글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Phys Med Biol .] MOQUI: an open-source GPU-based Monte Carlo code for proton dose calculation with efficient data structure
Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School / 이호연*
- 출처
- Phys Med Biol .
- 등재일
- 2022 Aug 30
- 저널이슈번호
- 67(17):10.1088/1361-6560/ac8716. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac8716.
- 내용
Abstract
Objective.Monte Carlo (MC) codes are increasingly used for accurate radiotherapy dose calculation. In proton therapy, the accuracy of the dose calculation algorithm is expected to have a more significant impact than in photon therapy due to the depth-dose characteristics of proton beams. However, MC simulations come at a considerable computational cost to achieve statistically sufficient accuracy. There have been efforts to improve computational efficiency while maintaining sufficient accuracy. Among those, parallelizing particle transportation using graphic processing units (GPU) achieved significant improvements. Contrary to the central processing unit, a GPU has limited memory capacity and is not expandable. It is therefore challenging to score quantities with large dimensions requiring extensive memory. The objective of this study is to develop an open-source GPU-based MC package capable of scoring those quantities.Approach.We employed a hash-table, one of the key-value pair data structures, to efficiently utilize the limited memory of the GPU and score the quantities requiring a large amount of memory. With the hash table, only voxels interacting with particles will occupy memory, and we can search the data efficiently to determine their address. The hash-table was integrated with a novel GPU-based MC code, moqui.Main results.The developed code was validated against an MC code widely used in proton therapy, TOPAS, with homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms. We also compared the dose calculation results of clinical treatment plans. The developed code agreed with TOPAS within 2%, except for the fall-off and regions, and the gamma pass rates of the results were >99% for all cases with a 2 mm/2% criteria.Significance.We can score dose-influence matrix and dose-rate on a GPU for a 3-field H&N case with 10 GB of memory using moqui, which would require more than 100 GB of memory with the conventionally used array data structure.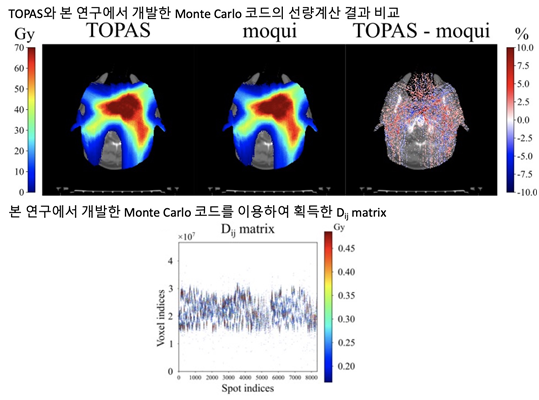
Affiliations
Hoyeon Lee 1, Jungwook Shin 2, Joost M Verburg 1, Mislav Bobić 1 3, Brian Winey 1, Jan Schuemann 1, Harald Paganetti 1
1Dept. of Radiation Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, United States of America.
2Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD 20850, United States of America.
3Department of Physics, ETH, Zürich 8092, Switzerland.
- 키워드
- Monte Carlo; graphic processing unit; proton therapy.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구에서는 양성자치료 과정 중 종양의 크기 혹은 환자의 체적 변화를 보완하기 위한 맞춤형 치료 방사선치료를 진행하는 과정에서 정확한 선량을 빠르게 계산하기 위한 GPU 기반의 Monte Carlo 양성자 선량 계산 코드를 개발하였습니다. 본 연구에서 개발한 Monte Carlo 코드는 key-value 데이터 구조 중에 하나인 hash table 을 이용해 GPU의 제한된 메모리를 최대한 활용하여 3차원 선량 계산뿐만 아니라 방사선 치료계획 최적화에 이용되는 dose influence matrix (Dij matrix)를 획득할 수 있습니다. 개발한 코드는 치료용 양성자 빔의 선량, linear energy transfer, dose-rate 등의 다양한 물리량을 계산할 수 있으며 open-source로 공개되어 양성자 치료 관련 연구를 진행하는 기관에서 자유롭게 이용하실 수 있습니다.
- 덧글달기









