글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
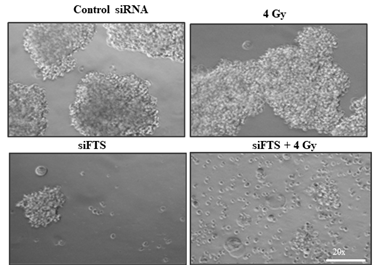
- [Int J Biol Macromol.] Silencing of FTS increases radiosensitivity by blocking radiation-induced Notch1 activation and spheroid formation in cervical cancer cells.
충북의대 / D.S.Prabakaran, 박우윤*
- 출처
- Int J Biol Macromol.
- 등재일
- 2018 Sep 20. pii: S0141-8130(18)33509-8. doi: 10.1
- 저널이슈번호
- 내용
Abstract
Increasing evidence(s) suggests that cancer stem cells (CSC) in tumours contribute to radio-resistance and recurrence. Notch plays an important role in the maintenance of CSC in many cancers including cervical cancer. Previously, we have reported the role of Fused Toes Homolog (FTS) in conferring radioresistance in cervical cancer cells in vitro and human subjects. The present study investigated the regulatory role of FTS in Notch signaling and maintenance of CSC upon irradiation of cervical cancer cells. The expression of Notch1, 2, 3, cleaved Notch1 and its downstream target Hes1, and spheroid formation was increased by irradiation. Silencing of FTS prevented the radiation-induced increase in the expression of Notch signaling molecules and spheroid formation. Immunoprecipitation showed FTS binds Notch1 and Hes1. Also in silico structural analysis identified putative residues responsible for the binding between FTS and Notch1. Spheroid formation and the expression of CSC markers, Nanog, Oct4A and Sox2 were greatly reduced by combining silencing of FTS and radiation. Taken together, these results suggest that FTS is involved in the regulation of irradiation-induced Notch signaling and CSC activation and can be used as a target to increase radiosensitivity in cervical cancer.
Author informationPrabakaran DS1, Muthusami S2, Sivaraman T3, Yu JR4, Park WY5.
1
Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju 28644, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Biochemistry, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Eachanari, Coimbatore 641 021, Tamilnadu, India.
3
Department of Biotechnology, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Eachanari, Coimbatore 641 021, Tamilnadu, India.
4
Department of Environmental and Tropical Medicine, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Chungju 27478, Republic of Korea.
5
Department of Radiation Oncology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju 28644, Republic of Korea. Electronic address: wynpark@chungbuk.ac.kr.
- 키워드
- Cancer stem cells; Cervical cancer; Fused Toes Homolog; Notch; Radiation
- 연구소개
- 본 연구팀은 FTS(Fused Toes Homolog)가 자궁경부암의 진행 및 방사선감수성에 관여한다는 것을 처음으로 보고한 바 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 자궁경부암 세포에서 방사선 조사에 의해 Notch 및 암 줄기세포 관련 단백질이 증가하나 이는 FTS 유전자의 발현 억제에 의해 감소하고, 면역 침강 및 in silico 구조 분석에서 FTS와 Notch1의 결합을 확인했습니다. 이 결과는 FTS가 방사선에 의한 Notch 신호 및 암줄기세포 활성화의 조절에 관여하고 방사선 민감성을 증가시키는 표적으로 사용될 수 있음을 시사합니다.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cancer Sci.] Hypoxia-inducible transgelin 2 selects epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and γ-radiation-resistant subtypes by focal adhesion kinase-associated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor activation in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.
- 다음글 [J Clin Invest.] Mitochondrial reprogramming via ATP5H loss promotes multimodal cancer therapy resistance.









