글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Radiat Oncol.] Effect of changes in monitor unit rate and energy on dose rate of total marrow irradiation based on Linac volumetric arc therapy.
서울대병원 / 손재만, 강현철*, 최창헌*
- 출처
- Radiat Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2019 May 27
- 저널이슈번호
- 14(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1296-y.
- 내용
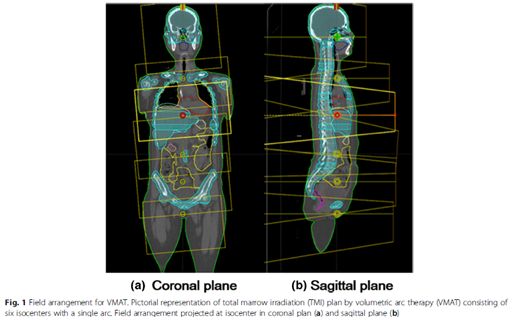
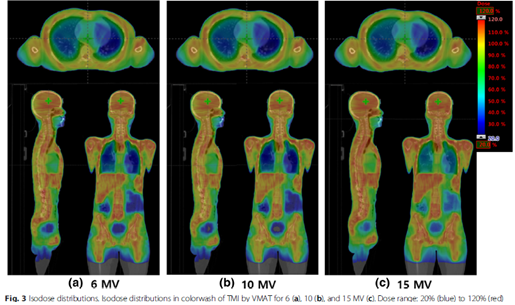
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
This study set out to evaluate the effect of dose rate on normal tissues (the lung, in particular) and the variation in the treatment efficiency as determined by the monitor unit (MU) and energy applied in Linac-based volumetric arc therapy (VMAT) total marrow irradiation (TMI).METHODS:
Linac-based VMAT plans were generated for the TMI for six patients. The planning target volume (PTV) was divided into six sub-volumes, each of which had their own isocenter. To examine the effect of the dose rate and energy, a range of MU rates (40, 60, 80, 100, 300, and 600 MU/min) were selected for 6, 10, and 15 MV. All the plans were verified by portal dosimetry.RESULTS:
The dosimetric parameters for the target and normal tissue were consistent in terms of the energy and MU rate. The beam-on time was changed from 59.6 to 6 min for 40 and 600 MU/min. When 40 MU/min was set for the lung, the dose rate delivered to the lung was less than 6 cGy/min (that is, 90%), while the beam-on time was approximately 10 min. The percentage volume of the lung receiving 20 cGy/min was 1.47, 3.94, and 6.22% at 6, 10, and 15 MV, respectively. However, for 600 MU/min, the total lung volume received over 6 cGy/min regardless of the energy, and over 20 cGy/min for 10 and 15 MV (i.e., 54.4% for 6 MV).CONCLUSIONS:
In TMI treatment, reducing the dose rate administered to the lung can decrease the incidence of pulmonary toxicity. To reduce the probability of normal tissue complications, the selection of the lowest MU rate is recommended for fields including the lung. To minimize the total treatment time, the maximum MU rate can be applied to other fields.
Author informationSon J1, Choi N2,3, Kim JI1,4,5, Park JM1,4,5,6, Wu HG1,3,4,5, Kang HC7, Choi CH8,9,10.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Radiation Oncology, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea.
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
4
Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5
Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
6
Center for Convergence Research on Robotics, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Republic of Korea.
7
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea. shule@snu.ac.kr.
8
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea. dm140@naver.com.
9
Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea. dm140@naver.com.
10
Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea. dm140@naver.com.
- 키워드
- Dose rate; Monitor unit rate; Pulmonary toxicity; Total marrow irradiation; Volumetric arc therapy
- 덧글달기









