글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [J Appl Clin Med Phys .] A comprehensive evaluation of advanced dose calculation algorithms for brain stereotactic radiosurgery
University of Rochester Medical Center / 윤지형*
- 출처
- J Appl Clin Med Phys .
- 등재일
- 2023 Nov
- 저널이슈번호
- 24(11):e14169. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14169. Epub 2023 Sep 29.
- 내용
Abstract
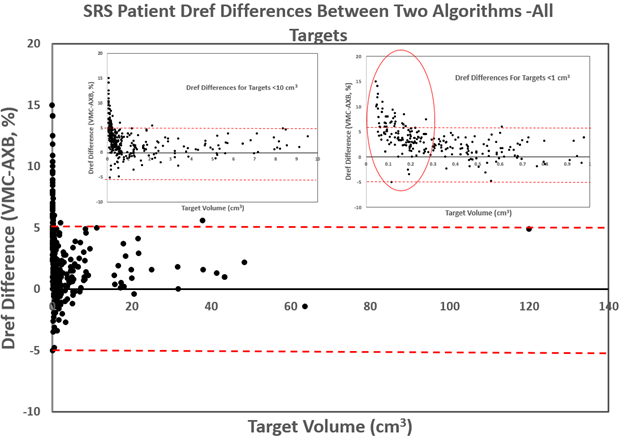
Purpose: Accurate dose calculation is important in both target and low dose normal tissue regions for brain stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). In this study, we aim to evaluate the dosimetric accuracy of the two advanced dose calculation algorithms for brain SRS.Methods: Retrospective clinical case study and phantom study were performed. For the clinical study, 138 SRS patient plans (443 targets) were generated using BrainLab Elements Voxel Monte Carlo (VMC). To evaluate the dose calculation accuracy, the plans were exported into Eclipse and recalculated with Acuros XB (AXB) algorithm with identical beam parameters. The calculated dose at the target center (Dref), dose to 95% target volume (D95), and the average dose to target (Dmean) were compared. Also, the distance from the skull was analyzed. For the phantom study, a cylindrical phantom and a head phantom were used, and the delivered dose was measured by an ion chamber and EBT3 film, respectively, at various locations. The measurement was compared with the calculated doses from VMC and AXB.
Results: In clinical cases, VMC dose calculations tended to be higher than AXB. It was found that the difference in Dref showed > 5% in some cases for smaller volumes < 0.3 cm3 . Dmean and D95 differences were also higher for small targets. No obvious trend was found between the dose difference and the distance from the skull. In phantom studies, VMC dose was also higher than AXB for smaller targets, and VMC showed better agreement with the measurements than AXB for both point dose and high dose spread.
Conclusion: The two advanced calculation algorithms were extensively compared. For brain SRS, AXB sometimes calculates a noticeable lower target dose for small targets than VMC, and VMC tends to have a slightly closer agreement with measurements than AXB.
Affiliation
Jihyung Yoon 1, Hyunuk Jung 1, Sean M Tanny 1, Olga Maria Dona Lemus 1, Michael T Milano 1, Sara J Hardy 1, Kenneth Y Usuki 1, Dandan Zheng 1
1Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, USA.
- 키워드
- AXB; Monte Carlo; SRS; VMC; acuros; eclipse; elements.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구에서는 뇌 SRS의 소형 필드에 대해 대표적인 선량 계산 알고리즘인 AcurosXB (Varian Eclipse)와 Monte Carlo (BrainLab Elements) 간의 선량 계산 정확도를 평가하였습니다. Phantom 측정 결과, Monte Carlo의 계산 값이 AcurosXB의 것보다 더 정확하게 나타났습니다. 특히 PTV 부피가 작아질수록 Monte Carlo와 AcurosXB 간의 차이가 커진다는 것을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이는 MLC의 구조 모델링에 의한 차이로 해석됩니다. MLC 사이의 간격이 작아짐에 따라 두 계산 결과의 차이가 더 커짐을 확인할 수 있었습니다. 따라서 특히 소형 PTV (<0.3cc)의 경우, AcurosXB의 계산 결과보다 실제 환자에게 전달된 선량이 더 커질 것으로 예측되므로 치료 계획 수립 시 주의가 필요합니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [J Appl Clin Med Phys .] A study on inter-planner plan quality variability using a manual planning- or Lightning dose optimizer-approach for single brain lesions treated with the Gamma Knife® Icon™
- 다음글 [Med Phys .] Improvement of phoswich detector-based β+/γ-ray discrimination algorithm with deep learning










편집위원
본 논문은 주로 소조사면을 많이 쓰는 뇌 정위 방사선 수술을 위한 선량 계산 알고리즘의 선량 측정 정확도를 평가한 논문으로, Voxel Monte Carlo가 작은 표적에 있어서 AXB에 비해 측정값과 더 잘 일치하는 경향이 있음을 증명하여 임상적 의미가 있다.
2024-01-08 11:25:18
편집위원2
본 논문에서는 선형가속기 기반의 방사선수술 시행시 방사선치료계획시스템(TPS)의 오차와 TPS간의 차이를 연구하였다. 통상의 방사선치료용 TPS는 직경 약 3 cm 이상의 넓은 조사면의 선량계산에 최적화되어 있어, 0.5×0.5㎠ ~ 3×3 ㎠와 같은 방사선수술용 소조사면에 대한 선량계산의 정확성 평가가 필요하다.
본 논문에서는 최신 알고리즘이 탑재된 치료계획시스템 2종(VMC와 Acurus XB)에 대하여 다양한 소조사면 조건에서 상호 차이 및 정확성을 분석하였으며, 그 결과 TPS간의 상호 차이와 오차의 발생이 계산 알고리즘 뿐 아니라 MLC의 모델링 파라미터가 원인으로 작용할 수 있음을 보였다.
따라서 본 논문은 선형가속기 기반의 방사선수술 분야에서 치료계획시스템 품질관리에 활용할 수 있는 유용한 연구결과를 제공하며, 다양한 후속 연구의 필요성을 제안하고 있다.
뇌정위방사선수술(SRS)은 주로 감마나이프와 사이버나이프와 같은 전용 장비를 사용하여 시행하고 있지만, 최근 고분해능 다엽콜리메이터(MLC)를 장착한 선형가속기를 이용한 SRS가 시행되고 있다.
선형가속기 기반의 SRS는 비침습적(non-invasive) frameless 방법으로 환자를 고정하고, 영상장치로 표적 오차를 확인할 수 있으며, FFF beam을 이용하여 치료시간도 단축할 수 있어 1회 조사대신에 분할 조사를 시행할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
SRS와 통상적 방사선치료의 가장 큰 차이점은 SRS에서는 3×3 ㎠ cm 이내의 소조사면이 사용된다는 점이다. 소조사면의 경우에 측정이 어려운 것으로 알려져 있고, 특히 MLC로 형성되는 소조사면의 경우에는 선량계산의 정확성이 치료계획시스템의 MLC 모델링과 계산 알고리즘에 따라 차이를 보일 수 있어, 환자 치료시 높은 수준의 정도관리가 요구된다. 본 논문의 작성 배경은 여기에 있다고 볼 수 있다
2024-01-08 11:25:54