글로벌 연구동향
방사선방호 및 안전
- 2018년 02월호
[Health Physics] Screening Criteria for the General Public in Radiation Emergencies From Liquid Scintillation UrinalysisKIRAMS / 윤석원, 진영우*
- 출처
- Health Physics
- 등재일
- 2018 Jan
- 저널이슈번호
- January 2018 Volume 114 - Issue 1 - p 27–31
- 내용

Abstract
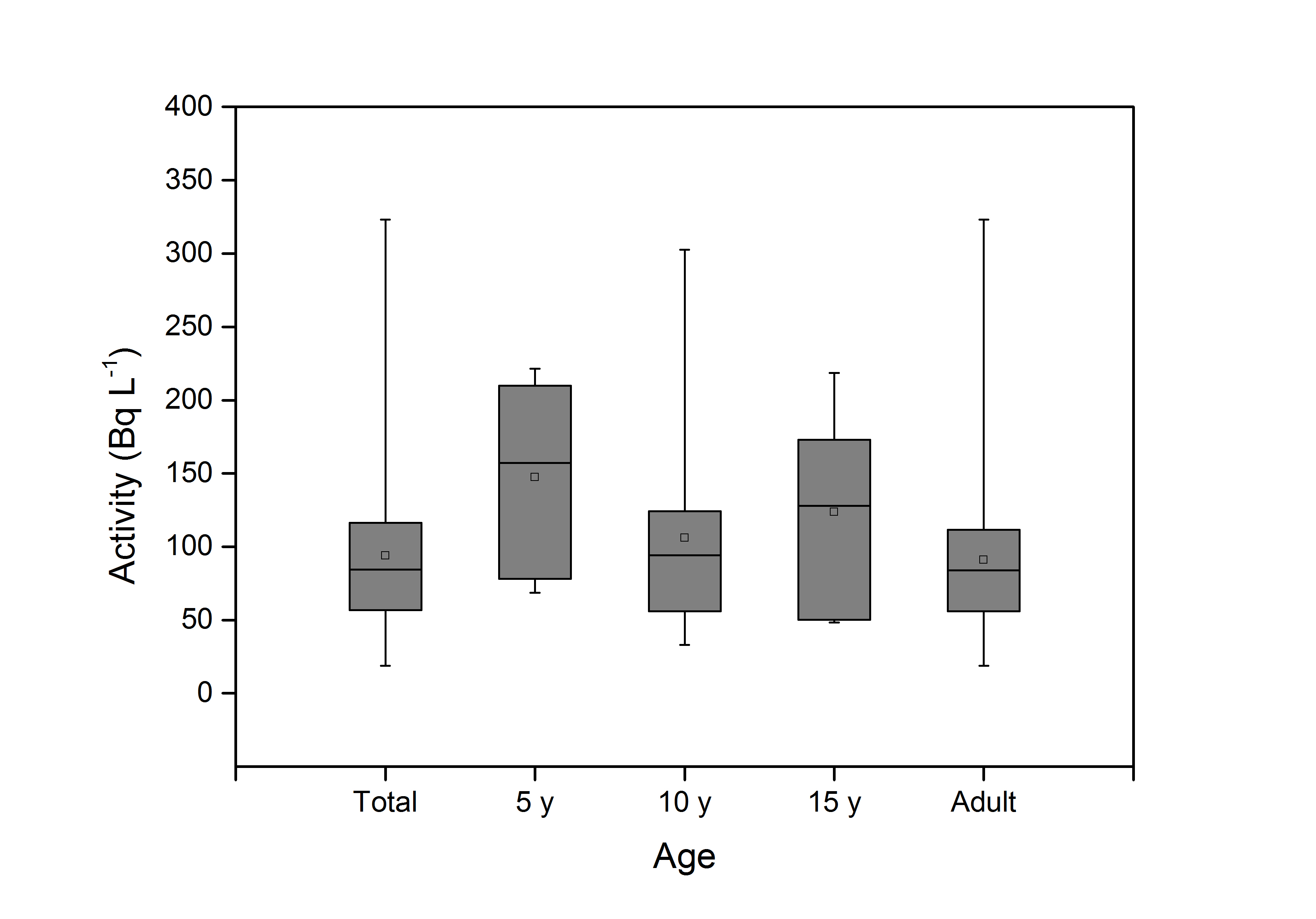
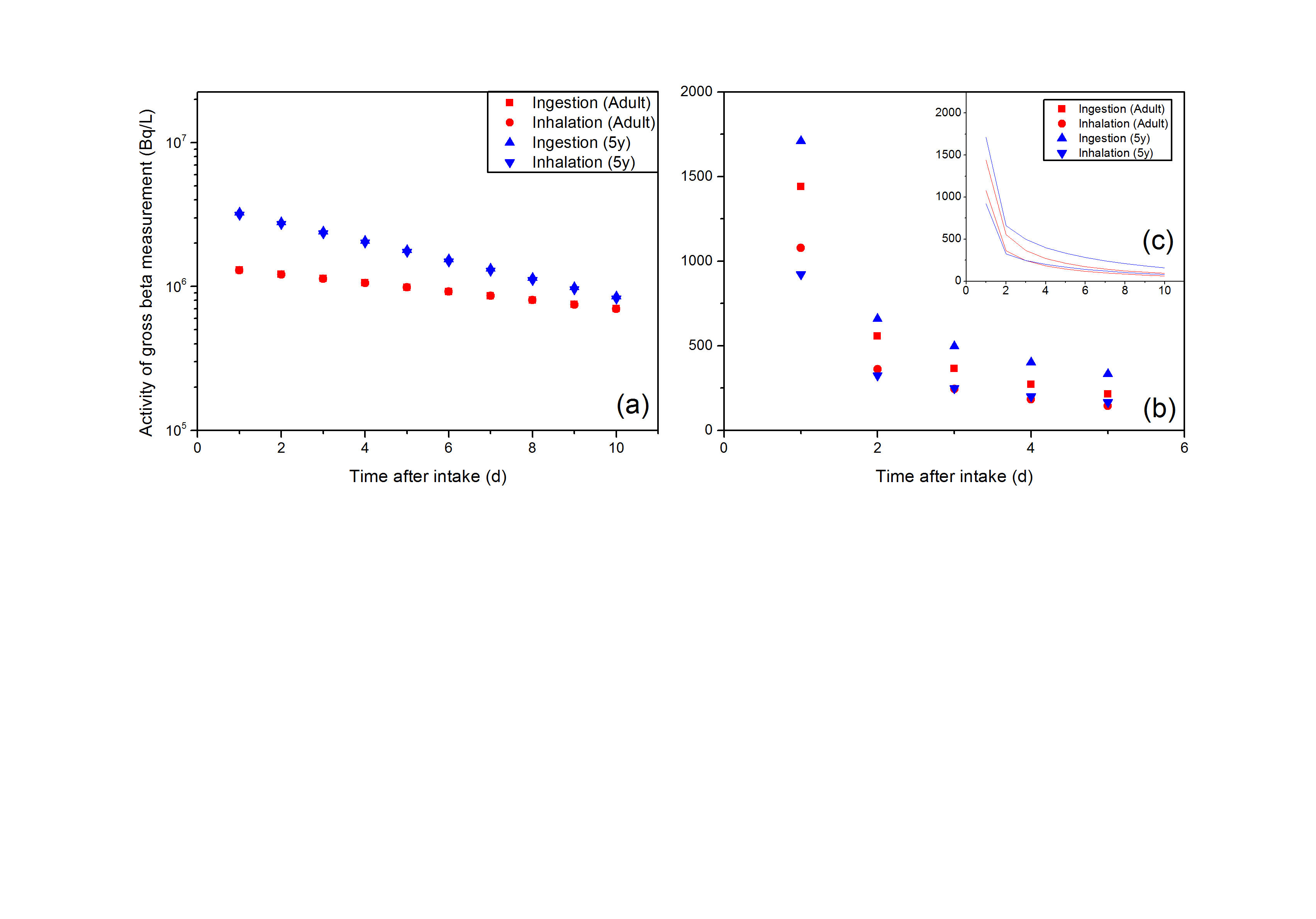
Gross alpha/beta screening of urine samples was performed to evaluate internal contamination and dose assessment. Data on background radioactivity concentration were extracted by analyzing the urine samples of non-contaminated individuals who had visited a radiation effect medical clinic since 2012. Screening criteria were studied and established for radiation emergencies based on these results. In particular, pure beta-emitting radionuclides (3H and 90Sr) with a high dose conversion factor were considered to be the source of contamination. Moreover, the screening criteria for the general public were determined based on age groups. The liquid scintillation counting method was used for gross alpha/beta radiation counting. A standardized procedure of correction for chemical and color quenching was performed and validated. The gross beta counting method was validated by analyzing