글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [In Vivo .] Association Between Thyroid Radiation Dose and Hypothyroidism in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Regional Nodal Irradiation
한림의대 / 고현강, 박영희, 구태률*
- 출처
- In Vivo .
- 등재일
- 2023 Sep-Oct
- 저널이슈번호
- 37(5):2340-2346. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13338.
- 내용
Abstract
Background/aim: To investigate the association between the thyroid dysfunction and thyroid radiation dose in regional nodal irradiation (RNI) using volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for breast cancer.Patients and methods: We reviewed medical data of 67 patients with breast cancer who underwent curative surgery followed by adjuvant radiotherapy, including RNI using VMAT, between 2018 and 2021. All patients had normal thyroid functional test results, including thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), T3, and free-T4. We defined subclinical hypothyroidism as increased TSH with or without decreased levels of free-T4 and T3 after the completion of VMAT. We calculated dose-volume histogram parameters (DVHPs), including the mean dose and relative thyroid volume receiving at least 10, 20, 30, and 40 Gy.
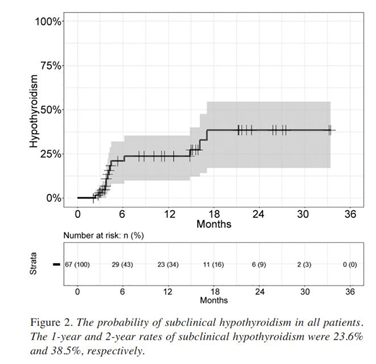
Results: The median follow-up time was 23.2 months. The 3-year locoregional failure-free survival, progression-free survival, and overall survival rates were 96.3%, 94.7%, and 96.2%, respectively. The mean thyroid dose was 21.4 Gy (range=11.5-29.4 Gy). Subclinical hypothyroidism was noted in 14 patients (20.9%) and the median time to the event was 4.1 months. Among the DVHPs, the relative volume receiving ≥20 Gy (V20Gy) was associated with subclinical hypothyroidism. The 2-year rates of subclinical hypothyroidism were 24.8% and 59.1% in patients with V20Gy ≤46.3% and >46.3%, respectively.
Conclusion: A significant proportion of patients with breast cancer developed subclinical hypothyroidism after undergoing VMAT for RNI. Our findings highlight the importance of considering the thyroid as an organ at risk for VMAT planning, and suggest that V20Gy could be a useful dose-volume constraint.
Affiliations
Hyeon Kang Koh # 1, Younghee Park # 2, Taeryool Koo 3, Kwang-Ho Cheong 4, Me Yeon Lee 4, Hae Jin Park 5, Kyoung Ju Kim 6, Soah Park 6, Taejin Han 7, Sei-Kwon Kang 7, Boram Ha 8, Jai-Woong Yoon 8, Me Young Kim 9, Hoonsik Bae 9
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Konkuk University School of Medicine and Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Ewha Womans University Seoul Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea; kootaeryool@hallym.or.kr.
4Department of Radiation Oncology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea.
5Department of Radiation Oncology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
6Department of Radiation Oncology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
7Department of Radiation Oncology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
8Department of Radiation Oncology, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea.
9Department of Radiation Oncology, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Gangwon-do, Republic of Korea.
#Contributed equally.
- 키워드
- Hypothyroidism; breast cancer; radiotherapy; volumetric modulated arc therapy.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [In Vivo .] Predictors of Outcomes in Patients With Clinically Lymph Node Positive Prostate Cancer After Definitive Radiotherapy
- 다음글 [Diagnostics (Basel) .] Evaluating the Necessity of Adaptive RT and the Role of Deformable Image Registration in Lung Cancer with Different Pathologic Classifications










편집위원
유방암에서 영역림프절을 포함하여 VMAT으로 치료 시 갑상선 선량과 갑상선기능 저하증에 대해 분석한 논문으로 V20을 dose-volume constraint로 제안함
2023-11-08 13:56:25