(구)글로벌 핫이슈
방사선종양학
- [J Clin Oncol.] Sequencing of Postoperative Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced or Incompletely Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.
University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute / Kristine E. Kokeny*
- 출처
- J Clin Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2018 Feb 1
- 저널이슈번호
- 36(4):333-341.
- 내용
Abstract
Purpose
Although several feasibility studies have demonstrated the safety of adjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) for locallyadvanced or incompletely resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), it remains uncertain whether this approach is superior to sequential chemotherapy followed by postoperative radiotherapy (C→PORT). We sought to determine the most effective treatment sequence.
Patients and Methods
Using the National Cancer Database, we selected two cohorts of patients with nonmetastatic NSCLC who had received at least a lobectomy followed by multiagent chemotherapy and radiotherapy; cohort one included patients with R0 resection and pN2 disease, whereas cohort two included patients with R1-2 resection regardless of nodal status. Overall survival (OS) was examined using a propensity score-matched analysis with a shared frailty Cox regression.
Results
A total of 747 patients in cohort one and 277 patients in cohort two were included, with a median follow-up of 32.8 and 27.9 months, respectively. The median OS was 58.8 months for patients who received C→PORT versus 40.4 months for patients who received CRT in cohort one (log-rank P < .001). For cohort two, the median OS was 42.6 months for patients who received C→PORT versus 38.5 months for patients who received CRT (log-rank P = .42). After propensity score matching, C→PORT remained associated with improved OS compared with CRT in cohort one (hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .019), and there was no statistical difference in OS between the sequencing groups for cohort two (hazard ratio, 1.35; P = .19).
Conclusion
Patients with NSCLC who undergo R0 resection and are found to have pN2 disease have improved outcomes when adjuvant chemotherapy is administered before, rather than concurrently with, radiotherapy. For patients with positive margins after surgery, there is not a clear association between treatment sequencing and survival.
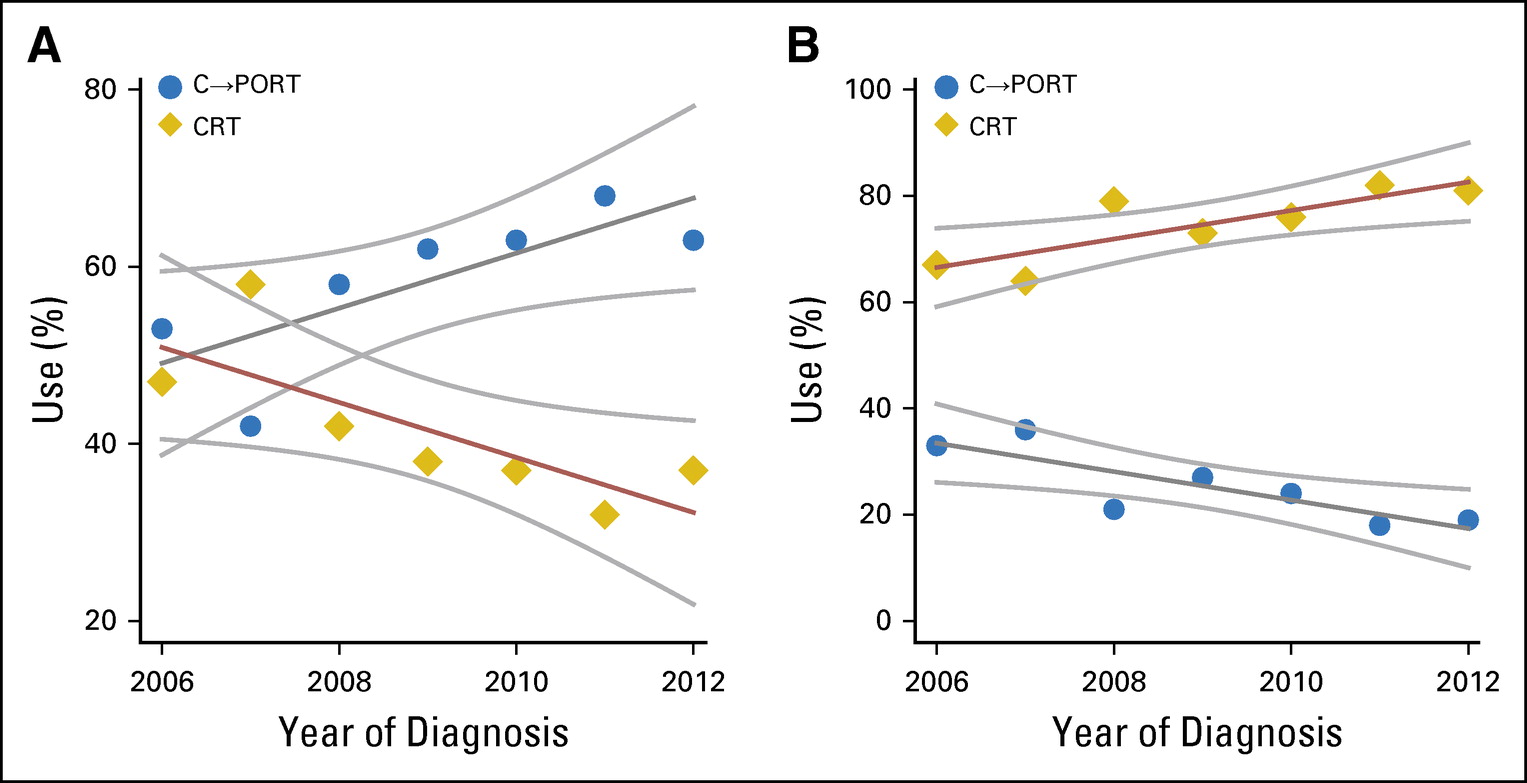
Fig 3.Use of adjuvant treatment over time. (A) Cohort one: R0 pN2 group. (B) Cohort two: positive margins (R1-2) group.
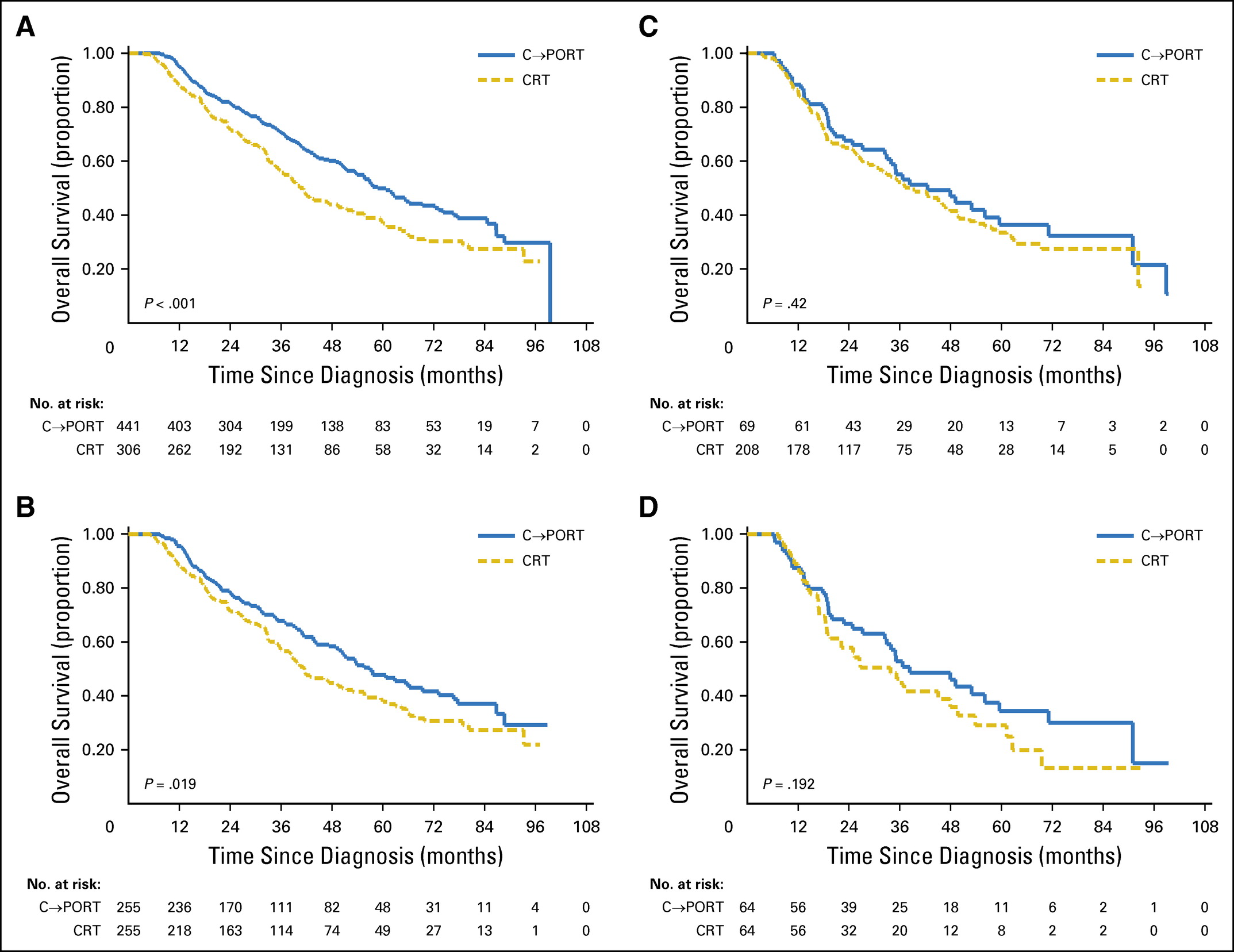
