글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Front Oncol .] Optimal planning target margin for prostate radiotherapy based on interfractional and intrafractional variability assessment during 1.5T MRI-guided radiotherapy
연세의대 / 김진아, 김준원*
- 출처
- Front Oncol .
- 등재일
- 2023 Dec 20:13:1337626. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.133
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
Introduction: We analyzed daily pre-treatment- (PRE) and real-time motion monitoring- (MM) MRI scans of patients receiving definitive prostate radiotherapy (RT) with 1.5 T MRI guidance to assess interfractional and intrafractional variability of the prostate and suggest optimal planning target volume (PTV) margin.Materials and methods: Rigid registration between PRE-MRI and planning CT images based on the pelvic bone and prostate anatomy were performed. Interfractional setup margin (SM) and interobserver variability (IO) were assessed by comparing the centroid values of prostate contours delineated on PRE-MRIs. MM-MRIs were used for internal margin (IM) assessment, and PTV margin was calculated using the van Herk formula.
Results: We delineated 400 prostate contours on PRE-MRI images. SM was 0.57 ± 0.42, 2.45 ± 1.98, and 2.28 ± 2.08 mm in the left-right (LR), anterior-posterior (AP), and superior-inferior (SI) directions, respectively, after bone localization and 0.76 ± 0.57, 1.89 ± 1.60, and 2.02 ± 1.79 mm in the LR, AP, and SI directions, respectively, after prostate localization. IO was 1.06 ± 0.58, 2.32 ± 1.08, and 3.30 ± 1.85 mm in the LR, AP, and SI directions, respectively, after bone localization and 1.11 ± 0.55, 2.13 ± 1.07, and 3.53 ± 1.65 mm in the LR, AP, and SI directions, respectively, after prostate localization. Average IM was 2.12 ± 0.86, 2.24 ± 1.07, and 2.84 ± 0.88 mm in the LR, AP, and SI directions, respectively. Calculated PTV margin was 2.21, 5.16, and 5.40 mm in the LR, AP, and SI directions, respectively.
Conclusions: Movements in the SI direction were the largest source of variability in definitive prostate RT, and interobserver variability was a non-negligible source of margin. The optimal PTV margin should also consider the internal margin.
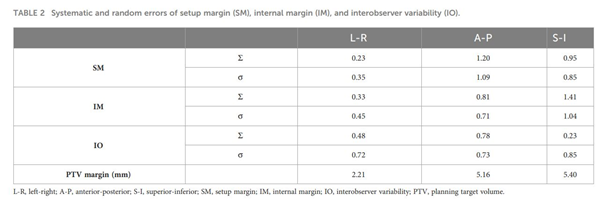
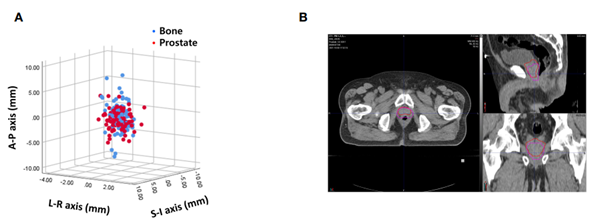
그림1.
(A) 골반뼈와 전립선을 기준으로 영상 registration을 하였을 때의 interfractional variability, (B) interfractional variability 최대값을 보인 케이스
그림2.
(A) 골반뼈와 전립선을 기준으로 영상 registration을 하였을 때의 연구자 간의 interobserver variability, (B) interobserver variability 최대값을 보인 케이스
Affiliations
Jina Kim 1, Jiwon Sung 1, Seo Jin Lee 1, Kang Su Cho 2, Byung Ha Chung 2, Dongjoon Yang 1, Jihun Kim 1, Jun Won Kim 1
1Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Urology, Prostate Cancer Center, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38173837/
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 강남세브란스병원에 최근 새로 도입된 MR-LINAC인 Unity를 이용한 연구입니다. MR-LINAC은 방사선치료기와 치료 시 영상유도를 위한 MRI를 결합한 장비로 기존의 CT 영상유도 방사선치료기와 비교하였을 때 연부조직의 해상도가 뛰어나 치료표적 부위와 주변 정상 장기를 더 선명하게 구별할 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다. 또한 치료 중 실시간 영상을 획득하여 표적의 움직임도 확인할 수 있습니다. 본 연구진은 MR-LINAC의 이러한 특성을 이용하여 전립선암 방사선치료를 시행함에 있어 전립선의 interfractional, 그리고 intrafractional movement를 측정하였습니다. 또 획득된 MRI 영상에 여러 연구자들이 타겟을 도식화한 것을 분석하여 interobserver variability도 평가하였습니다. 마지막으로 이러한 데이터를 기반으로 하여 전립선암 방사선치료에 있어 필요한 적정 margin이 얼마인지 도출하였습니다. 본 연구는 전립선암 환자들을 대상으로 방사선치료 중 획득한 MRI 영상을 통해 방사선치료에 필요한 margin을 분석하였다는 점에서 그 의의가 있습니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cancers (Basel) .] Treatment Outcomes after Dose-Escalated Moderately Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Frail Patients with High-Grade Glioma
- 다음글 [Sci Rep .] Long-term findings of rectal endoscopy and rectal bleeding after moderately hypofractionated, intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer










편집위원
전립선암의 MRI-guided radiotherapy 시 interfractional 및 intrafractional variability를 분석함으로써 적절한 target margin을 분석한 연구로, 실제 임상에서 전립선암의 방사선치료 시에 참고할 만한 논문으로 의미 있어 보임.
2024-02-05 16:34:24