글로벌 연구동향
방사선종양학
- [Jpn J Clin Oncol.] Severe late dysphagia after multimodal treatment of stage III/IV laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer.
서울대병원 / 허진, 안순현*
- 출처
- Jpn J Clin Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2020 Feb 17
- 저널이슈번호
- 50(2):185-192. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz158.
- 내용
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Long-term side effects after radiotherapy for organ preservation 'could deteriorate' the laryngeal function. This study intended to identify the incidence of severe late dysphagia following the multimodal treatment for stage III/IV laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer 'to evaluate the function of larynx'.METHODS:
The medical records of patients successfully treated for laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer with a multimodal approach, including radiotherapy, were retrospectively analyzed. 'Functional larynx was defined as tolerable oral diet without severe late dysphagia or tracheostoma'.RESULTS:
The study included 99 patients with a median follow-up period of 72 months. 'Tracheostomy during the follow-up period was required in only one patient due to aspiration pneumonia, and dysphagia is the main determinant for functional larynx'. The probability of maintaining functional larynx was 63% for 10 years, when the treatment was started with radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy. In upfront surgery (operation first and adjuvant radiotherapy/concurrent chemoradiotherapy) group, 37% of patients required total laryngectomy as primary treatment and 43% of patients could maintain laryngeal function for 10 years. And severe late dysphagia in the latter group developed mainly after laryngeal preservation surgery. The patients aged ≥65 years showed significantly higher incidence of dysphagia. Severe late dysphagia was very rare in laryngeal cancer successfully cured with radiotherapy/concurrent chemoradiotherapy (1/25, 4%); however, it gradually increased over time in hypopharyngeal cancer patients showing a statistically significant difference from laryngeal cancer patients (P = 0.040).CONCLUSION:
Severe late dysphagia occurred in 19.2% of patients treated for laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers, regardless of whether treatment started with radiotherapy/concurrent chemoradiotherapy or surgery.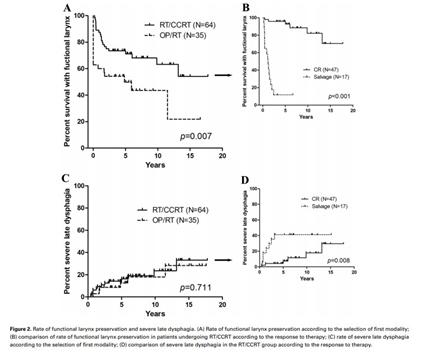
Author informationHuh G1, Ahn SH1, Suk JG1, Lee MH1, Kim WS1, Kwon SK1, Ock CY2, Keam B2, Heo DS2, Kim JH3, Wu HG3.
1
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
2
Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, and.
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 키워드
- hypopharyngeal cancer; laryngeal cancer; late dysphagia; radiotherapy
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Clin Breast Cancer.] Aggressive Surgical Excision of Supraclavicular Lymph Node Did Not Improve the Outcomes of Breast Cancer With Supraclavicular Lymph Node Involvement (KROG 16-14).
- 다음글 [Breast.] Outcome of breast-conserving treatment for axillary lymph node metastasis from occult breast cancer with negative breast MRI.










편집위원
Laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer에서 organ preservation aim으로 definitive RT/CCRT가 표준치료로 권고되지만 장기간 경과관찰시 severe late dysphagia가 상당수 발생할 수 있고, 이는 surgery followed by RT/CCRT시에도 비슷하게 발생함을 유의해야 하겠습니다.
2020-04-01 16:13:03