글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Yonsei Med J .] Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer Using a Machine Learning Model Based on PET/CT Radiomics
연세의대 / 김소영, 이재훈*, 강정현*
- 출처
- Yonsei Med J .
- 등재일
- 2023 May
- 저널이슈번호
- 64(5):320-326. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0548.
- 내용
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the feasibility of preoperative 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) radiomics with machine learning to predict microsatellite instability (MSI) status in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.Materials and methods: Altogether, 233 patients with CRC who underwent preoperative FDG PET/CT were enrolled and divided into training (n=139) and test (n=94) sets. A PET-based radiomics signature (rad_score) was established to predict the MSI status in patients with CRC. The predictive ability of the rad_score was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) in the test set. A logistic regression model was used to determine whether the rad_score was an independent predictor of MSI status in CRC. The predictive performance of rad_score was compared with conventional PET parameters.
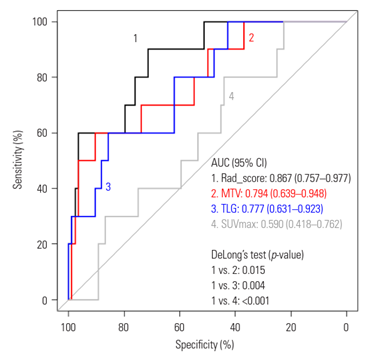
Results: The incidence of MSI-high was 15 (10.8%) and 10 (10.6%) in the training and test sets, respectively. The rad_score was constructed based on the two radiomic features and showed similar AUROC values for predicting MSI status in the training and test sets (0.815 and 0.867, respectively; p=0.490). Logistic regression analysis revealed that the rad_score was an independent predictor of MSI status in the training set. The rad_score performed better than metabolic tumor volume when assessed using the AUROC (0.867 vs. 0.794, p=0.015).
Conclusion: Our predictive model incorporating PET radiomic features successfully identified the MSI status of CRC, and it also showed better performance than the conventional PET image parameters.
Affiliations
Soyoung Kim 1, Jae-Hoon Lee 2, Eun Jung Park 3, Hye Sun Lee 4, Seung Hyuk Baik 3, Tae Joo Jeon 1, Kang Young Lee 5, Young Hoon Ryu 1, Jeonghyun Kang 6
1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. docnuke@yuhs.ac.
3Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Biostatistics Collaboration Unit, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
5Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
6Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ravic@naver.com.
- 키워드
- Colorectal cancer; image analysis; machine learning; microsatellite instability; positron emission tomography.
- 연구소개
- 대장암 환자들을 대상으로 수술전에 시행한 PET/CT 검사를 이용하여 환자의 MSI 상태를 확인하는 머신러닝에 대한 논문입니다. MSI 는 immunotherapy 의 반응을 예측하는데 중요한 biomarker 로 생각됩니다. 그렇지만 tissue를 얻기 어려운 상황에서 MSI를 확인하는 것이 어려운 상황도 있습니다. 본 연구를 통해서 대장암 환자에서 PET/CT를 이용하여 MSI를 예측할 수 있을 경우 이러한 어려움을 극복하는데 도움이 될 수 있을것으로 생각됩니다.
- 덧글달기









