글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys .] An Investigation of the Effect of Virtual Reality on Alleviating Anxiety in Patients With Breast Cancer Undergoing Radiation Therapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial방사선치료를 받는 유방암 환자에서 가상 현실의 불안 완화 효과 연구: 무작위 배정 임상시험
Cornell University, 연세의대 / 신재용, 장지석, 윤소연*, 김용배*
- 출처
- Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys .
- 등재일
- 2023 Dec 1
- 저널이슈번호
- 117(5):1191-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.06.275. Epub 2023 Jul 13.
- 내용
이달의 연구자 바로가기 Click!
Abstract
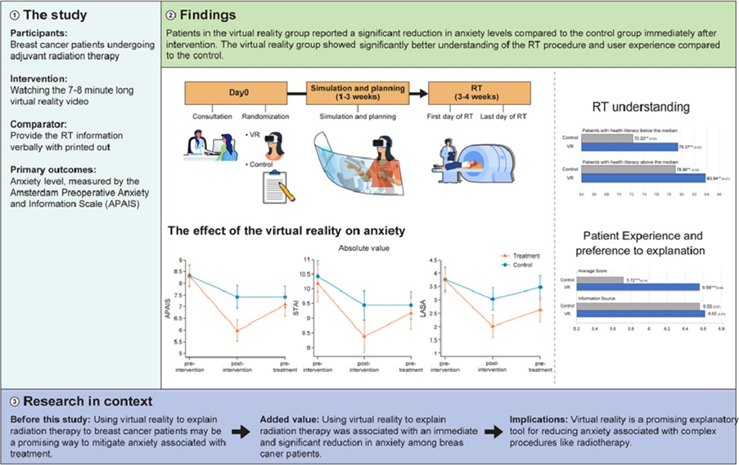
Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the anxiety-reducing effects of virtual reality (VR) on patients with breast cancer undergoing adjuvant radiation therapy (RT).Methods and materials: This randomized controlled trial was conducted among patients with breast cancer receiving RT at a single institution. Of 196 enrolled and randomized patients, 97 were assigned to a VR explanation group (intervention) and 99 were assigned to the standard-of-care group (control). Anxiety levels were measured using the Amsterdam Preoperative Anxiety and Information Scale (APAIS) as the primary endpoint and the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) and Linear Analogue Scale Assessment (LASA) as secondary endpoints. Knowledge of the RT procedure, patient satisfaction, and time spent for counseling were also assessed.
Results: Intervention significantly reduced patient anxiety immediately, not only on the primary endpoint, APAIS, but also on the STAI and LASA anxiety scales. Specifically, in the intervention group, there were immediate reductions of 26.0%, 16.1%, and 55.8% for APAIS, STAI, and LASA, respectively, whereas in the control group, the respective reductions were 8.1%, 8.5%, and 13.7%. Among the 3 anxiety scales, long-term anxiety reduction was observed only when anxiety was measured by LASA. Subgroup analyses showed that the effect on anxiety did not differ based on the physician, baseline anxiety level, use of hormone therapy, or health literacy. The intervention also significantly improved knowledge of the RT procedure (81.9/100 vs 76.8/100; P = .006) and patient satisfaction with the explanation manner (6.56 vs 5.72; P < .001) compared with the control group.
Conclusions: Immersive VR applied to the current procedure reduces anxiety during RT planning for patients with breast cancer. Further research is necessary to investigate the long-term effects of VR on anxiety.
연구에 대한 전반적인 설명 및 연구 결과 정리

Affiliations
Jaeyong Shin 1, Jee Suk Chang 2, Jin Sung Kim 2, Ji-Yeon An 3, Seung Yeun Chung 4, So-Yeon Yoon 5, Yong Bae Kim 6
1Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; Institute of Health Services Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Economics, Graduate School, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea.
4Department of Radiation Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
5Design Environment and Analysis, College of Human Ecology, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York. Electronic address: sy492@cornell.edu.
6Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Electronic address: ybkim3@yuhs.ac.
- 연구소개
- 방사선 치료와 관련된 대면 상담 및 여러 시각적 안내 자료에도 불구하고, 많은 암환자들은 (특히 유방암) 방사선 치료 과정을 잘 모르기 때문에 치료 전 불안감이 높은 상태이다. 만약 가상 현실 콘텐츠를 통해 방사선 치료준비 및 치료과정을 설명한다면 환자들은 몰입감 높은 치료 치료 경험을 미리 할 수 있을 것이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 가상 현실 보조 설명을 시청하는 것이, 현재의 표준 치료설명에 비해, 유방암 환자의 불안 수준을 감소하는지 조사하고자, 전향적인, 의사-맹검, 무작위 대조 시험을 실시했습니다. 불안 수준의 측정은 암스테르담 수술 전 불안 및 정보 척도(APAIS), 상태-특성 불안 척도(STAI)와 선형 유사 척도 평가(LASA) 등의 설문조사를 시행하였습니다. 방사선 치료 절차에 대한 지식, 환자 만족도, 상담에 소요된 시간 등 그 외 다양한 요인들도 함께 평가하였습니다. 총 196명의 환자를 무작위 배정하여 97명은 VR 99명은 표준치료 설명을 시행하였고, 그 결과 VR 설명은 즉각적으로 환자의 불안을 현저히 감소시켰으며, 이는 주요 평가 변수였던APAIS뿐만 아니라 STAI 및 LASA 불안 척도에서도 비슷한 결과를 나타냈습니다. 그 외에도 환자의 이해도 관련 점수에서도 VR 그룹에서 유의하게 높게 나타났습니다. 이를 근거로 가상 현실 기반 설명이 개입 직후 즉시 유방암 환자의 치료 관련 불안을 감소시킬 수 있고, 방사선 치료에 대한 환자들의 이해를 향상시킨다는 결론을 도출하였습니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
최근 일상생활에서 글이나 사진보다 영상촬영물이 보편화되었는데, 임상 진료에 있어서도 환자들에게 생소한 방사선치료 과정을 말로 설명하거나 간단한 사진을 보여주는 것보다 영상촬영물을 통해 보다 직접적으로 체험할 수 있게 함으로써 방사선치료에 대한 이해도를 높일 수 있다는 연구 결과로 최신 흐름을 반영한 흥미로운 연구입니다.
2024-02-05 16:40:49