글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Med Phys .] Development of a real-time in vivo dosimetry tool for electron beam therapy using a flexible thin film solar cell coated with scintillator powder
국립암센터 / 정성훈, 이세병*
- 출처
- Med Phys .
- 등재일
- 2023 Jan
- 저널이슈번호
- 50(1):557-569. doi: 10.1002/mp.15947. Epub 2022 Sep 4.
- 내용
Abstract
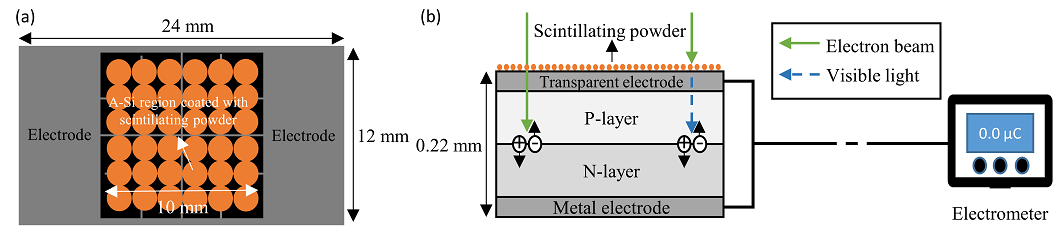
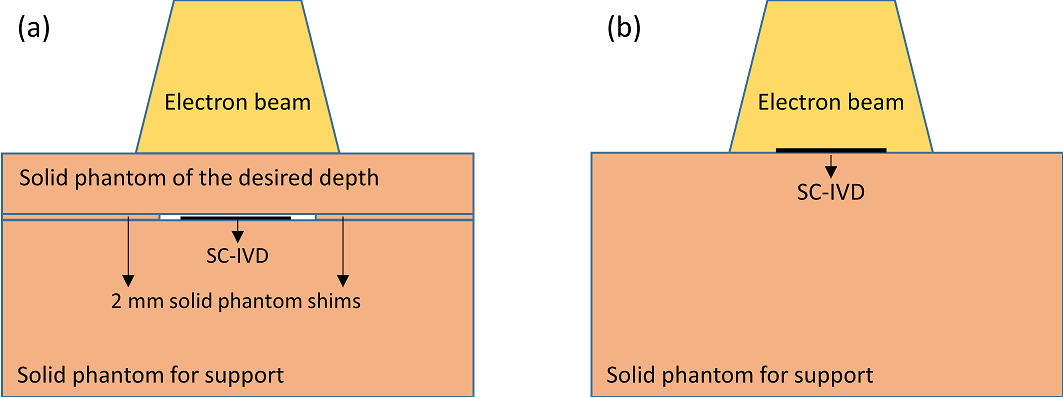
Purpose: A real-time solar cell based in vivo dosimetry system (SC-IVD) was developed using a flexible thin film solar cell and scintillating powder. The present study evaluated the clinical feasibility of the SC-IVD in electron beam therapy.Methods: A thin film solar cell was coated with 100 mg of scintillating powder using an optical adhesive to enhance the sensitivity of the SC-IVD. Calibration factors were obtained by dividing the dose, measured at a reference depth for 6-20 MeV electron beam energy, by the signal obtained using the SC-IVD. Dosimetric characteristics of SC-IVDs containing variable quantities of scintillating powder (0-500 mg) were evaluated, including energy, dose rate, and beam angle dependencies, as well as dose linearity. To determine the extent to which the SC-IVD affected the dose to the medium, doses at R90 were compared depending on whether the SC-IVD was on the surface. Finally, the accuracy of surface doses measured using the SC-IVD was evaluated by comparison with surface doses measured using a Markus chamber.
Results: Charge measured using the SC-IVD increased linearly with dose and was within 1% of the average signal according to the dose rate. The signal generated by the SC-IVD increased as the beam angle increased. The presence of the SC-IVD on the surface of a phantom resulted in a 0.5%-2.2% reduction in dose at R90 for 6-20 MeV electron beams compared with the bare phantom. Surface doses measured using the SC-IVD system and Markus chamber differed by less than 5%.
Conclusions: The dosimetric characteristics of the SC-IVD were evaluated in this study. The results showed that it accurately measured the surface dose without a significant difference of dose in the medium when compared with the Markus chamber. The flexibility of the SC-IVD allows it to be attached to a patient's skin, enabling real-time and cost-effective measurement.
Affiliations
Seonghoon Jeong 1, Seohyeon An 1 2, Yong-Cheol Kwon 3, Sang-Il Pak 1, Wonjoong Cheon 1, Dongho Shin 1, Young Kyung Lim 1, Jong Hwi Jeong 1, Haksoo Kim 1, Se Byeong Lee 1
1Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Physics, Hanyang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- electron beam therapy; flexible thin film solar cell; in vivo dosimetry; real-time measurement.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 전자선 치료시 비결정질 실리콘 기반의 박막 태양전지를 이용하여 환자 표면에 조사되는 전자선을 측정하여 계획된대로 환자에게 전자선이 조사되고 있는지 검증하는 방법론에 대한 가능성을 확인한 결과입니다. 이전에 박막 태양전지를 X-ray의 측정에 사용할 수 있다는 논문을 게재한 적이 있었는데, 이번 연구 결과는 보다 직접적으로 전자선 치료를 받는 환자에게 직접적으로 사용할 수 있음을 시사하는 결과이기 때문에 보다 의미가 있다고 생각됩니다. 또한, 박막 태양전지의 물리적 두께는 마이크로미터 단위로 매우 얇은 편이라 기존의 생체선량 측정에 사용되는 검출기들보다 환자에게 전달되는 선량을 방해하지 않는다는 장점이 있다는 점이 이 연구의 중요한 결과 중 하나라고 생각됩니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
솔라셀을 이용하여 전자선 치료에 대한 In-vivo 측정을 체계를 개발하는 연구로서 솔라셀을 이용했다는 점과 결과가 5%이내에서 일치한다는 점에서 흥미로웠음
2023-03-07 09:28:48