글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Radiother Oncol .] Risk of on-treatment lymphopenia is associated with treatment outcome and efficacy of consolidation immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy
연세의대 / 양고운, 김경환*
- 출처
- Radiother Oncol .
- 등재일
- 2023 Dec:189:109934. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.10
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
Background and purpose: The ability of the effective dose to immune cells (EDIC) and the pre-radiotherapy (RT) absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) to predict lymphopenia during RT, treatment outcomes, and efficacy of consolidation immunotherapy in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer was investigated.Methods and materials: Among 517 patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy, EDIC was calculated using the mean doses to the lungs, heart, and total body. The patients were grouped according to high and low EDIC and pre-RT ALC, and the correlations with radiation-induced lymphopenia and survival outcomes were determined.
Results: Altogether, 195 patients (37.7%) received consolidation immunotherapy. The cutoff values of EDIC and pre-RT ALC for predicting severe lymphopenia were 2.89 Gy and 2.03 × 109 cells/L, respectively. The high-risk group was defined as EDIC ≥ 2.89 Gy and pre-RT ALC < 2.03 × 109 cells/L, while the low-risk group as EDIC < 2.89 Gy and pre-RT ALC ≥ 2.03 × 109 cells/L, and the rest of the patients as the intermediate-risk group. The incidences of severe lymphopenia during RT in the high-, intermediate-, and low-risk groups were 90.1%, 77.1%, and 52.3%, respectively (P < 0.001). The risk groups could independently predict both progression-free (P < 0.001) and overall survival (P < 0.001). The high-risk group showed a higher incidence of locoregional and distant recurrence (P < 0.001). Consolidation immunotherapy showed significant survival benefit in the low- and intermediate-risk groups but not in the high-risk group.
Conclusions: The combination of EDIC and pre-RT ALC predicted severe lymphopenia, recurrence, and survival. It may potentially serve as a biomarker for consolidation immunotherapy.
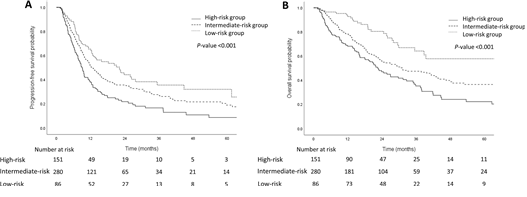
EDIC와 pre-RT ALC로 분류한 위험군에 따른 무진행 생존율과 전체 생존율. 무진행 생존율 (A), 전체 생존율 (B).
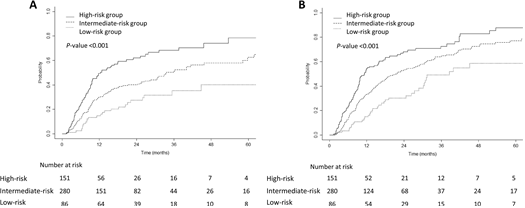
위험군에 따른 국소 재발 및 원격 전이+/-국소 재발의 누적 발생률. 국소 재발 (A), 원격 전이+/-국소 재발 (B).
Affiliations
Gowoon Yang 1, Hong In Yoon 1, Joongyo Lee 1, Jihun Kim 2, Hojin Kim 1, Jaeho Cho 1, Chang Geol Lee 1, Jee Suk Chang 1, Yeona Cho 2, Jin Sung Kim 1, Kyung Hwan Kim 3
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1, Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 211 Eon-ju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06273, Republic of Korea.
3Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1, Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: KYUNGHKIM@yuhs.ac.
- 키워드
- Carcinoma; Chemoradiotherapy; Immunotherapy; Lymphopenia; Non-Small-Cell Lung; Progression-free survival; Survival.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 국소 진행성 비소세포폐암 환자들 중에 근치적 동시항암화학방사선치료를 시행한 517명의 환자를 대상으로 하였습니다. 면역 세포에 대한 예측 선량 (estimated dose to the immune cells, EDIC)과 방사선치료 전 절대 림프구 수 (pre-radiotherapy absolute lymphocyte count, pre-RT ALC)의 조합이 EDIC 단독 또는 pre-RT ALC 단독에 비해 방사선치료로 인해 유발되는 림프구 감소증과 생존률을 더 잘 예측할 수 있을 것이라는 가정을 하였습니다. 연구 결과 EDIC, pre-RT ALC는 치료 중 중증 림프구 감소증과 관련이 있었고, 이 두 변수의 조합은 EDIC 또는 pre-RT ALC 단독보다 방사선 유발 림프구 감소증을 더 잘 예측하였습니다. 또한 EDIC와 pre-RT ALC의 조합은 생존률과도 유의미한 연관성을 보였으며 원격 전이뿐만 아니라 국소 재발도 예측하였습니다. 더 나아가 공고면역요법을 시행한 하위 그룹에서 EDIC와 pre-RT ALC의 조합이 치료 중 림프구 감소증의 위험도를 예측하였으며 궁극적으로 공고면역요법의 효능을 예측하였습니다. 본 연구를 통해 EDIC를 최소화함으로써 림프구 감소증을 줄여 궁극적으로 치료 결과를 향상시킬 수 있음을 시사하였고 방사선치료 계획을 최적화하는 것의 중요성을 강조하였습니다.
- 덧글달기









