글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [BMC Cancer.] MASTL inhibition promotes mitotic catastrophe through PP2A activation to inhibit cancer growth and radioresistance in breast cancer cells.
KIRAMS / 윤이나, 김재성*
- 출처
- BMC Cancer.
- 등재일
- 2018 Jul 5
- 저널이슈번호
- 18(1):716. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4600-6.
- 내용
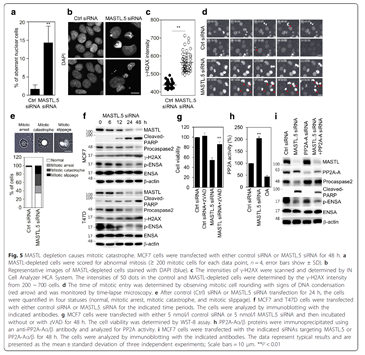
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Although MASTL (microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase-like) is a key mitotic kinase that regulates mitotic progression through the inactivation of tumor suppressor protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), the antitumor mechanism of MASTL targeting in cancer cells is still unclear.METHODS:
MASTL expression was evaluated by using breast cancer tissue microarrays and public cancer databases. The effects of MASTL depletion with siRNAs were evaluated in various breast cancer cells or normal cells. Various methods, including cell viability, cell cycle, soft agar, immunoblotting, immunofluorescence, PP2A activity, live image, and sphere forming assay, were used in this study.RESULTS:
This study showed the oncosuppressive mechanism of MASTL targeting that promotes mitotic catastrophe through PP2A activation selectively in breast cancer cells. MASTL expression was closely associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in breast cancer. The depletion of MASTL reduced the oncogenic properties of breast cancer cells with high MASTL expression, but did not affect the viability of non-transformed normal cells with low MASTL expression. With regard to the underlying mechanism, we found that MASTL inhibition caused mitotic catastrophe through PP2A activation in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, MASTL depletion enhanced the radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells with increased PP2A activity. Notably, MASTL depletion dramatically reduced the formation of radioresistant breast cancer stem cells in response to irradiation.CONCLUSION:
Our data suggested that MASTL inhibition promoted mitotic catastrophe through PP2A activation, which led to the inhibition of cancer cell growth and a reversal of radioresistance in breast cancer cells.
Author informationYoon YN1,2, Choe MH1,3, Jung KY4, Hwang SG1, Oh JS5, Kim JS6,7.
1
Division of Radiation Cancer Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, 215-4 Gongneung-Dong, Nowon-Ku, Seoul, 139-706, South Korea.
2
Radiological and Medico-Oncological Sciences, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, South Korea.
3
Department of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, College of Life Science and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea.
4
Center for Medicinal Chemistry, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Daejeon, South Korea.
5
Department of Integrative Biotechnology, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, South Korea. ohjs@skku.edu.
6
Division of Radiation Cancer Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, 215-4 Gongneung-Dong, Nowon-Ku, Seoul, 139-706, South Korea. jaesung@kirams.re.kr.
7
Radiological and Medico-Oncological Sciences, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, South Korea. jaesung@kirams.re.kr.
- 키워드
- Breast cancer; MASTL; Mitotic catastrophe; Radiation
- 연구소개
- 신규 표적항암제인 MASTL의 억제시, 나타나는 효과를 확인한 논문입니다. MASTL은 세포분열 시 주요한 단백질로써, 종양억제단백질 PP2A를 과도하게 차단하여 세포분열을 지속할 수 있는 역할을 합니다. 위 논문에서는 암세포에서 특이적으로 MASTL 억제 시, mitotic catastrophe에 의한 극적인 세포사멸을 확인함으로써, 향후의 표적항암제 후보군으로 제시하고 있습니다.
- 덧글달기









