글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.] Deep learning-based interpretation of basal/acetazolamide brain perfusion SPECT leveraging unstructured reading reports
서울대병원 / 유현지, 최홍윤*, 이동수*
- 출처
- Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
- 등재일
- 2020 Aug
- 저널이슈번호
- 47(9):2186-2196. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04670-4. Epub 2020 Jan 7.
- 내용
Abstract
Purpose: Basal/acetazolamide brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) has been used to evaluate functional hemodynamics in patients with carotid artery stenosis. We aimed to develop a deep learning model as a support system for interpreting brain perfusion SPECT leveraging unstructured text reports.Methods: In total, 7345 basal/acetazolamide brain perfusion SPECT images and their text reports were retrospectively collected. A long short-term memory (LSTM) network was trained using 500 randomly selected text reports to predict manually labeled structured information, including abnormalities of basal perfusion and vascular reserve for each vascular territory. Using this trained LSTM model, we extracted structured information from the remaining 6845 text reports to develop a deep learning model for interpreting SPECT images. The model was based on a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN), and the performance was tested on the other 500 cases by measuring the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC). We then applied the model to patients who underwent revascularization (n = 33) to compare the estimated output of the CNN model for pre- and post-revascularization SPECT and clinical outcomes.
Results: The AUC of the LSTM model for extracting structured labels was 1.00 for basal perfusion and 0.99 for vascular reserve for all 9 brain regions. The AUC of the CNN model designed to identify abnormal perfusion was 0.83 for basal perfusion and 0.89 for vascular reserve. The output of the CNN model was significantly improved according to the revascularization in the target vascular territory, and its changes in brain territories were concordant with clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: We developed a deep learning model to support the interpretation of brain perfusion SPECT by converting unstructured text reports into structured labels. This model can be used as a support system not only to identify perfusion abnormalities but also to provide quantitative scores of abnormalities, particularly for patients who require revascularization.
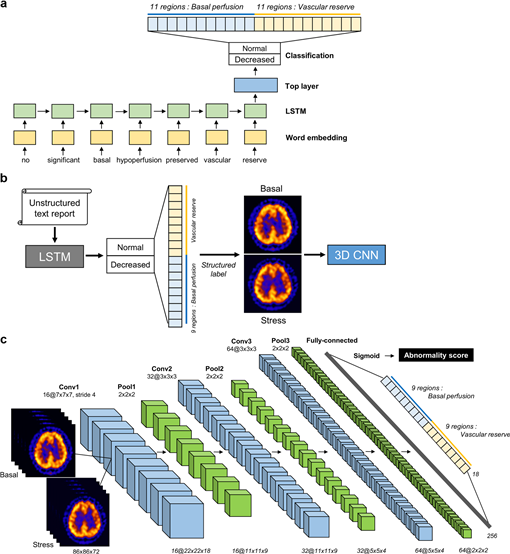
그림 1> 뇌혈류 SPECT 딥러닝 모델의 전체 모식도 (a) 구조화되지 않은 영상 판독문으로부터 뇌혈류 상태에 대한 구조화된 정보를 학습 및 추출하기 위한 LSTM 모델. (b) LSTM 모델을 이용하여 판독문으로부터 영상에 대한 구조화된 레이블을 추출하고, (c) SPECT 영상에서 영역별 기저 뇌혈류 및 혈류 예비능 상태에 대한 비정상 스코어를 학습 및 예측하기 위한 3D CNN 모델.
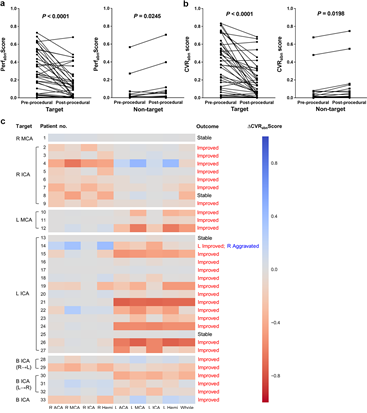
그림 2> 뇌혈관 재개통술 전-후 표적-비표적 뇌혈관 영역에 대한 임상적 결과와 딥러닝 기반 뇌혈류 SPECT 영상 비정상 스코어가 일치하는 경향을 보임 (a: 기저 뇌혈류, b: 혈류 예비능, c: heatmap).
Affiliations
1 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 28 Yongon-Dong, Jongno-Gu, Seoul, 110-744, South Korea.
2 Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, and College of Medicine or College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 28 Yongon-Dong, Jongno-Gu, Seoul, 110-744, South Korea. chy1000@snu.ac.kr.
4 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 28 Yongon-Dong, Jongno-Gu, Seoul, 110-744, South Korea. dsl@plaza.snu.ac.kr.
5 Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, and College of Medicine or College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. dsl@plaza.snu.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- 3D convolutional neural network; Brain perfusion SPECT; Deep learning; Long short-term memory; Vascular reserve.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 구조화되지 않은 영상 판독문을 이용하여 기저/아세타졸아미드 부하 뇌혈류 SPECT 영상 분석 딥러닝 모델을 개발한 논문입니다. 종래의 뇌혈류 SPECT 영상판독은 임상의의 시각적 판단에 의해 결정되었으나, 숙련도에 따라 진단 정확도에 차이가 있을 수 있고, 임상의 간에도 판독 소견에 차이가 있을 수 있는 한계가 있었습니다. 본 연구에서는 1) 뇌혈류 SPECT의 구조화되지 않은 영상 판독문으로부터 뇌혈류 상태에 대한 구조화된 정보를 학습 및 추출하기 위한 알고리즘 모델을 개발하였으며, 2) 판독문으로부터 관심 영역 별 뇌혈류 상태에 대한 구조화된 레이블을 추출하여 SPECT 영상의 뇌혈류 상태를 분류할 수 있도록 딥러닝 모델을 학습시켜, 영역별 기저 뇌혈류 및 혈류 예비능 상태에 대한 비정상 스코어를 예측하는 알고리즘 모델을 개발하였습니다. 본 연구에서 개발한 딥러닝 모델은 보다 빠르고 효율적인 딥러닝 학습을 위한 의료 영상 레이블 방법 및 장치를 제공하고, 뇌혈류 SPECT 영상 분석의 자동화 및 객관화, 그리고 보다 신뢰도 높은 예측이 수행될 수 있도록 할 수 있는 방법입니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.] Imaging phenotype using 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-based radiomics and genetic alterations of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- 다음글 [Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.] Slice-selective learning for Alzheimer's disease classification using a generative adversarial network: a feasibility study of external validation










편집위원
Deep learning으로 뇌관류 SPECT를 판독하는 알고리듬을 개발하고 임상적 유용성을 평가한 연구임. 인공지능을 이용한 핵의학 영상 해석에 대한 의료영상 인공지능 연구자, 뇌혈관질환 임상가, 핵의학적 정량화 관심 전문가에게 관심을 유도할 연구로 생각됨.
2020-10-05 17:42:25