글로벌 연구동향
의학물리학
- [Med Phys.] Technical Note: A proposal of air ventilation system design criteria for a clinical room in a heavy-ion medical facility.
경북대 / 금오연*
- 출처
- Med Phys.
- 등재일
- 2018 Apr 16.
- 저널이슈번호
- doi: 10.1002/mp.12914. [Epub ahead of print]
- 내용
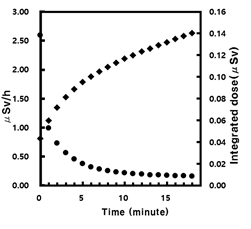
Residual gamma effective dose rate and accumulated dose as a function of decay time just after 1 fraction irradiation with maximum energy (430 MeV/u) and the beam intensity of 1 x 109 particles per second in normal operation in the treatment room
Abstract
PURPOSE:
An optimized air ventilation system design for a treatment room in Heavy-ion Medical Facility is an important issue in the aspects of nuclear safety because the activated air produced in a treatment room can directly affect the medical staff and the general public in the radiation-free area.METHODS:
Optimized design criteria of air ventilation system for a clinical room in 430 MeV/u carbon ion beam medical accelerator facility was performed by using a combination of MCNPX2.7.0 and CINDER'90 codes. Effective dose rate and its accumulated effective dose by inhalation and residual gamma were calculated for a normal treatment scenario (2 min irradiation for one fraction) as a function of decay time. Natural doses around the site were measured before construction and used as reference data.RESULTS:
With no air ventilation system, the maximum effective dose rate was about 3 μSv/h (total dose of 90 mSv/y) and minimum 0.2 μSv/h (total dose of 6 mSv/y), which are over the legal limits for medical staff and for the general public. Although inhalation dose contribution was relatively small, it was considered seriously because of its long-lasting effects in the body. The integrated dose per year was 1.8 mSv/y in the radiation-free area with the 20-min rate of air ventilation system.CONCLUSION:
An optimal air ventilation rate of 20 min is proposed for a clinical room, which also agrees with the best mechanical design value.
Author informationKum O1.
1
School of Electrical, Electronics, and Computer Engineering, Kyungpook National University, 80 Daehakro, Bukgu, Daegu, 41566, Korea.
- 키워드
- CINDER’90 code; MCNPX2.7.0 code; air ventilation system design; heavy-ion medical accelerator facility; inhalation dose; residual gamma dose
- 연구소개
- 부산 기장군에 지어진 중입자 치료 센터의 방사선 안전설계를 수행하는 과정에서 치료빔의 조사에 의한 주변공기 방사화의 피해를 입을 가능성이 있는 센터 임직원들과 환자 및 보호자들의 방사선 안전을 확보하기 위해 방사선 치료실에 설치할 공기순환장치(air ventilation system) 설계에 관한 기술적 내용을 소개하였다. Residual/remnant dose 와 inhalation dose를 중요한 변수로 분석하여 최적의 배기 시간을 계산/추정 하였다.
- 덧글달기









