글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Med Phys .] Development of a quasi-3D dosimeter using radiochromic plastic for patient-specific quality assurance
연세의대, 서울의대 / 조진동, 김진성*, 김정인*
- 출처
- Med Phys .
- 등재일
- 2023 Oct
- 저널이슈번호
- 50(10):6624-6636. doi: 10.1002/mp.16541. Epub 2023 Jul 5.
- 내용
Abstract
Background: Patient-specific QA verification ensures patient safety and treatment by verifying radiation delivery and dose calculations in treatment plans for errors. However, a two-dimensional (2D) dose distribution is insufficient for detecting information on the three-dimensional (3D) dose delivered to the patient. In addition, 3D radiochromic plastic dosimeters (RPDs) such as PRESAGE® represent the volume effect in which the dosimeters have different sensitivities according to the size of the dosimeters. Therefore, to solve the volume effect, a Quasi-3D dosimetry system was proposed to perform patient-specific QA using predetermined-sized and multiple RPDs.Purpose: For patient-specific quality assurance (QA) in radiation treatment, this study aims to assess a quasi-3D dosimetry system using an RPD.
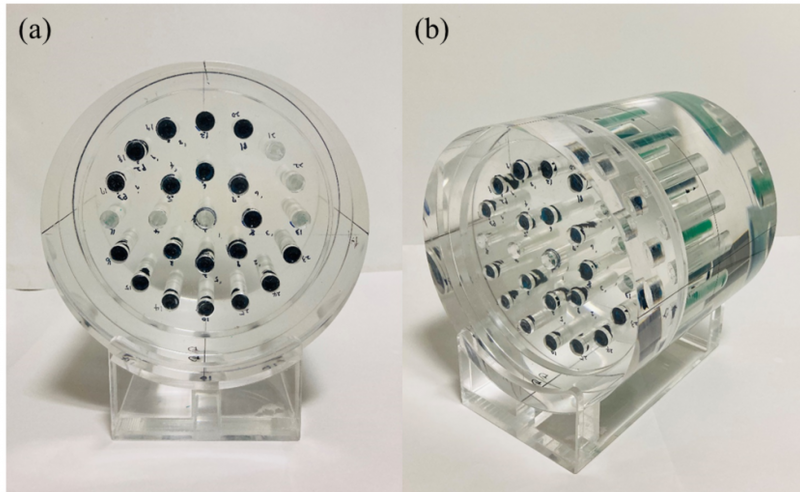
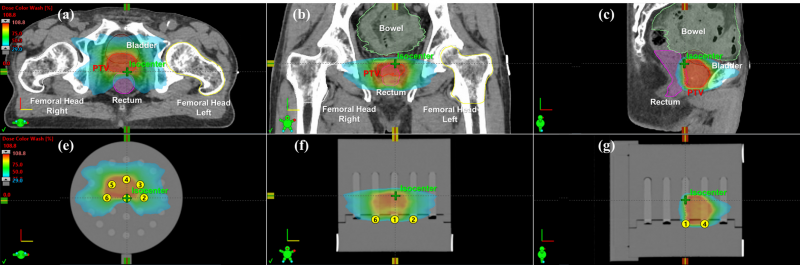
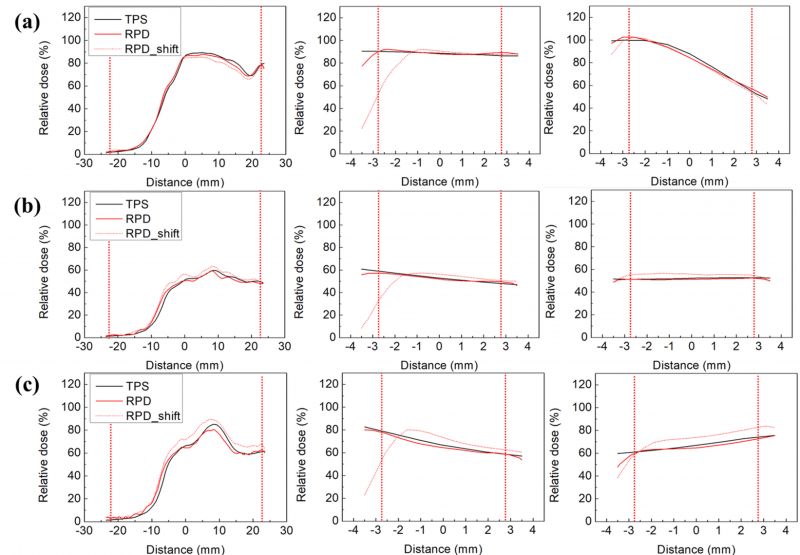
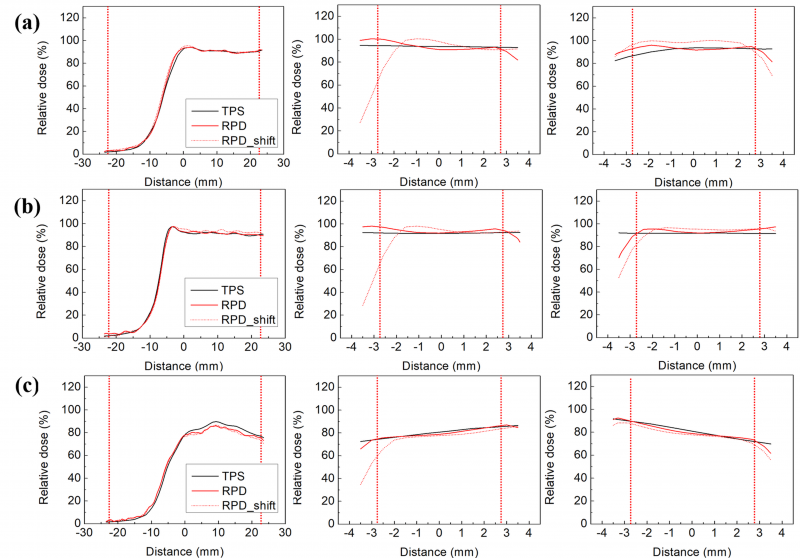
Methods: Gamma analysis was performed to verify the agreement between the measured and estimated dose distributions of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT). We fabricated cylindrical RPDs and a quasi-3D dosimetry phantom. A