글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Med Phys.] Depth-of-interaction positron emission tomography detector with 45° tilted silicon photomultipliers using dual-ended signal readout
서울의대 / 서민지, 박해욱, 고근배, 이재성*
- 출처
- Med Phys.
- 등재일
- 2023 Mar 12.
- 저널이슈번호
- doi: 10.1002/mp.16355. Online ahead of print.
- 내용
Abstract
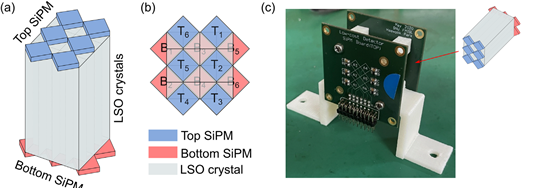
Background: Small-animal positron emission tomography (PET) systems are widely used in molecular imaging research and drug development. There is also growing interest in organ-dedicated clinical PET systems. In these small-diameter PET systems, the measurement of the depth-of-interaction (DOI) of annihilation photons in scintillation crystals allows for the correction of parallax error in PET system, leading to an improvement on the spatial resolution uniformity. The DOI information is also useful for improving the timing resolution of PET system as it enables the correction of DOI-dependent time walk in the arrival time difference measurement of annihilation photon pairs. The dual-ended readout scheme is one of the most widely investigated DOI measurement methods, which collects visible photons using a pair of photosensors located at both ends of the scintillation crystal. Although the dual-ended readout allows for simple and accurate DOI estimation, it requires twice the number of photosensors compared to the single-ended readout scheme.Purpose: To effectively reduce the number of photosensors in a dual-ended readout scheme, we propose a novel PET detector configuration that employs 45° tilted and sparsely arranged silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs). In this configuration, the angle between the scintillation crystal and SiPM is 45°. Therefore, and thus, the diagonal of the scintillation crystal matches one of the lateral sides of the SiPM. Accordingly, it allows for the use of SiPM device larger than the scintillation crystal, thereby improving light collection efficiency with a higher fill factor and reducing SiPM quantity. In addition, all scintillation crystals can achieve more uniform performance than other dual-ended readout methods with a sparse SiPM arrangement because 50% of the scintillation crystal cross section is commonly in contact with the SiPM.
Methods: To demonstrate the feasibility of our proposed concept, we implemented a PET detector that employs a 4 ×× 4 LSO block with a single crystal dimension of 3.03 × 3.03 × 20 mm3 and a 45° tilted SiPM array. The 45° tilted SiPM array consists of 2 × 3 SiPM elements at the top ("Top SiPM") and 3 × 2 SiPM elements at the bottom ("Bottom SiPM"). Each crystal element of the 4 × 4 LSO block is optically coupled with each quarter section of the Top SiPM and Bottom SiPM pair. To characterize the performance of the PET detector, the energy, DOI, and timing resolution were measured for all 16 crystals. The energy data was obtained by summing all the charges from the Top SiPMs and Bottom SiPMs, and the DOI resolution was measured by irradiating the side of the crystal block at five different depths (2, 6, 10, 14, and 18 mm). The timing was estimated by averaging the arrival time of the annihilation photons measured at the Top SiPMs and Bottom SiPMs (Method 1). The DOI-dependent time-walk effect was further corrected by using DOI information and statistical variations in the trigger times at the Top SiPMs and Bottom SiPMs (Method 2).
Results: The average DOI resolution of the proposed PET detector was 2.5 mm, thereby resolving the DOI at five different depths, and the average energy resolution was 16% full width at half maximum (FWHM). When Methods 1 and 2 were applied, the coincidence timing resolutions were 448 and 411 ps FWHM, respectively.
Conclusions: We expect that our novel low-cost PET detector design with 45° tilted SiPMs and a dual-ended readout scheme would be a suitable solution for constructing a high-resolution PET system with DOI encoding capability.
Affiliations
Minjee Seo 1 2, Haewook Park 1 2, Seungeun Lee 1 2, Guen Bae Ko 3 4, Jae Sung Lee 1 2 3 4
1Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
4Brightonix Imaging Inc., Seoul, South Korea.
- 키워드
- depth-of-interaction (DOI); dual-ended signal readout; high-resolution; positron emission tomography (PET); silicon photomultiplier (SiPM).
- 연구소개
- 본 논문은 DOI PET 검출기 중에서도 dual-ended readout을 활용한 새로운 검출 디자인을 제안하는 연구입니다. 이 연구에서는 광센서의 배치를 45도 회전시킴으로써 기존의 dual-ended readout에서 요구되는 광센서의 수를 감소시키고, 더 큰 광센서를 사용할 수 있어 검출기의 구성 비용을 절감할 수 있는 장점을 갖고 있습니다. 이러한 디자인은 다른 비슷한 컨셉의 디자인에 비해 광 수집 효율이 높다는 장점을 가지며, PET 검출기의 다양한 디자인 중 하나로, 관련 연구자들에게 흥미를 불러일으킬 수 있는 연구로 판단됩니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
DOI 정보는 소동물 및 특정 장기 전용 PET 시스템에서 공간해상도 균일도 및 타이밍 해상도 개선에 중요한 역할을 함. 본 연구에서는 dual-ended readout scheme 기반 DOI 측정 PET 검출기를 위해 45도 경사 SiPM를 활용한 새로운 구조를 제안하여 DOI 검출기 제작 비용 절감 가능성을 제시하였음.
2023-05-08 17:38:16
편집위원2
PET은 보통 betta 입자가 생생되는 위치와 쌍소멸이 일어나는 위치가 차이가 나지만 이를 감안하여 스캔을 하는 데 반해 동물을 위한 소형 PET에서는 이 차이가 PET영상의 해상도에 영향을 많이 주게되는 모양이다. 이를 극복하는 방법으로 디텍터의 형태를 여러 가지로 구성하는 방법이 있는데, 그 중에서 45도로 회전시킨 이중 디텍터 구조에 대해 제작하고 실험하였다. 앞으로 동물을 위한 기술이 점점 발전하리라 예상한다.
2023-09-06 14:20:27