글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- 2020년 03월호
[Radiother Oncol.] Tumor mutation burden, immune checkpoint crosstalk and radiosensitivity in single-cell RNA sequencing data of breast cancer.서울의대 / 장범섭, 김인아*
- 출처
- Radiother Oncol.
- 등재일
- 2020 Jan
- 저널이슈번호
- 142:202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 22.
- 내용
Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
We analyzed transcriptional and mutational profile mainly focused on tumor mutation burden (TMB), immune checkpoint crosstalk, and radiosensitivity using scRNA-seq data derived from breast cancer and immune cells.MATERIALS AND METHODS:
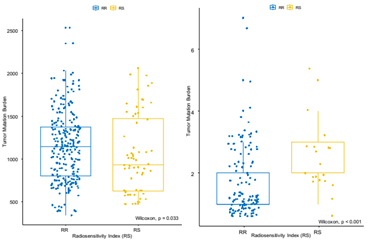
scRNA-seq transcriptome data were acquired from the GEO database (GSE75688). The radiosensitivity index (RSI) was used to evaluate radiosensitivity of each cell. CD274 mRNA expression was used to surrogate PD-L1 expression status. A computational approach was utilized for the immune and tumor cell group (N = 492) to identify potential interactions between tumor and immune cells with respect to immune checkpoint ligand-receptor gene pairs. Mutation data was profiled from raw scRNA-seq data of tumor cells acquired from both primary tumor and metastatic lymph node (N = 317). TMB and mutational signatures were compared between radiosensitive (RS) and radioresistant (RR) tumor cells.RESULTS:
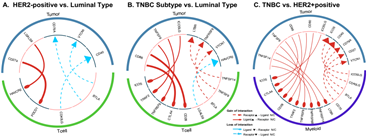
Most RR cells were a basal subtype and showed the higher rate of PD-L1 positivity. The patients with TNBC or HER2 subtype showed increased number of immune checkpoint ligand-receptor interactions between tumor and immune cells. PD-L1 ligand-receptor interactions between tumor cells and T cells were differentially increased in patients with the HER2 subtype compared to patients with the luminal subtype. Meanwhile, CTLA-4 ligand-receptor interactions were increased in patients with the TNBC subtype. TMB was significantly higher in RR cells than RS cells. Mutational signatures including microsatellite instability (MSI) and NRF2 pathway were altered in RR cells.CONCLUSIONS:
RR cells exhibited a basal subtype, high PD-L1 expression, and high TMB with mutational signature found in tumors having MSI. Differential crosstalk between tumor and immune cells was associated with the patient subtype of breast cancer. These findings could be useful to identify potential biomarker(s) and optimal combination strategies of immune checkpoint blockades and radiation therapy in the management of breast cancer.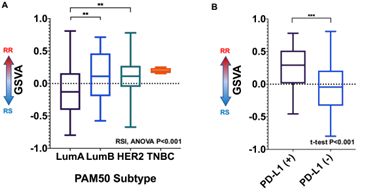
Author informationJang BS1, Han W2, Kim IA3.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Surgery, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Republic of Korea.
3
Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Republic of Korea; Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: inah228@snu.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Breast cancer; Immune checkpoint; Immunotherapy; Radiosensitivity; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Tumor mutation burden
- 연구소개
- 유방암 환자들의 single cell RNA sequencing 데이터를 통해 종양세포의 radiosensitivity와 tumor mutational burden과의 관계 및 종양세포와 면역세포들간의 면역체크포인트를 통한 cross talk 을 분석한 논문입니다. 방사선 저항성이 있는 종양세포는 basal subtype이면서 PD-L1 발현이 높고, 상대적으로 높은 mutation brden을 보였습니다. 또한 종양세포와 면역세포들간의 상호작용은 환자의 subtype별로 다른 것을 알 수 있었습니다. 이러한 결과들은 앞으로 유방암 환자들의 면역치료와 방사선치료에 있어 바이오마커를 발굴하거나 최적의 치료법을 찾는 데 도움이 될 것으로 사료됩니다.
- 덧글달기