practicability test for a pancreatic patient utilized a quasi-3D dosimetry device, an in-house RPD, and a quasi-3D phantom. The dose distribution of the VMAT design dictated the placement of nine RPDs. Moreover, a 2D diode array detector was used for 2D gamma analysis (MapCHECK2). The patient-specific QA was performed for IMRT, VMAT, and stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) in 20 prostate and head-and-neck patients. For each patient, six RPDs were positioned according to the dose distribution. VMAT SABR and IMRT/VMAT plans employed a 2%/2 mm gamma criterion, whereas IMRT/VMAT plans used a 3%/2 mm gamma criterion, a 10% threshold value, and a 90% passing rate tolerance. 3D gamma analysis was conducted using the 3D Slicer software.
Results: The average gamma passing rates with 2%/2 mm and 3%/3 mm criteria for relative dose distribution were 91.6% ± 1.4% and 99.4% ± 0.7% for the 3D gamma analysis using the quasi-3D dosimetry system, respectively, and 97.5% and 99.3% for 2D gamma analysis using MapCHECK2, respectively. The 3D gamma analysis for patient-specific QA of 20 patients showed passing rates of over 90% with 2%/2 mm, 3%/2 mm, and 3%/3 mm criteria.
Conclusions: The quasi-3D dosimetry system was evaluated by performing patient-specific QAs with RPDs and quasi-3D phantom. The gamma indices for all RPDs showed more than 90% for 2%/2 mm, 3%/2 mm, and 3%/3 mm criteria. We verified the feasibility of a quasi-3D dosimetry system by performing the conventional patient-specific QA with the quasi-3D dosimeters.

