을 적용하여, 양성자빔의 range 및 Spread-Out Bragg Peak (SOBP)를 예측하는 방법을 탐구하였습니다. 이전의 분석 기반의 방법이 겪었던 어려움을 극복하기 위해, 2차원 형광체 광분포를 2차원 선량 분포로 변환하는 것을 목표로 하였고, 시뮬레이션을 통해 다양한 양성자 빔 조건에 대한 데이터셋을 구축하고 이를 이용하여 모델을 학습시켰습니다. 연구 결과로는, 예측된 빔 range 및 SOBP의 정확도가 매우 뛰어나다는 것이 확인하였고, 다양한 빔 조건에서의 환경에서도 빔 range 및 SOBP의 예측이 높은 일치도를 보였으며, 브래그피크 피팅 및 감마 지수 맵을 통한 분석에서도 모델의 높은 성능을 확인할 수 있었습니다. 이러한 결과는 광학 시스템을 통한 딥러닝 학습이 양성자빔 range 및 SOBP 예측에 효과적인 방법임을 시사하고 있습니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Med Phys .] Fully-automated detection of small bowel carcinoid tumors in CT scans using deep learning
- 다음글 [J Appl Clin Med Phys .] A study on inter-planner plan quality variability using a manual planning- or Lightning dose optimizer-approach for single brain lesions treated with the Gamma Knife® Icon™









