글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- 2018년 08월호
[Cancer Metastasis Rev.] Targeting the enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism to improve radiotherapy.부산대 / 김완연, 윤부현*
- 출처
- Cancer Metastasis Rev.
- 등재일
- 2018 Jul 3. doi: 10.1007/s10555-018-9742-0.
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
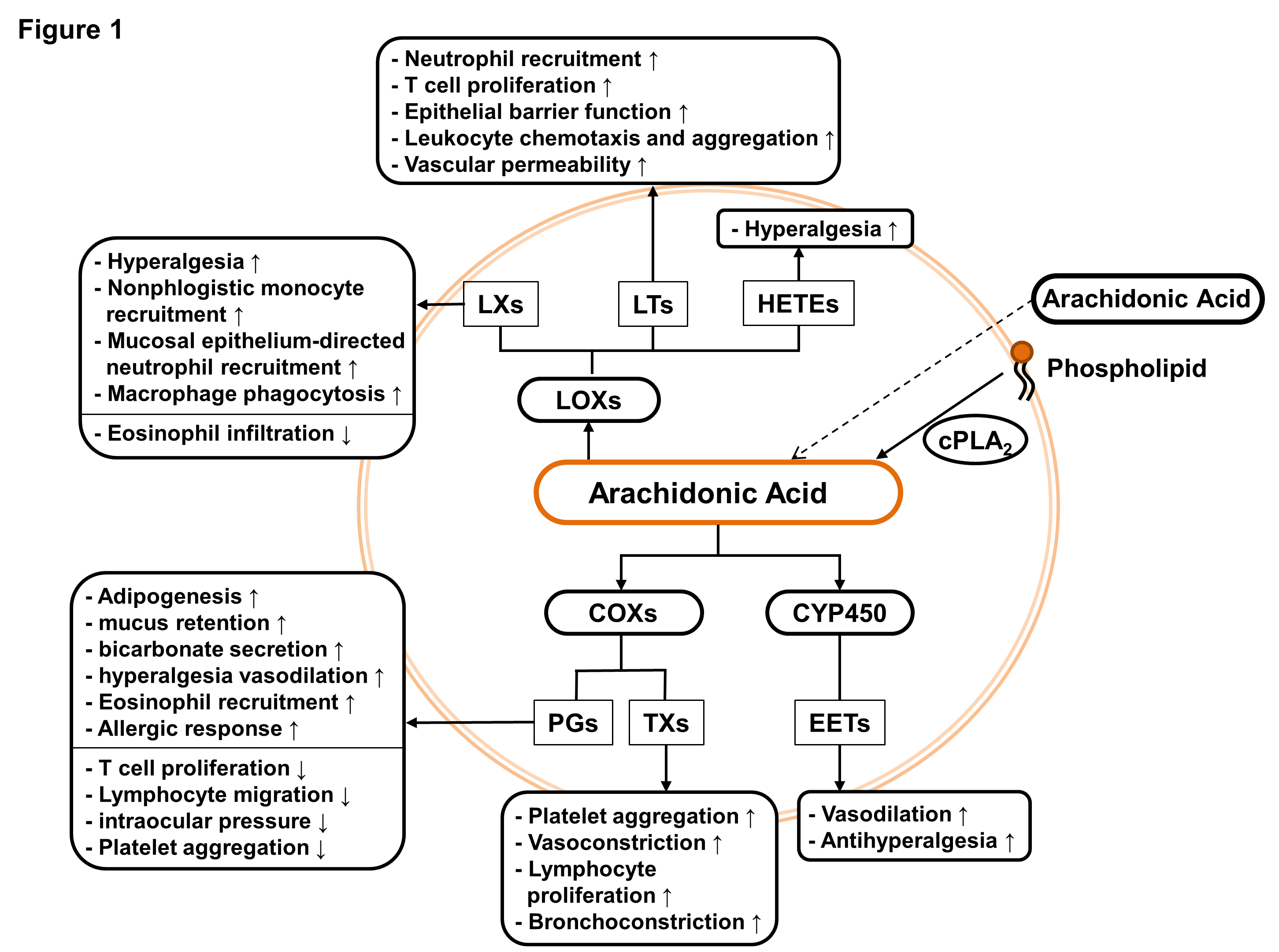
During radiotherapy, an inflammatory response might be induced by activating various enzymes involved in membrane lipid metabolism. The eicosanoid pathway associated with cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), cyclooxygenases (COXs), and lipoxygenases (LOXs) can be induced by radiation, and many lipid metabolites might contribute to cancer-associated inflammation, cell proliferation, and cell survival in cancer. The lipid metabolites are also involved in the establishment of the tumor-associated microenvironment through promotion of angiogenesis and formation of vascular network. These biological activities of lipid metabolites are responsible for malignant progression with the acquisition of radioresistance, leading to unsatisfactory outcome of cancer radiotherapy. Many efforts have been made to identify the mechanisms associated with bioactive lipid metabolites and radiation signaling that lead to radioresistance and to develop potent radiosensitizers to improve therapeutic efficacy. Beneficial outcomes would be achieved by targeting the enzymes, such as cPLA2, COXs, and LOXs, responsible for arachidonic acid metabolism and cancer-associated inflammation during cancer radiotherapy. The current study demonstrated a brief review for the radioresistant effects of bioactive lipid metabolites and their enzymes in cancer and the radiosensitizing effects of inhibitors for the enzymes on cancer therapy.
Author informationKim W1, Son B2, Lee S2, Do H1, Youn B3,4.
1
Department of Biology Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju-si, Chungbuk, 28173, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan, 46241, Republic of Korea.
3
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan, 46241, Republic of Korea. bhyoun72@pusan.ac.kr.
4
Department of Biological Sciences, Pusan National University, Busandaehak-ro 63beon-gil, Geumjeong-gu, Busan, 46241, Republic of Korea. bhyoun72@pusan.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Arachidonic acid; Cyclooxygenase; Cytosolic phospholipase A2; Lipoxygenase; Radioresistance
- 연구소개
- 원형질막 지질 대사를 촉매하는 일부 효소들(Cytosolic phospholipase A2, Cyclooxygenase, Lipoxygenase, Cytochrome P450 등)은 방사선에 대한 반응으로 활성화될 수 있습니다. 이들 효소에 의한 작용으로 생성되는 여러 종류의 지질 대사체들(Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, Leukotrienes, Lipoxins, Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes 등)은 다양한 세포 내 신호경로를 활성화시키는 2차 신호분자로 작용하여 종양-촉진 염증반응, 세포 증식, 혈관신생, 세포 생존, 종양미세환경 변화 등을 통한 방사선저항성 및 종양 악성화를 유발할 수 있습니다. 이번 연구를 통하여 방사선과 관련하여 생체 활성을 보이는 지질 대사체들의 세포 반응 조절에 대한 영향력을 살펴보고 이들을 생성하는 효소의 저해 방법에 대하여 분석하고 정리하였습니다.
- 덧글달기







