글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Cells.] Cellular Stress Responses in Radiotherapy.
세종대, 부산대 / 김완연, 이성민, 윤혜숙*, 윤부현*
- 출처
- Cells.
- 등재일
- 2019 Sep 18
- 저널이슈번호
- 8(9). pii: E1105. doi: 10.3390/cells8091105.
- 내용
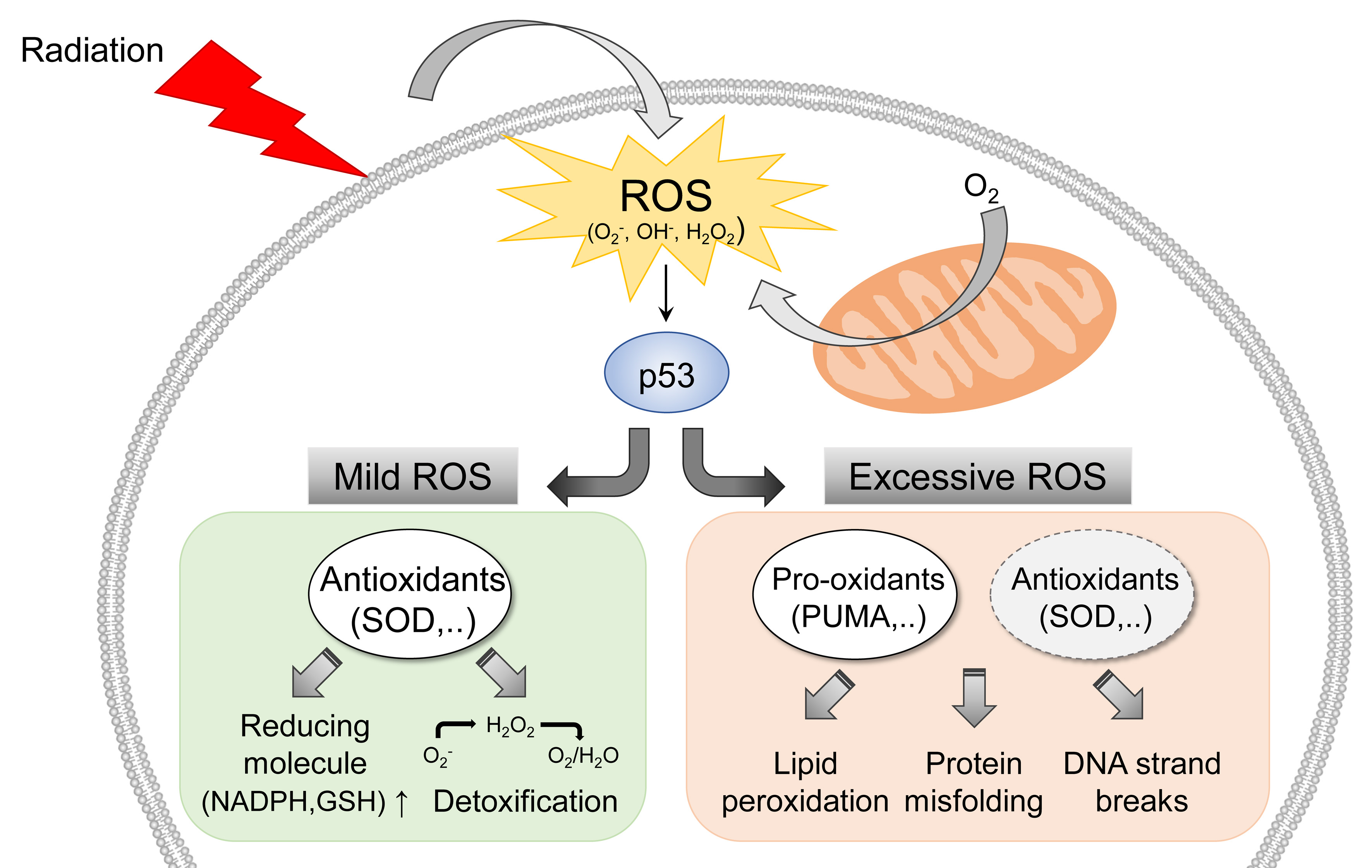
Abstract
Radiotherapy is one of the major cancer treatment strategies. Exposure to penetrating radiation causes cellular stress, directly or indirectly, due to the generation of reactive oxygen species, DNA damage, and subcellular organelle damage and autophagy. These radiation-induced damage responses cooperatively contribute to cancer cell death, but paradoxically, radiotherapy also causes the activation of damage-repair and survival signaling to alleviate radiation-induced cytotoxic effects in a small percentage of cancer cells, and these activations are responsible for tumor radio-resistance. The present study describes the molecular mechanisms responsible for radiation-induced cellular stress response and radioresistance, and the therapeutic approaches used to overcome radioresistance.
Author informationKim W1,2, Lee S3, Seo D4, Kim D5, Kim K6, Kim E7, Kang J8, Seong KM9, Youn H10, Youn B11,12.
1
Department of Biology Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju-si, Chungbuk 28173, Korea. wykim82@knue.ac.kr.
2
Department of Science Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju-si, Chungbuk 28173, Korea. wykim82@knue.ac.kr.
3
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. smlee1048@gmail.com.
4
Department of Science Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju-si, Chungbuk 28173, Korea. dbseo130@gmail.com.
5
Department of Science Education, Korea National University of Education, Cheongju-si, Chungbuk 28173, Korea. ekdls5371@gmail.com.
6
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. minnnny@gmail.com.
7
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. eungikim89@gmail.com.
8
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. jhkang4293@gmail.com.
9
Laboratory of Low Dose Risk Assessment, National Radiation Emergency Medical Center, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Korea. skmhanul@kirams.re.kr.
10
Department of Integrative Bioscience and Biotechnology, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Korea. hsyoun@sejong.ac.kr.
11
Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. bhyoun72@pusan.ac.kr.
12
Department of Biological Sciences, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. bhyoun72@pusan.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- DNA damage response; ER stress; Radiation response; autophagy; lipid peroxidation; mitochondrial damage; radioresistance; reactive oxygen species
- 연구소개
- Radiotherapy는 ROS의 발생을 기반으로 암세포의 사멸을 유도한다. 하지만 동시에 암세포에서는 다양한 stress response의 활성화를 통해 세포 내 피해를 줄이고 방사선 저항성을 유도할 수 있다. 본 리뷰에서는 radiotherapy 이후 활성화되는 세포 기전의 이해를 통하여 방사선 저항성을 극복하기 위해 접근을 다루고자 한다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Int J Mol Sci.] Antitumor Activity of a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AIU2001 Due to Abrogation of the DNA Damage Repair in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.
- 다음글 [Int J Radiat Biol.] Targeted next-generation DNA sequencing identifies Notch signaling pathway mutation as a predictor of radiation response.