standard urine samples. The fluctuation of the screening criteria was large, based on the time elapsed after intake. A screening criterion of 150 Bq L−1 can be applied within 5 d after intake considering the minimum detectable activity. A standard screening criterion set to 250 Bq L−1 will be used as an important reference for decision making and additional monitoring. Although early evaluation and accurate identification of contaminated radionuclides is preferred, these relatively simple criteria were proposed to address radiation emergency situations involving several casualties.
Author Information
Yoon, Seokwon; Kim, Yejin; Ha, Wi-Ho; Jin, Young-Woo*
*National Radiation Emergency Medical Center, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences 75, Nowon-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul, 01812, Republic of Korea.
- 연구소개
- 일본 후쿠시마 원전사고와 같은 대규모 방사능재난시 다수 검사소요에 대비하여 핵종별 내부오염 스크리닝 기준치를 합리적으로 추정하여 신속하게 실제상황에 적용하기 위한 주제로 연구논문을 준비하였습니다. 한국원자력의학원 방사선영향클리닉에 내원한 297명의 기저 전베타 방사능농도를 연령별로 평가하였고 뇨시료 특성을 고려한 전베타 액체섬광계수 측정효율교정에 대한 새로운 접근방법을 제안하였습니다. 아울러 방사선 비상시 Sr-90, H-3 핵종에 대한 선량기반 스크리닝 기준치를 산출하였습니다. 이는 전베타 방사능 측정결과만으로 사고정보와 연계하여 내부오염 의심자를 현장에서 신속히 분류할 수 있고 측정스펙트럼으로 오염 의심핵종을 추정 할 수 있는 기반이 될 것으로 기대합니다.
- 덧글달기







