글로벌 연구동향
방사선생물학
- [Cell Death Dis.] Kinesin light chain-4 depletion induces apoptosis of radioresistant cancer cells by mitochondrial dysfunction via calcium ion influx.
KIRAMS / 백정화, 황상구*
- 출처
- Cell Death Dis.
- 등재일
- 2018 May 2
- 저널이슈번호
- 9(5):496. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0549-2.
- 내용
Abstract
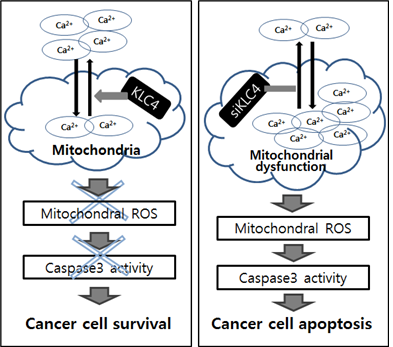
Kinesins act as molecular microtubule-dependent motor proteins and have various important cellular functions related to cell division, intracellular transport, and membrane trafficking. However, the function of kinesin light chain 4 (KLC4) in cancer, especially radioresistance, has not been previously described. Thus, we investigated KLC4 function in lung cancer cells and radioresistant R-H460 cells by analyzing alterations in radiosensitivity after gene knockdown with siRNA and by evaluating cellular phenotypes and xenograft tumor growth. KLC4 was upregulated in human lung cancer cell lines. Moreover, in paired clinical specimens of lung cancer patients, KLC4 expression was significantly higher in tumor tissues than in paired adjacent normal tissues. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis showed that apoptosis rates and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and cleaved caspase-3 levels in KLC4-knockdown lung cancer cells were significantly increased compared with those in control cells. Colony formation decreased as the radiation dose increased in KLC4-knockdown lung cancer cells, demonstrating an essential role for KLC4 in radioresistance. Importantly, KLC4 silencing suppressed tumor growth in an in vivo xenograft model, accompanied by increased apoptosis. Finally, KLC4-knockdown cells exhibited impaired mitochondrial respiration, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production, and enhanced mitochondrial calcium uptake, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction. Thus, KLC4 as a kinesin superfamily-targeted therapy may represent a novel, effective anticancer strategy, particularly for patients showing radioresistance.
Author informationBaek JH1,2, Lee J1, Yun HS1, Lee CW2, Song JY1, Um HD1, Park JK1, Park IC1, Kim JS1, Kim EH3, Hwang SG4.
1
Division of Applied Radiation Bioscience, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Korea.
2
Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, 440-746, Korea.
3
Division of Applied Radiation Bioscience, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Korea. eh140149@kirams.re.kr.
4
Division of Applied Radiation Bioscience, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, 01812, Korea. sgh63@kcch.re.kr.
- 연구소개
- 본 연구는 암세포의 방사선 저항성에 기여하는 KLC4의 세포 사멸 메커니즘을 규명함으로서 암환자의 치료효율을 증진시키는 시스템 구축의 가능성을 확보하고자함. KLC4는 세포내 미토콘드리아에 위치하고 있으며, KLC4의 발현을 억제하였을 때 미토콘드리아 내 칼슘의 증가로 인한 기능장애가 일어남을 관찰하였음. KLC4 억제에 의한 미토콘드리아의 기능장애는 caspase 3를 활성화시킴으로서 세포 사멸을 유도하는 분자적 메커니즘을 규명함. 이를 통하여 방사선 치료와 항암제 치료에 저항성을 가지는 환자의 치료법 개발 및 개서의 방향성을 제시할 수 있음.
- 덧글달기
- 이전글 [Cell Death Differ.] Integrin α6β4-Src-AKT signaling induces cellular senescence by counteracting apoptosis in irradiated tumor cells and tissues.
- 다음글 [BMC Cancer.] Identification of genes inducing resistance to ionizing radiation in human rectal cancer cell lines: re-sensitization of radio-resistant rectal cancer cells through down regulating NDRG1.