Fig 4.Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival. Cohort one, R0 pN2 group, (A) before and (B) after propensity score matching. Cohort two, positive margins (R1-2) group, (C) before and (D) after PS matching. C→PORT, chemotherapy followed by postoperative radiotherapy; CRT, chemoradiotherapy.
Author information
Francis S1, Orton A1, Stoddard G1, Tao R1, Hitchcock YJ1, Akerley W1, Kokeny KE1.
1 Samual Francis, Andrew Orton, Randa Tao, Ying J. Hitchcock, Wallace Akerley, and Kristine E. Kokeny, University of Utah Huntsman CancerInstitute; Greg Stoddard, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
Adjuvant setting에서 R0pN2에서는 sequential chemo-RT가 postop CCRT보다 생존율이 유의하게 향상되었는데, 이는 sequential chemo-RT가 부작용이 낮고, 수술에 따른 급성 부작용을 회복하는데 보다 tolerable하며,
2018-02-07 11:47:13
편집위원
수술 후 miscroscopic disease control이 목적이므로 gross disease에 시행되는 definitive CCRT에 비해서 국소제어율이 생존율 향상으로 translation 되지 못한 것으로 해석하였다. 반면에 R1-2 resection에서는 두가지 순서에 차이가 없었다.
2018-02-07 11:48:25
편집위원
2006년에서 2012년까지 적용실태도 이와 비슷하게 R0pN2에서는 sequential chemo-RT 적용이, R1-2에서는 CCRT가 증가하여 본 연구와 실제 임상행태가 비슷하다고 하였다. National Cancer Database에서 추출한 데이터로 시행된 후향적 분석이므로 validation을 위한 전향적인 연구가 필요하지만,
2018-02-07 11:49:59
편집위원
adjuvant setting에서 방사선치료를 시행할 때 본 연구결과를 참고하는 것이 좋겠습니다.
2018-02-07 11:52:09