글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Cancers (Basel).] Deficiency of 15-LOX-1 Induces Radioresistance through Downregulation of MacroH2A2 in Colorectal Cancer.대장암 세포에서 방사선 조사, 15-LOX-1 expression과 DNA damage에 대한 연구
고려의대 / 나유진, 오상철*, 이대희*
- 출처
- Cancers (Basel).
- 등재일
- 2019 Nov 11
- 저널이슈번호
- 11(11). pii: E1776. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111776.
- 내용
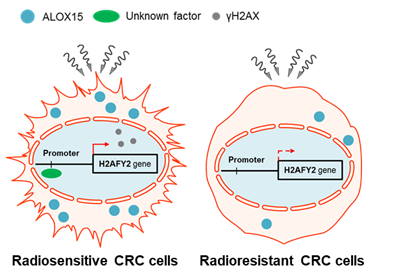
지방산 분해효소(ALOX15; 15-LOX-1) 발현 여하에 따른 방사선 감수성 차이는 지방산 분해 효소에 의해 조절되는 히스톤(H2AFY2; MacroH2A2)에 의한 방사선 반응성 조절에 기인한다.
Abstract
Despite the importance of radiation therapy, there are few radiation-related markers available for use in clinical practice. A larger catalog of such biomarkers is required to help clinicians decide when radiotherapy should be replaced with a patient-specific treatment. Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX-1) enzyme is involved in polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism. When colorectal cancer (CRC) cells were exposed to radiation, 15-LOX-1 was upregulated. To verify whether 15-LOX-1 protects against or induces DNA damage, we irradiated sh15-LOX-1 stable cells. We found that low 15-LOX-1 is correlated with radioresistance in CRC cells. These data suggest that the presence of 15-LOX-1 can be used as a marker for radiation-induced DNA damage. Consistent with this observation, gene-set-enrichment analysis based on microarray experiments showed that UV_RESPONSE was decreased in sh15-LOX-1 cells compared to shCon cells. Moreover, we discovered that the expression of the histone H2A variant macroH2A2 was sevenfold lower in sh15-LOX-1 cells. Overall, our findings present mechanistic evidence that macroH2A2 is transcriptionally regulated by 15-LOX-1 and suppresses the DNA damage response in irradiated cells by delaying H2AX activation.
Author informationNa YJ1, Kim BR2, Kim JL2, Kang S3, Jeong YA1, Park SH1, Jo MJ1, Kim JY4, Kim HJ5, Oh SC2, Lee DH2,6.
1
Graduate School of Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 02841, Korea.
2
Department of Oncology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 08308, Korea.
3
Department of Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 08308, Korea.
4
Division of Radiation Cancer Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Korea.
5
Division of Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul 02447, Korea.
6
Department of Marine Food Science and Technology, Gangneung-Wonju National University, 120 Gangneung, Gangwon 210-702, Korea.
- 키워드
- 15-LOX-1; DNA damage; colorectal cancer; macroH2A2; radiation
- 연구소개
- 환자 별 맞춤 치료가 주목받고 있는 현시점에 방사선 치료 또한 환자별로 상이해야 한다고 생각했습니다. 이번 논문에서 방사선 감수성을 예측할 수 있는 바이오 마커로 지방산 분해효소를 제시했습니다. 지방산 분해효소가 결여되어 있는 세포주가 방사선에 저항성을 보이는 것으로 관찰, 그 원인을 특정 히스톤 감소에 기인한 것으로 보았습니다. 이 히스톤 단백질의 감소는 방사선 조사 시, 유전자 본체의 손상에 대한 반응성을 감소시켜 대조군에 비해 방사선에 저항성을 보이도록 합니다. 방사선이 정상세포에 비해 암세포에 더 큰 타격을 주지만, 부작용이 전혀 없는 것은 아니므로 기존보다 적은 선량이 들어가도 충분한 환자를 구별해내는 밑바탕이 되었으면 하는 바람입니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
Radiation-related markers는 patient-specific treatment에 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 15-LOX-1이 colorectal cancer에서 radiation에 의해 증가하며, histone H2A variant macroH2A2가 15-LOX-1에 의해 전사적으로 조절되어 DNA damage response를 억제함을 규명했다. 이를 통해 15-LOX-1이 radiation-induced DNA damage의 marker로 작용할 수 있음을 제시했다.
2020-01-03 15:57:25