글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.] Imaging phenotype using 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-based radiomics and genetic alterations of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma FDG PET영상특성분석으로 췌장암 유전자변이예측
성균관의대 / 임채홍, 현승협*
- 출처
- Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
- 등재일
- 2020 Aug
- 저널이슈번호
- 47(9):2113-2122. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04698-x. Epub 2020 Jan 31.
- 내용
-
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to determine if major gene mutations including in KRAS, SMAD4, TP53, and CDKN2A were related to imaging phenotype using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)-based radiomics in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).Methods: Data on 48 PDAC patients with pretreatment FDG PET/CT who underwent genomic analysis of their tumor tissue were retrospectively analyzed. A total of 35 unique quantitative radiomic features were extracted from PET images, including imaging phenotypes such as pixel intensity, shape, and textural features. Targeted exome sequencing using a customized cancer panel was used for genomic analysis. To assess the predictive performance of genetic alteration using PET-based radiomics, areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were used.
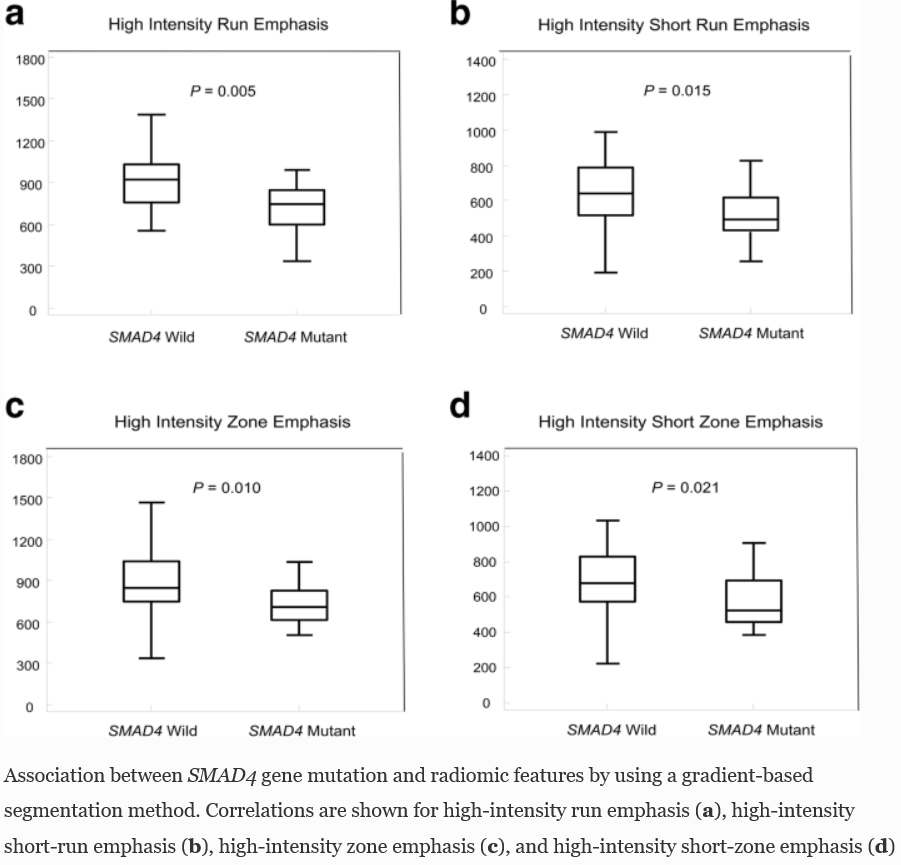
Results: Mutation frequencies were KRAS 87.5%, TP53 70.8%, SMAD4 25.0%, and CDKN2A 18.8%. KRAS gene mutations were significantly associated with low-intensity textural features, including long-run emphasis (AUC = 0.806), zone emphasis (AUC = 0.794), and large-zone emphasis (AUC = 0.829). SMAD4 gene mutations showed significant relationships with standardized uptake value skewness (AUC = 0.727), long-run emphasis (AUC = 0.692), and high-intensity textural features such as run emphasis (AUC = 0.775), short-run emphasis (AUC = 0.736), zone emphasis (AUC = 0.750), and short-zone emphasis (AUC = 0.725). No significant associations were seen between the imaging phenotypes and genetic alterations in TP53 and CDKN2A.
Conclusion: Genetic alterations of KRAS and SMAD4 had significant associations with FDG PET-based radiomic features in PDAC. PET-based radiomics may help clinicians predict genetic alteration status in a noninvasive way.
Affiliations
Chae Hong Lim 1 , Young Seok Cho 1 , Joon Young Choi 1 , Kyung-Han Lee 1 , Jong Kyun Lee 2 , Ji Hye Min 3 , Seung Hyup Hyun 4
1 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81, Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 06351, South Korea.
2 Department of Gastroenterology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
3 Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea.
4 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81, Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 06351, South Korea. shnm.hyun@samsung.com.
- 키워드
- FDG PET/CT; Gene mutation; Genetic alteration; Pancreatic cancer; Radiomics.
- 연구소개
- 췌장암은 아직까지도 낮은 생존률을 보여줍니다. 최근 췌장암 관련 연구들은 유전자의 변이와 종양의 대사적인 변화에 초점을 맞추면서 이러한 생존률의 한계를 극복하고자 노력하고 있습니다. FDG PET/CT는 종양의 대사 변화를 간접적으로 보여줄 수 있는 영상이므로 이번 연구에서 우리는 종양의 FDG 섭취 패턴이 유전자 변이와 상관성을 갖는지 검증하였습니다. 췌장암에서 가장 흔한 유전자 변이를 보이는 KRAS, TP53, SMAD4, CDKN2A 4가지 유전자 중에서 KRAS, SMAD4 유전자가 FDG 종양의 섭취 패턴과 가장 큰 연관성을 보여 주었습니다. 이러한 연관성은 FDG 섭취의 분포 패턴이 췌장암에서 유전자 변이 여부를 예측하는 중요한 이미징 바이오마커로서의 잠재적 가능성을 보여줍니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
췌장암에서 FDG PET의 radiomic feature가 KRAS 및 SMAD4 유전자변이와 상관성이 있음을 밝힌 연구로 비침습적인 FDG PET 영으로 췌장암의 유전자변이를 예측 할 수 있을 가능성을 보여줌. 췌장암 관련 임상가, 핵의학 의사 및 인공지능연구자에게 에게 관심을 끌 논문으로 생각됨.
2020-10-05 17:40:33