글로벌 연구동향
분자영상 및 방사화학
- [Biomaterials.] Porous platinum nanoparticles as a high-Z and oxygen generating nanozyme for enhanced radiotherapy in vivo.
국립암센터 / 리안, 최용두*
- 출처
- Biomaterials.
- 등재일
- 2019 Mar
- 저널이슈번호
- 197:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 4.
- 내용
Abstract
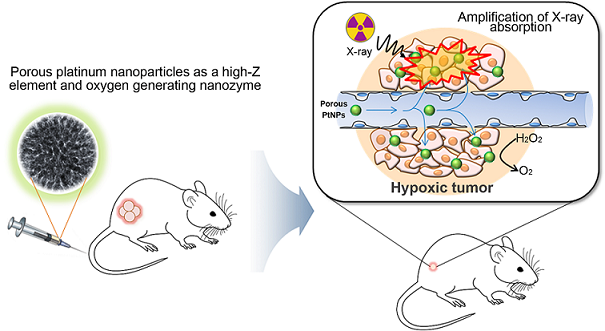
Radiotherapy (RT), along with surgery and chemotherapy, is a major modality of cancer therapy. Nevertheless, insufficient deposition of radiation energy in tumors and hypoxia-associated radioresistance remain the greatest challenges in RT. Here, we propose porous platinum nanoparticles as a new nanomedicine platform for solving these two problems at the same time using a single agent. Because of the combined advantages of a high-Z element and oxygen generation capability, porous platinum nanoparticles can significantly increase radiation-induced DNA damage, ROS stress, and cell cycle arrest by effectively depositing X-ray radiation energy within the cancer cells. Further, porous platinum nanoparticles increase tumor oxygenation by converting endogenic H2O2 to O2, thus greatly enhancing RT with no apparent in vivo toxicity to animals. This study presents a new nanomedicine strategy based on the use of porous high-Z metal nanoparticles with oxygen generation function for the synergistic enhancement of RT in cancer treatment.
Author informationLi Y1, Yun KH1, Lee H1, Goh SH2, Suh YG3, Choi Y4.
1
Biomarker Branch, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do 10408, Republic of Korea.
2
Therapeutic Target Discovery Branch, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do 10408, Republic of Korea.
3
Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do 10408, Republic of Korea.
4
Biomarker Branch, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do 10408, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: ydchoi@ncc.re.kr.
- 키워드
- Hypoxia; In vivo; Nanozyme; Oxygen generation; Radiotherapy
- 연구소개
- 방사선 치료는 암 치료에 있어서 자주 사용되고 매우 중요한 치료법임에도 불구하고, 정상세포에 미치는 부작용 때문에 방사선량을 높이는데 제한이 있고 따라서 방사선 에너지를 종양에 충분히 전달하는데 한계가 있다. 또한, 빠르게 성장하는 종양에서 유발되는 저산소증과 이에 따른 방사선 저항성은 방사선 치료에 있어서 커다란 제약이 되고 있다. 본 연구에서는, 다공성 백금 나노입자를 개발하고 방사선 치료에 적용함으로써 이러한 문제점을 동시에 해결하고자 하였다. 백금 원소에 의한 종양에서의 방사선 에너지의 흡수 및 산란 효율 극대화를 통하여 방사선 치료 효과 향상 뿐 아니라, 종양에 존재하는 과산화 수소를 다공성 백금나노입자에 의하여 효과적으로 산소로 변환시켜 줌으로써 종양에서의 저산소증까지 극복할 수 있음을 세포 및 동물 모델에서 보여 주었다. 조직 검사 및 혈액 검사 등으로부터, 투여된 다공성 백금나노입자가 생체 적합하다는 것도 확인 하였다.
- 덧글달기









