글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- 2020년 03월호
[Radiother Oncol.] Radiotherapy can increase the risk of ischemic cerebrovascular disease in head and neck cancer patients: A Korean population-based cohort study.서울의대 / 이진용, 김수지*
- 출처
- Radiother Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2020 Jan
- 저널이슈번호
- 142:85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.09.025. Epub 2019 Oct 17.
- 내용
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Several reports suggested that radiotherapy (RT) was related to an increased risk of cerebrovascular disease (CVD) in head and neck cancer (HNC) patients, but other risk factors of CVD were not properly considered in estimating the risk of RT. The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of RT on the risk of CVD in HNC patients.MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The Korean Central Cancer Registry data and Korean National Health Insurance Service data were used. A total of 5570 patients with newly diagnosed HNC between the years 2003-2005 was included in our study cohort. We analyzed the effect of treatment modality and other socioeconomic variables on ischemic CVD incidence using the Cox proportional hazard regression model both in the entire cohort (n = 5570) and in the propensity score matching (PSM) cohort (n = 3310).RESULTS:
RT increased the CVD risk by 40.8% (aHR: 1.408, p = 0.006) in the entire cohort and by 44.3% (aHR: 1.443, p = 0.047) in the PSM cohort, respectively.CONCLUSION:
The risk of ischemic CVD increased by RT after adjusting for other socioeconomic and clinical risk factors. Regular follow up and appropriate screening for CVD are required for HNC patients who received RT, and focus should be on advanced-age patients with a low socioeconomic status and known clinical risk factors of CVD.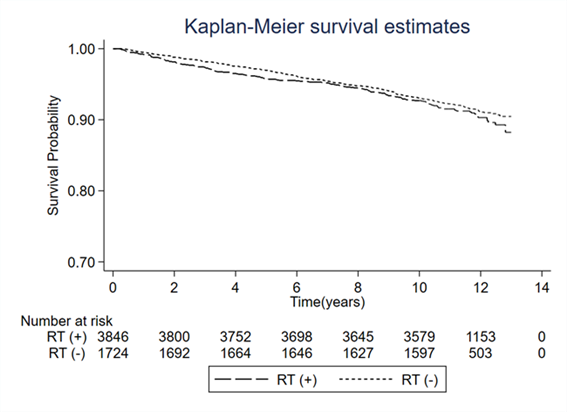
Author informationLee JY1, Kim YA2, Kim HS2, Back JH3, Jung YH4, Lee DH5, Kim S6.
1
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea; Department of Health Policy and Management, Seoul National University College of Medicine, South Korea.
2
National Cancer Control Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea.
3
Health Insurance Policy Research Institute, National Health Insurance Service, South Korea.
4
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, South Korea.
5
National Cancer Control Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea; Korea Public Tissue Bank, Seoul, South Korea.
6
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. Electronic address: suzy101@snu.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Head and neck cancer; Ischemic cerebrovascular disease; Radiotherapy
- 연구소개
- 두경부에 방사선이 조사되었을 때, 방사선에 의한 뇌혈관이나 경동맥 손상으로 허혈성 뇌졸중의 발생 위험이 증가하는가에 관한 연구논문입니다. 2003년부터 2005년까지 중앙암등록본부에 등록된 두경부암 환자 데이터를 바탕으로 방사선치료 여부에 따른 두경부암 환자의 뇌졸중 발생 위험도를 비교 분석했습니다. 연구팀은 혼란변수들(나이, 성별, 흡연, 고혈압, 당뇨, 고콜레스테롤혈증, 사회경제적 지위, 수술 여부)을 조정한 다변량 로지스틱 회귀분석을 통해 뇌졸중 발생의 위험도(HR)를 비교 분석한 결과, 방사선치료를 받은 그룹의 뇌졸중 발생위험은 1.403으로 방사선치료를 받지 않는 환자 그룹 대비 약 40%가량 높은 것으로 보고했습니다. 방사선치료에 의한 뇌줄중의 위험도는 고혈압이나 당뇨에 의한 뇌졸중의 위험도보다는 낮은 수준이었습니다. 따라서 고혈압이나 당뇨가 있으면서 두경부암으로 방사선치료를 받은 고령의 저소득계층 환자들은 치료 후 뇌혈관 또는 경동맥 협착 여부에 대한 장기적인 추적관찰 및 선별 검사가 필요합니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cancer Res Treat.] SUVmax Predicts Disease Progression after Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.
- 다음글 [Oncol Lett.] Treatment time to the end of thoracic radiotherapy has more predictive power for survival than radiation dose intensity in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer receiving concurrent chemoradiation of more than 45 Gy.








편집위원
국민건강보험공단 자료와 한국중앙암등록사업 자료를 활용하여 두경부암에서 방사선치료가 cerebrovascular disease 발생 위험도를 증가시킨다는 연관성을 보여준 연구로 임상진료시 참고할만한 근거논문입니다.
덧글달기닫기2020-03-02 16:37:37
등록