글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Sci Rep.] Development of Oxytolerant Salmonella typhimurium Using Radiation Mutation Technology (RMT) for Cancer Therapy.종양치료를 위한RMT기술을 활용한 항암 살모넬라 균주개발
KAERI / Shuang Gao, 서호성*, 임상용*
- 출처
- Sci Rep.
- 등재일
- 2020 Feb 28
- 저널이슈번호
- 10(1):3764. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60396-6.
- 내용
Abstract
A critical limitation of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) as an anti-cancer agent is the loss of their invasive or replicative activities, which results in no or less delivery of anti-cancer agents inside cancer cells in cancer therapy. Here we developed an oxytolerant attenuated Salmonella strain (KST0650) from the parental KST0649 (ΔptsIΔcrr) strain using radiation mutation technology (RMT). The oxytolerant KST0650 strain possessed 20-times higher replication activity in CT26 cancer cells and was less virulent than KST0649. Furthermore, KST0650 migrated effectively into tumor tissues in mice. KST0650 was further equipped with a plasmid harboring a spliced form of the intracellular pro-apoptotic protein sATF6, and the expression of sATF6 was controlled by the radiation-inducible recN promoter. The new strain was named as KST0652, in which sATF6 protein expression was induced in response to radiation in a dose-dependent manner. This strain was effectively delivered inside cancer cells and tumor tissues via the Salmonella type III secretion system (T3SS). In addition, combination treatment with KST0652 and radiation showed a synergistic anti-tumor effect in murine tumor model with complete inhibition of tumor growth and protection against death. In conclusion, we showed that RMT can be used to effectively develop an anti-tumor Salmonella strain for delivering anti-cancer agents inside tumors.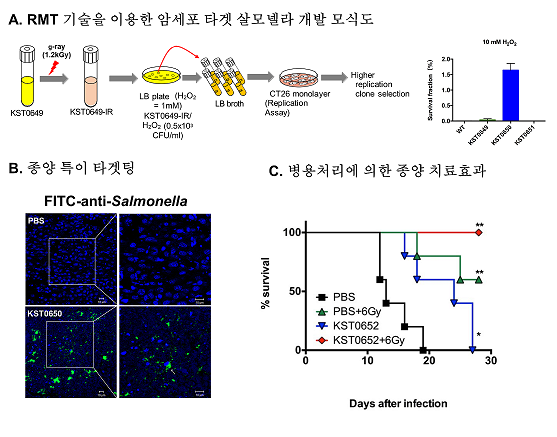
Author informationGao S1,2, Jung JH1,3, Lin SM1,2, Jang AY1,4, Zhi Y1,3, Bum Ahn K1, Ji HJ1, Hyang Lim J5, Guo H6, Choy HE2, Lim S7,8, Seo HS9,10.
1
Research Division for Radiation Science, Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Jeongeup, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Molecular Medicine (BrainKorea21 Plus), Chonnam National University Graduate School, Gwangju, Republic of Korea.
3
Department of Radiation Science, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea.
4
Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5
Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 07985, Republic of Korea.
6
State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, National Foot and Mouth Disease Reference Laboratory, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Lanzhou, China.
7
Research Division for Radiation Science, Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Jeongeup, Republic of Korea. saylim@kaeri.re.kr.
8
Department of Radiation Science, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea. saylim@kaeri.re.kr.
9
Research Division for Radiation Science, Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Jeongeup, Republic of Korea. hoseongseo@kaeri.re.kr.
10
Department of Radiation Science, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea. hoseongseo@kaeri.re.kr.
- 연구소개
- 방사선 돌연변이 유도 기술(Radiation Mutation Technology; RMT)을 이용하여 암세포에 특이적이고 생존율이 높은 종양치료용 신규 살모넬라 균주를 개발하였음. 개발한 신규치료용 균주는 마우스모델에서 종양에 특이적으로 이동을 하여 방사선과 병용처리를 하였을 경우 효과적으로 종양을 제거하여 마우스의 생존률을 높이는 것을 확인하였음.
- 덧글달기









