글로벌 연구동향
방사선방호 및 안전
- [Nuclear Engineering and Technology] Determination of counting efficiency considering the biodistribution of I-131 activity in the whole-body counting measurement전신계수 측정시 I-131의 체내분포를 고려한 계측효율 연구
KIRAMS / 박민석*
- 출처
- Nuclear Engineering and Technology
- 등재일
- January 2023
- 저널이슈번호
- Volume 55, Issue 1, Pages 295-303
- 내용
-
Abstract
Whole-body counters are widely used to assess internal contamination after a nuclear accident. However, it is difficult to determine radioiodine activity due to limitations in conventional calibration phantoms. Inhaled or ingested radioiodine is heterogeneously distributed in the human body, necessitating time-dependent biodistribution for the assessment of the internal contamination caused by the radioiodine intake. This study aims at calculating counting efficiencies considering the biodistribution of 131I in whole-body counting measurement. Monte Carlo simulations with computational human phantoms were performed to calculate the whole-body counting efficiency for a realistic radioiodine distribution after its intake. The biodistributions of 131I for different age groups were computed based on biokinetic models and applied to age- and gender-specific computational phantoms to estimate counting efficiency. After calculating the whole-body counting efficiencies, the efficiency correction factors were derived as the ratio of the counting efficiencies obtained by considering a heterogeneous biodistribution of 131I over time to those obtained using the BOMAB phantom assuming a homogeneous distribution. Based on the correction factors, the internal contamination caused by 131I can be assessed using whole-body counters. These correction factors can minimize the influence of the biodistribution of 131I in whole-body counting measurement and improve the accuracy of internal dose assessment.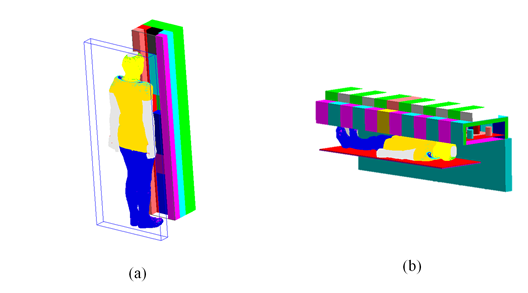
전산모사 기반 교정을 위한 전신계수기에 대한 전산모사 모사 모델링: (a) stand-up type WBC, (b) bed type WBC
Affiliations
MinSeok Park a c, Jaeryong Yoo a,Minho Kim b, Won Il Jang a, Sunhoo Park a
a
National Radiation Emergency Center, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Republic of Korea
b
Department of RI Application, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Republic of Korea
c
Department of Nuclear Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 04763, Republic of Korea
- 키워드
- Whole-body counter;Monte Carlo simulation;Computational phantom;Counting efficiency;Radioiodine
- 연구소개
- 방사선사고 이후 주민에 대한 적절한 보호조치 수행을 위해 주민오염감시(population monitoring)를 수행하고, 주로 전신계수기를 이용하여 주민에 대한 내부오염을 평가합니다. 하지만 기존 전신계수검사는 물리 팬텀 기반 교정의 한계로 측정 대상과 물리 팬텀 사이의 해부학적 구조 차이 및 섭취 핵종의 체내 분포에 인한 계통오차가 발생합니다. 발생한 계통오차로 인해 내부오염 측정 결과의 정확도가 감소하게 되어 관련한 보정이 필요합니다. 특히 방사성 아이오딘의 경우 섭취 후 불균등한 체내 분포를 나타내어 전신계수기를 이용한 내부오염 평가를 수행하는데 어려움이 있습니다. 따라서 기존 전신계수검사에서 발생하는 계통오차를 보완하고 방사성 아이오딘에 대한 측정능 확보를 위해 전산모사 기반 교정(virtual calibration)을 수행하였습니다. 본 연구를 통해 산출된 전신계수기에 대한 계측효율 보정인자의 적용으로 주민오염감시를 위한 내부오염 측정 결과의 정확성 및 효율성을 높일 것으로 기대합니다.
- 덧글달기