Affiliations
Jin Dong Cho 1 2, Hyeongmin Jin 1 2 3, Seongmoon Jung 1 2 3, Jaeman Son 1 2 3, Chang Heon Choi 1 2 3 4, Jong Min Park 1 2 3 4, Jin Sung Kim 5 6, Jung-In Kim 1 2 3 4
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
6Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- patient-specific quality assurances; quasi-3D dosimetry system; radiochromic three-dimensional dosimetry.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
- 본 논문은 RPD 소자를 이용하여 3차원적 선량분포를 측정함으로써 방사선치료 품질관리를 향상시킬 수 있음을 보인 논문이다.
- 강도조절방사선치료(IMRT) 치료계획 수립 후 치료전 치료부위의 선량분포를 측정으로 확인하는 것은 중요하다. 그러나 기술적 한계로 인해 기존에 필름이나 평면 배열형 검출기(array detector)와 같은 2차원적 측정방법이 사용되고 있다. 이 때 배열형 검출기의 경우 3차원적 형태로 제작 가능하나 분해능이 낮은 단점이 있고, 폴리머 젤을 이용한 3차원적 측정은 아직 연구 중이며 실용화 단계는 아니다.
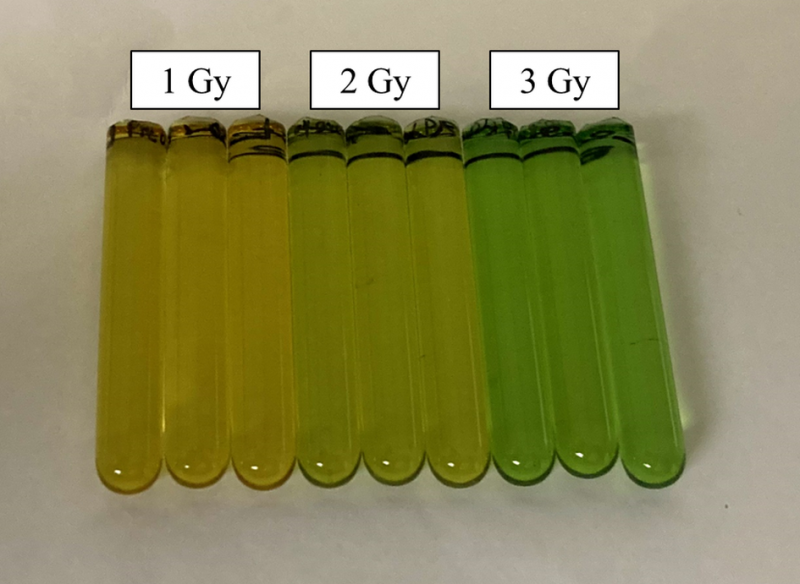
- 본 논문에서는 IMRT 환자의 품질관리(QA)를 위하여 RPD(Radiochromic plastic dosimeters)를 사용하여 팬텀속 3차원적 선량분포를 측정하고 분석하였다. RPD는 Radiochromic 필름과 유사하게 방사선에 의해 변색이 되는 고체 측정소자이다.
- 본 연구에서는 플러그 형태(직경 10 mm, 길이 61.2 mm)로 동일하게 제작한 다수의 RPD를 팬텀속에 삽입하는 방법으로 측정 시스템을 구성하였으며, 다양한 IMRT 치료계획 사례에 대하여 삽입 위치의 3차원적 선량분포를 측정하였고 감마분석(Gamma analysis)에서 우수한 결과를 보였다.
- 치료 체적 전체의 3차원적 선량분포를 측정하기 위해서는 큰 체적의 단일 RPD가 사용되어야 하지만, 본 연구에서는 RPD 소자의 체적 의존성으로 인해 소형 RPD 소자를 다수 사용하여 임상적용을 평가한 점에서 흥미로우며 완전한 3차원적인 측정은 아니므로 제목과 같이 Quasi‐3D 측정에 가깝다. 향후, 지속적 연구를 통해 RPD의 물리적 특성이 개선되고 큰 체적의 RPD가 적용 가능한 경우에 완전한 3차원적 측정이 가능할 것으로 본다.
2023-12-05 17:30:10