글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2024년 04월호
[Clin Transl Radiat Oncol .] Normal tissue complication probability models of hypothyroidism after radiotherapy for breast cancer연세의대 / 박예인, 홍채선*, 최서희*
- 출처
- Clin Transl Radiat Oncol .
- 등재일
- 2024 Jan 24:45:100734.
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
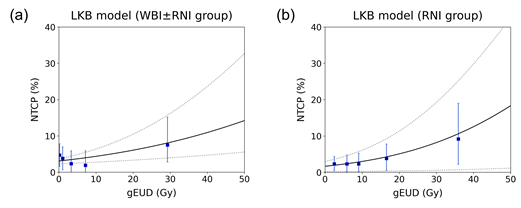
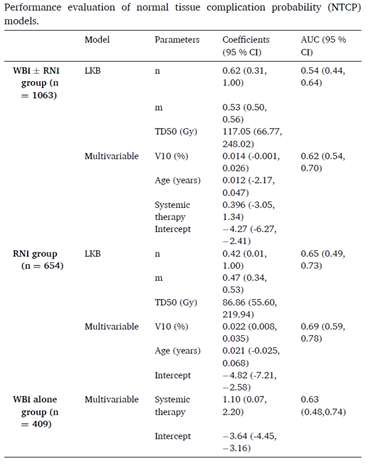
Purpose: We aimed to develop Lyman-Kutcher-Burman (LKB) and multivariable normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) models to predict the risk of radiation-induced hypothyroidism (RIHT) in breast cancer patients.Materials and methods: A total of 1,063 breast cancer patients who underwent whole breast irradiation between 2009 and 2016 were analyzed. Individual dose-volume histograms were used to generate LKB and multivariable logistic regression models. LKB model was fit using the thyroid radiation dose-volume parameters. A multivariable model was constructed to identify potential dosimetric and clinical parameters associated with RIHT. Internal validation was conducted using bootstrapping techniques, and model performance was evaluated using the area under the curve (AUC) and Hosmer-Lemeshow (HL) goodness-of-fit test.
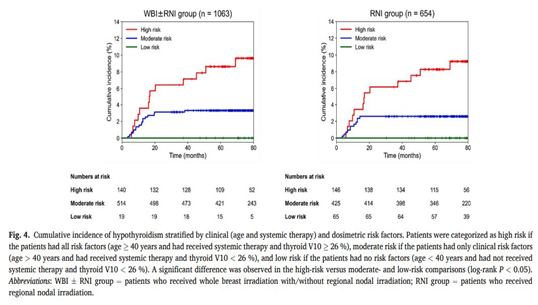
Results: RIHT developed in 4 % of patients with a median follow-up of 77.7 months. LKB and multivariable NTCP models exhibited significant agreement between the predicted and observed results (HL P values > 0.05). The multivariable NTCP model outperformed the LKB model in predicting RIHT (AUC 0.62 vs. 0.54). In the multivariable model, systemic therapy, age, and percentage of thyroid volume receiving ≥ 10 Gy (V10) were significant prognostic factors for RIHT. The cumulative incidence of RIHT was significantly higher in patients who exceeded the cut-off values for all three risk predictors (systemic therapy, age ≥ 40 years, and thyroid V10 ≥ 26 %, P < 0.005).
Conclusions: Systemic therapy, age, and V10 of the thyroid were identified as strong risk factors for the development of RIHT. Our NTCP models provide valuable insights to clinicians for predicting and preventing hypothyroidism by identifying high-risk patients.
Affiliations
Ye-In Park 1, Min-Seok Cho 2, Jee Suk Chang 1 3, Jin Sung Kim 1, Yong Bae Kim 1, Ik Jae Lee 1, Chae-Seon Hong 1, Seo Hee Choi 1
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, Gyeonggi do, South Korea.
3BC Cancer - Vancouver Centre, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
- 키워드
- Breast cancer; NTCP model; Radiation-induced hypothyroidism; Risk prediction.
- 연구소개
- 유방암으로 방사선치료를 시행 받은 총 1,063명 환자의 임상 정보와 선량학적 정보를 분석하여 방사선치료 후 갑상선기능저하증 발생 예측 NTCP 모델을 개발한 연구입니다. Lyman–Kutcher–Burman (LKB) model은 thyroid dose-volume parameter만을 이용한 예측 모델이고 multivariate NTCP model은 선량 정보뿐 아니라 환자 임상학적 정보를 통합하여 만든 예측 모델입니다. 개발한 두 모델 모두에서 우수한 예측력이 확인되었고 전신약물치료 시행 여부, 나이 (40세 이상), 갑상선량 V10 수치 (10 Gy 이상 조사된 갑상선 부피(%)로, 26%가 유의한 cut-off)가 가장 중요한 위험 인자였습니다. 본 연구에서는 대규모의 유방암 방사선치료를 시행 받은 환자군을 대상으로 하여 갑상선기능저하증 발생 예측을 위한 NTCP model을 최초로 개발하였습니다. 뿐만 아니라, 선량 지표와 환자의 임상 정보를 통합함으로써 우수한 예측력을 갖는 모델을 성공적으로 개발하였으며, 방사선치료 계획에 활용 가능한 갑상선 선량 지표를 제시하였습니다. 더불어, 특정 위험 인자들이 동반된 환자들에게는 갑상선기능저하증과 관련된 고려가 더욱 필수적임을 제시한 연구로서 의의가 있습니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Medicina (Kaunas) .] A Potential Radiomics-Clinical Model for Predicting Failure of Lymph Node Control after Definite Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer
- 다음글 [Medicine (Baltimore) .] Gamma knife radiosurgery as primary management for intracranial meningioma identified as growing on serial imaging








편집위원
유방암 방사선치료 후 갑상선기능저하증 발생률을 multivariable NTCP model을 이용하여 분석한 결과로, systemic therapy, age, thyroid V10Gy가 유의한 인자로 분석되었음.
덧글달기닫기2024-03-28 11:08:41
등록
편집위원2
수술 후 방사선치료를 받은 유방암 환자 1063명 중 61.5%가 regional LN (level 4 in 18.1% and SCL 43.5%)포함하여 방사선치료를 받았을 때 4%에서 hypothyroidism를 보고하였습니다.
덧글달기닫기2024-03-28 11:09:06
등록