글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [J Biophotonics.] Comparison between reflectance confocal microscopy and 2-photon microscopy in early detection of cutaneous radiation injury in a mouse model in vivo.
KIRAMS, 포항공대 / 장원혁, 박선후*, 김기현*
- 출처
- J Biophotonics.
- 등재일
- 2018 Oct
- 저널이슈번호
- 11(10):e201700337. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201700337. Epub 2018 Jul 5.
- 내용
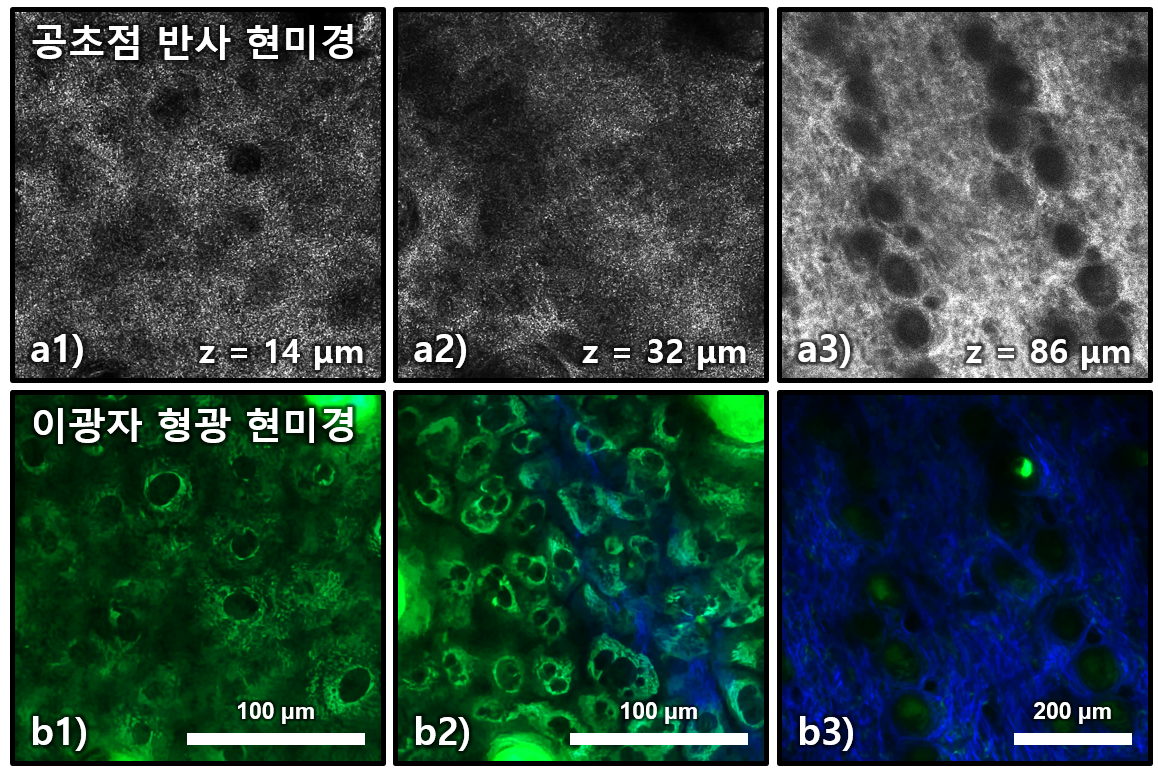
Abstract
Cutaneous radiation injury (CRI) is a skin injury caused by high-dose exposure of ionizing radiation (IR). For proper treatment, early detection of CRI before clinical symptoms is important. Optical microscopic techniques such as reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) and 2-photon microscopy (TPM) have been tested as the early diagnosis method by detecting cellular changes. In this study, RCM and TPM were compared in the detection of cellular changes caused by CRI in an in vivo mouse model. CRI was induced on the mouse hindlimb skin with various IR doses and the injured skin regions were imaged longitudinally by both modalities until the onset of clinical symptoms. Both RCM and TPM detected the changes of epidermal cells and sebaceous glands before clinical symptoms in different optical contrasts. RCM detected changes of cell morphology and scattering property based on light reflection. TPM detected detail changes of cellular structures based on autofluorescence of cells. Since both RCM and TPM were sensitive to the early stage CRI by using different contrasts, the optimal method for clinical CRI diagnosis could be either individual methods or their combination.
Author informationJang WH1,2, Kwon S3, Shim S4, Jang WS5, Myung JK4,5,6, Yang S7,8, Park S4,5,6, Kim KH1,3.
1
Divison of Integrative Biosciences & Biotechnology, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, South Korea.
2
Biotech Center, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, South Korea.
3
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Gyeongbuk, South Korea.
4
National Radiation Emergency Medical Centre, Korea Cancer Centre Hospital, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), Seoul, South Korea.
5
Laboratory of Experimental Pathology, Korea Cancer Centre Hospital, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), Seoul, South Korea.
6
Department of Pathology, Korea Cancer Centre Hospital, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), Seoul, South Korea.
7
Medical Physics Division, Department of Radiation Oncology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California.
8
Department of Electronics Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, South Korea.
- 키워드
- 2-photon microscopy; an in vivo mouse model; cutaneous radiation injury; early detection; reflectance confocal microscopy
- 연구소개
- 방사선 피폭에 의한 피부 손상 범위를 잠복기 내에 조기 진단하기 위하여 피부 구성 세포를 비침습적으로 영상화하여 검사하는 방법을 연구한 논문입니다. 피부 세포 영상화 기술로 공초점 반사현미경과 이광자형광현미경을 사용하여 마우스 모델에서 방사선 피폭 후 피부의 변화를 정기적으로 관찰하였습니다. 현미경 영상에서 상피세포와 피지샘 구성 세포들이 잠복기 동안 손상이 되는 것을 탐지하였고, 영상처리를 통해 세포 손상 정량화 방법을 고안하였습니다. 이 현미경 기술들은 인체 피부 촬영에 사용할 수 있어 효율적인 방사선 피폭 범위 진단 방법으로 활용 할 수 있을 것으로 기대합니다.
- 덧글달기









