(구)글로벌 핫이슈
방사선종양학
- [Clin Cancer Res.] Induction Chemotherapy plus Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Endemic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Individual Patient Data Pooled Analysis of Four Randomized Trials.
Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center / Jun Ma *
- 출처
- Clin Cancer Res.
- 등재일
- 2018 Apr 15
- 저널이슈번호
- 24(8):1824-1833. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2656. Epub 2018 Feb 5.
- 내용
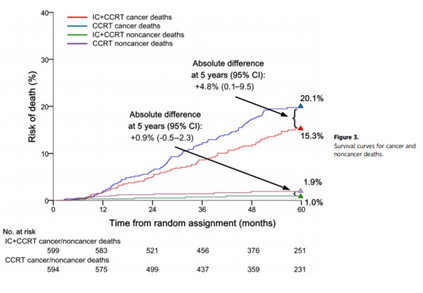
Abstract
Purpose: Because of the uneven geographic distribution and small number of randomized trials available, the value of additional induction chemotherapy (IC) to concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) remains controversial. This study performed an individual patient data (IPD) pooled analysis to better assess the precise role of IC + CCRT in locoregionally advanced NPC.Experimental Design: Four randomized trials in endemic areas were identified, representing 1,193 patients; updated IPD were obtained. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were the primary and secondary endpoints, respectively.Results: Median follow-up was 5.0 years. The HR for PFS was 0.70 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.56-0.86; P = 0.0009; 9.3% absolute benefit at 5 years] in favor of IC + CCRT versus CCRT alone. IC + CCRT also improved OS (HR = 0.75; 95% CI, 0.57-0.99; P = 0.04) and reduced distant failure (HR = 0.68; 95% CI, 0.51-0.90; P = 0.008). IC + CCRT had a tendency to improve locoregional control compared with CCRT alone (HR = 0.70; 95% CI, 0.48-1.01; P = 0.06). There was no heterogeneity between trials in any analysis. No interactions between patient characteristics and treatment effects on PFS or OS were found. After adding two supplementary trials to provide a more comprehensive overview, the conclusions remained valid and were strengthened. In a supplementary Bayesian network analysis, no statistically significant differences in survival between different IC regimens were detected.Conclusions: This IPD pooled analysis demonstrates the superiority of additional IC over CCRT alone in locoregionally advanced NPC, with the survival benefit mainly associated with improved distant control.
Author informationChen YP#1, Tang LL#1, Yang Q#2, Poh SS#3, Hui EP#4, Chan ATC4, Ong WS5, Tan T3, Wee J3, Li WF1, Chen L1, Ma BBY4, Tong M4, Tan SH5, Cheah SL3, Fong KW3, Sommat K3, Soong YL3, Guo Y6, Lin AH7, Sun Y1, Hong MH2, Cao SM8, Chen MY8, Ma J9.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, P.R. China.
2
Department of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, P.R. China.
3
Division of Radiation Oncology, National Cancer Centre, Singapore.
4
Partner State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sir Y K Pao Centre for Cancer, Department of Clinical Oncology, Hong Kong Cancer Institute and Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
5
Division of Clinical Trials and Epidemiological Sciences, National Cancer Centre, Singapore.
6
Clinical Trials Centre, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Centre, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Centre of Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou, P.R. China.
7
Department of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, P.R. China.
8
Department of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, P.R. China. majun2@mail.sysu.edu.cn chenmy@sysucc.org.cn caosm@sysucc.org.cn.
9
Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, P.R. China. majun2@mail.sysu.edu.cn chenmy@sysucc.org.cn caosm@sysucc.org.cn.
#
Contributed equally
- 덧글달기










편집위원
오랫동안 논란이 되어왔던 induction chemotherapy의 역할에 대한 현재까지 가장 높은 수준의 evidence
2018-05-09 10:01:53