글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Mol Imaging Biol .] A Machine Learning Approach Using [18F]FDG PET-Based Radiomics for Prediction of Tumor Grade and Prognosis in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor
성균관의대 / 박용진, 현승협*
- 출처
- Mol Imaging Biol .
- 등재일
- 2023 Oct
- 저널이슈번호
- 25(5):897-910. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01832-7. Epub 2023 Jul 3.
- 내용
Abstract
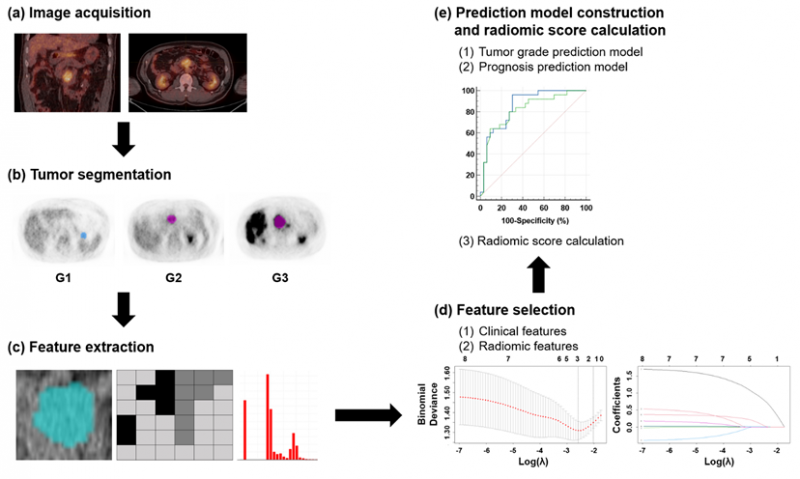
Purpose: We sought to develop and validate machine learning (ML) models for predicting tumor grade and prognosis using 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)-based radiomics and clinical features in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs).Procedures: A total of 58 patients with PNETs who underwent pretherapeutic [18F]FDG PET/computed tomography (CT) were retrospectively enrolled. PET-based radiomics extracted from segmented tumor and clinical features were selected to develop prediction models by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator feature selection method. The predictive performances of ML models using neural network (NN) and random forest algorithms were compared by the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) and validated by stratified five-fold cross validation.
Results: We developed two separate ML models for predicting high-grade tumors (Grade 3) and tumors with poor prognosis (disease progression within two years). The integrated models consisting of clinical and radiomic features with NN algorithm showed the best performances than the other models (stand-alone clinical or radiomics models). The performance metrics of the integrated model by NN algorithm were AUROC of 0.864 in the tumor grade prediction model and AUROC of 0.830 in the prognosis prediction model. In addition, AUROC of the integrated clinico-radiomics model with NN was significantly higher than that of tumor maximum standardized uptake model in predicting prognosis (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Integration of clinical features and [18F]FDG PET-based radiomics using ML algorithms improved the prediction of high-grade PNET and poor prognosis in a non-invasive manner.
Affiliations
Yong-Jin Park 1 2, Young Suk Park 3, Seung Tae Kim 3, Seung Hyup Hyun 4
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81, Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 06351, South Korea.
2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Ajou University Medical Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, 164, Worldcup-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, 16499, South Korea.
3Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, 06351, South Korea.
4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81, Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 06351, South Korea. shnm.hyun@samsung.com.
- 키워드
- Machine learning; PET/CT; Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; Prediction model; Prognosis; Radiomics; [18F]FDG.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 췌장 신경내분비종양의 [18F]FDG 라디오믹스 데이터를 이용해서 종양 등급과 예후를 예측하는 기계학습 모델에 대한 연구입니다. 종양 등급과 예후를 예측하는 모델 개발을 위해 임상변수 모델, [18F]FDG 라디오믹스 모델, 임상변수와 [18F]FDG 라디오믹스를 합친 모델로 총 3가지 형태의 예측 모델들을 비교·분석하였으며, 기계학습 알고리즘으로 neural network와 random forest을 사용하였습니다. 종양 등급과 예후를 예측하는데 있어서 임상변수와 [18F]FDG 라디오믹스를 합친 모델이 가장 좋은 성적을 보이는 것을 확인했습니다. [18F]FDG 라디오믹스 모델이 예후 예측보다는 종양 등급 예측에서 더 좋은 성능을 보이는 것으로 확인되었는데, 이러한 예측 모델간 [18F]FDG 라디오믹스의 예측 성능 차이는 각 예측 모델의 예측 클래스간의 [18F]FDG 라디오믹스 점수 차이로 인한 것을 확인한 연구입니다.
- 덧글달기









