글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- 2019년 04월호
[Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.] Hypermethylation of miR-205-5p by IR Governs Aggressiveness and Metastasis via Regulating Bcl-w and Src.방사선에 의한 마이크로RNA (miR-205-5p)의 메틸화에 의한 암의 악성화 및 전이 유도기능 규명KIRAMS / 김은숙, 배인화*
- 출처
- Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
- 등재일
- 2019 Mar 1
- 저널이슈번호
- 14:450-464. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.12.013. Epub 2018 Dec 31.
- 내용
Abstract
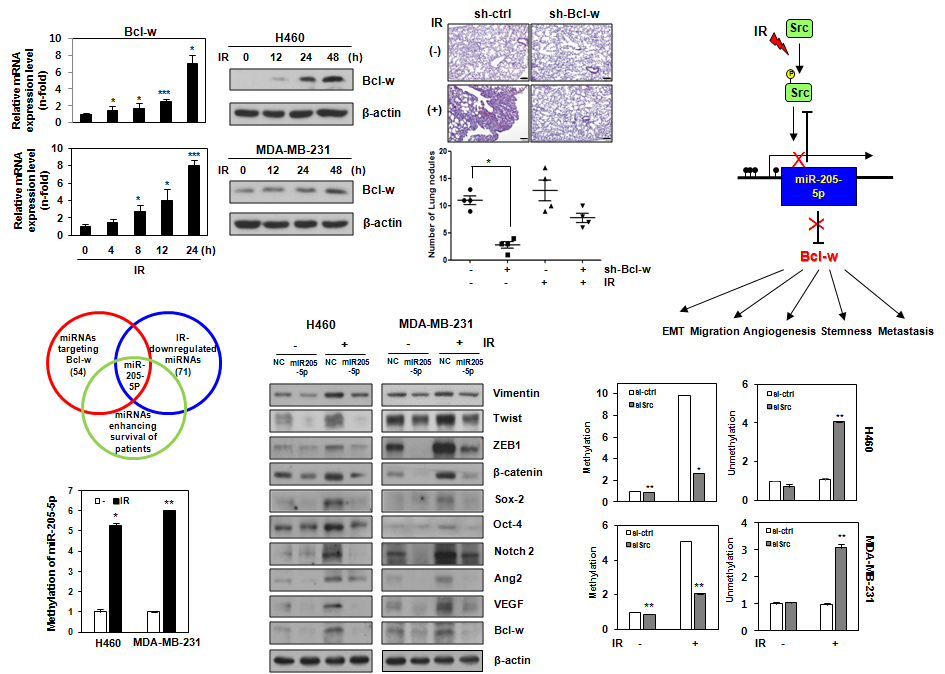
Although radiotherapy has been successfully applied to treat many cancer types, surviving cancer cells often acquire therapeutic resistance, leading to increased risk of local recurrence and distant metastases via modification of the tumor microenvironment. Previously, we reported that high expression of Bcl-w in cancer patients is significantly correlated with poor survival as well as malignant activity. However, the relationship between ionizing radiation (IR)-induced resistance and Bcl-w expression in cancer cells is currently unclear. We showed that IR-induced Bcl-w contributes to EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal transition), migration, angiogenesis, stemness maintenance, and metastasis by promoting the expression of factors related to these phenotypes, both in vitro and in vivo. Meanwhile, IR enhanced hypermethylation of miR-205-5p CpG islands through Src activation, leading to decreased miR-205-5p expression and, in turn, potentially stimulating Bcl-w-mediated malignant activity and metastasis. The clinical applicability of Bcl-w and miR-205-5p from cells or animal models was confirmed using tissues and plasma of breast carcinoma patients. Based on the collective findings, we propose that miR-205-5ps as important negative mediators of resistance in radiotherapy could serve as useful potential targets of concurrently applied genetic therapy aimed to inhibit tumor aggressiveness and enhance the efficiency of radiotherapy in cancer patients.
Author informationKim ES1, Choi JY1, Hwang SJ1, Bae IH2.
1
Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Republic of Korea.
2
Division of Radiation Biomedical Research, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul 01812, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: ihbae@kirams.re.kr
- 키워드
- Bcl-w; hypermethylation; metastasis; miR-205-5p; radioresistance
- 연구소개
- 방사선치료가 대표적인 암 치료법임에도 불구하고 치료과정에서 살아남은 암세포가 저항성을 획득하여 암 재발을 유도하고 더 나아가 전이까지 진행되는 경우가 많다. Bcl-w가 종양유도인자로서 암 악성화에 관여한다는 많은 보고가 있으나 방사선 저항성과의 관계에 대해서는 밝혀진 바가 없었다. 본 연구에서는 방사선 유도인자로서의 Bcl-w와 이의 발현을 조절하는 miR-205-5p를 발굴하였으며 방사선에 의해 활성화된 Src가 miR-205-5p의 과메틸화로 발현을 억제시키고 이로 인하여 증가한 Bcl-w가 암 악성화 및 전이 촉진에 관여함을 확인한 논문이다. 본 연구는 방사선 치료 시 병용치료로 이용될 RNAi 치료제로서 miRNA를 활용하여 방사선 치료의 효율을 향상시키는 또 하나의 방법을 제시한 정보라 생각한다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
방사선에 의해 암발생 및 억제, 전이 관련하여 microRNA가 관여할것이라는 추정은 되었으나, 그 중 주요 microRNA를 발굴했고, 이에 의해 암발생 및 전이에 direct하게 관여함을 증명한 논문이라고 사료됨
덧글달기닫기2019-04-17 16:08:18
등록
김진수
축하드려요 ~~
덧글달기닫기2019-04-25 19:28:44
등록