글로벌 연구동향
방사선방호 및 안전
- [Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.] Indoor radon concentration in Korea residential environments.
서경대 / 박태현, 이철민*
- 출처
- Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
- 등재일
- 2018 Feb 21. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1531-3. [Epub
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
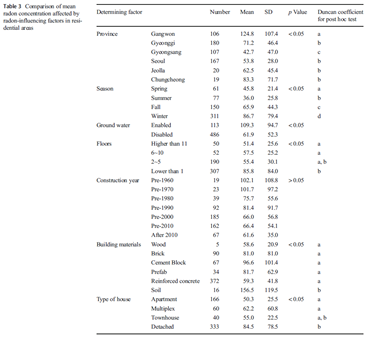
The purpose of this study is to provide basic data for the evaluation and management of health effects with respect to exposure to radon within residential environments in South Korea. It is part of a case-control study to develop a management plan based on indoor radon exposure levels and assess their impact on health. To investigate the long-term cumulative concentration levels of radon, 599 patients who have respiratory diseases were recruited in South Korea, and alpha track detectors were installed in their residences for a period of 3 months from mid-2015 to late 2016. A survey was then conducted to determine the factors affecting the radon concentration. The radon concentration levels were analyzed in conjunction with the survey results. The results show that the arithmetic mean of the radon concentrations in domestic residences was in the range of 70.8 ± 65.2 Bq/m3. An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was performed to identify the environmental factors affecting the radon concentration and contributing to variations in the residential radon concentration based on the height of the residence. The results show that the contribution of the local environmental factor to the variation in radon concentration (p < 0.05) was greater than that of other environmental factors. Although no statistically significant difference was found with regard to the construction year of the building before the control (p > 0.05), the same was found with regard to the construction year after the control (p < 0.05).
Author informationPark TH1, Kang DR2, Park SH3, Yoon DK3, Lee CM3.
1
Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, SeoKyeong University, Seoul, 02713, South Korea. thp119@skuniv.ac.kr.
2
Institute of Genomic Cohort, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, 26493, South Korea.
3
Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, SeoKyeong University, Seoul, 02713, South Korea.
- 키워드
- 222Rn; ANCOVA; Alpha track detector; Effective environmental factors; Residential environment
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 한국환경산업기술원 ‘생활공감 환경보건기술개발사업’의 일환으로 라돈노출에 대한 위해성평가 연구 중 실내라돈농도의 영향인자 도출을 통한 기초자료 확보를 목적으로 수행된 연구이다. 전국에 위치한 599개 거주지 내 실내라돈농도와 거주환경 특성에 관한 조사를 실시하였다. 실태조사를 통해 획득된 자료의 분석결과 지질학적 특성이 실내라돈농도에 가장 큰 영향을 미치는 것으로 조사되었으며 그 외 지하수이용유무, 거주층수, 건축자재, 건물유형이 라돈농도 증감에 기여하고 있는 것으로 조사되었다. 본 연구는 국내 거주환경 내 라돈농도 증감에 영향을 미치는 인자들을 규명하여 제시함으로써 향후 국내환경에 부합되는 라돈관리방안 도출 및 건강영향 평가에 관한 연구에 기초적 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
- 덧글달기









