글로벌 연구동향
방사선방호 및 안전
- 2020년 02월호
[J Radiol Prot.] Assessment of radioactive cesium deposition using ground-based gamma-ray spectrometry with a LaBr3(Ce) detector.LaBr3(Ce) 감마선분광장비 이용 방사성세슘 토양 침적 평가KAERI / 지영용*
- 출처
- J Radiol Prot.
- 등재일
- 2019 Aug 13
- 저널이슈번호
- 39(4):1006-1020. doi: 10.1088/1361-6498/ab3a9f. [Epub ahead of print]
- 내용
Abstract
Ground-based gamma-ray spectrometry using a LaBr3(Ce) detector was conducted to assess radioactive cesium deposition in soil contaminated by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) in Japan. Five sites, including a reference site with relatively low contamination, were selected as having different levels of ambient dose rate due to significant effects of radioactive fallout of 134Cs and 137Cs. According to ICRU Report 53, the radioactivity in the ground and dose rate at 1 m above the ground were determined from the measured net count rates of gamma-rays induced from radioactive cesium. Because the radioactivity and dose rate depended on the depth profile of radioactive cesium in the ground, a database of possible radioactivity and dose rate could be established according to several depth distributions. A new approach to estimate the depth profile was then developed by directly calculating dose rates of 134Cs and 137Cs at the same geometry through dose rate spectroscopy and comparing them with the database of possible dose rates of radioactive cesium. Once the depth profile was determined, radioactivity was estimated from the database depending on the depth profile in the ground. The activity ratio between two radioactive cesium was shown to average about 0.112, in December 2017. It was in good agreement with the originally same released amount of 134Cs and 137Cs at the time of the FDNPP accident, when physical decay correction was applied to the results of the radioactivity assessment.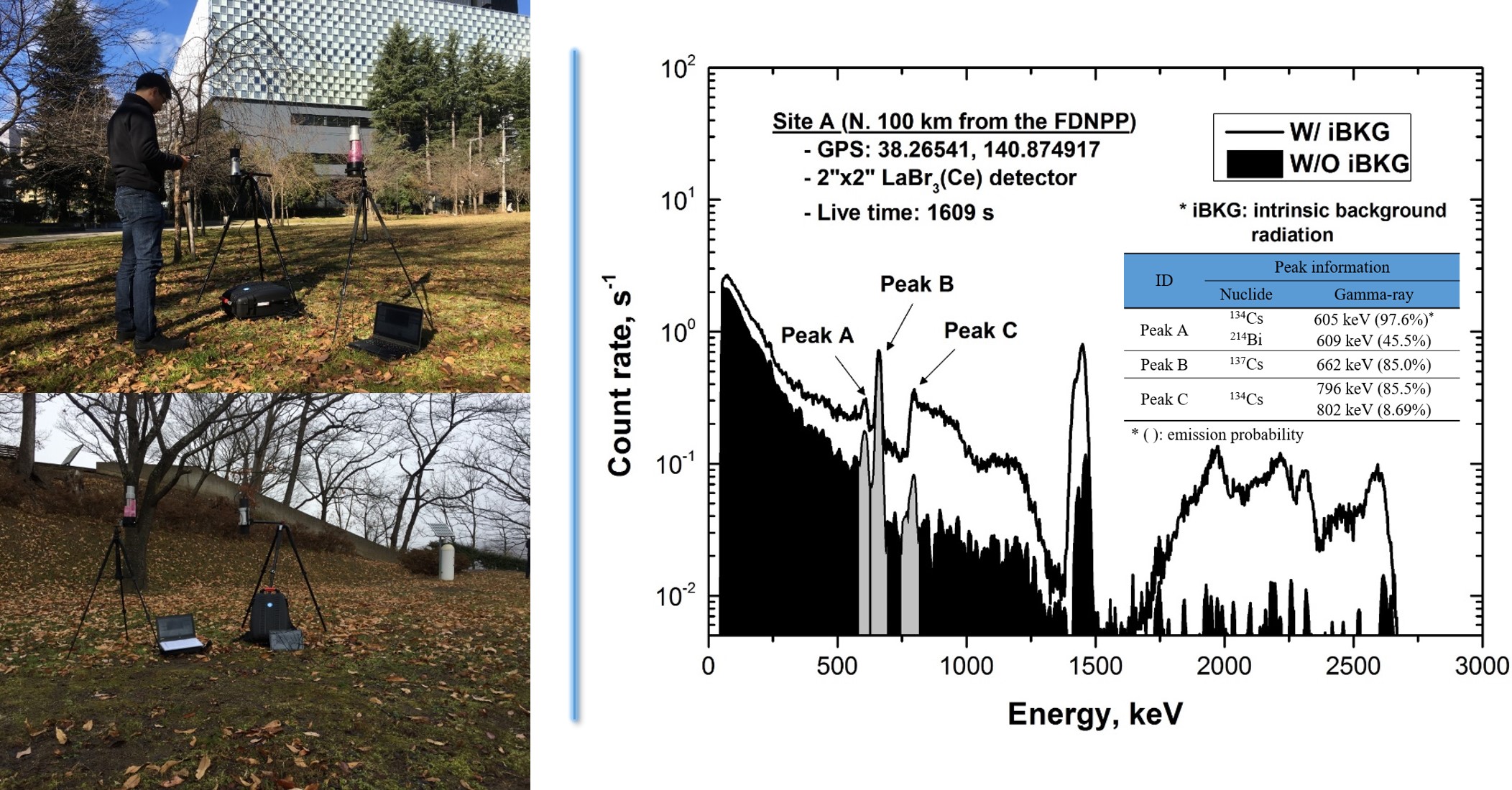
후쿠시마원전 방사성세슘 오염평가를 위한 삼각대 활용 지표면 고정측정 예 (왼쪽), LaBr3(Ce) 섬광검출기로 측정된 감마선에너지스펙트럼 및 방사성세슘 감마선피크 검출 예 (오른쪽)
Author informationJi YY1, Lim T, Hitomi K, Yajima T.
1
Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Daejeon 34057, Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 일본 후쿠시마원전 사고후 지표면에 침적된 방사성세슘(Cs-134 및 Cs-137)의 오염평가를 소개하는 논문임. 이를 위하여 2017년 12월 일본 동북(Tohoku) 대학교 Hitomi 교수팀과의 공동실험을 수행하였으며, 후쿠시마원전 주변 비거주지역과 원전으로부터 약 60km 떨어진 후쿠시마시내 거주지역에서의 방사성세슘 지표면 오염농도를 평가하였음. 국내에서 개발된 현장방사선측정 시스템 및 분석기술을 실제 사고현장에 적용하여 그 평가결과를 상호 비교함으로써 국내기술의 실험적 검증과 다양한 방사선량률 준위에서의 적용성을 확보할 수 있었음. 이로부터 국내 방사선비상상황에 대비하여 신속한 주민보호조치 등에 활용될 현장방사선분석관련 기술확보에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 판단됨.
- 덧글달기







