글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- [Thyroid.] A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Can Augment Radioactive Iodine Uptake Through Endogenous Sodium/Iodide Symporter Expression in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer.
경북의대 / 오지민, 안병철*
- 출처
- Thyroid.
- 등재일
- 2020 Apr
- 저널이슈번호
- 30(4):501-518. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0626. Epub 2020 Feb 14.
- 내용
Abstract
Background: Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy is an important strategy in the treatment of thyroid cancer. However, anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), a rare malignancy, exhibits severe dedifferentiation characteristics along with a lack of sodium iodide symporter (NIS) expression and function. Therefore, RAI therapy is ineffective and contributes toward poor prognosis of these patients. Recently, small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been used to treat thyroid cancer patients for restoring NIS expression and function and RAI uptake capacity. However, most results reported thus far are associated with differentiated thyroid cancer. In this study, we identified a new TKI and investigated its effects on cell redifferentiation, NIS function, and RAI therapy in ATC. Methods: We identified a new TKI, "5-(5-{4H, 5H,6H-cyclopenta[b]thiophen-2-yl}-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-1-methyl-1,2-dihydropyridin-2-one" (CTOM-DHP), using a high-throughput screening system. CTOM-DHP was exposed to 8505C ATC cells at different concentrations and time points. Concentrations of 12.5 and 25 μM and an incubation time of 72 hours were chosen as the conditions for subsequent NIS promoter assays and NIS mRNA and protein expression experiments. In addition, we examined factors related to iodide metabolism after CTOM-DHP treatment as well as the signaling pathways mediating the effects of CTOM-DHP on endogenous NIS expression. RAI uptake and 131I cytotoxicity effects caused by CTOM-DHP pretreatment were also evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Results: Promoter assays as well as mRNA and protein expression analyses confirmed that NIS expression was augmented by treatment of 8505C ATC cells with CTOM-DHP. Moreover, CTOM-DHP treatment robustly increased the expression of other thyroid-specific proteins and thyroid transcription factors related to iodide metabolism. Enhancement of NIS function was demonstrated by an increase in 125I uptake and 131I cytotoxicity. Increased endogenous NIS expression was associated with the inhibition of PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. In vivo results also demonstrated an increase in NIS promoter activity and RAI avidity in response to CTOM-DHP treatment. Furthermore, 131I-mediated therapeutic effects preferentially improved in a tumor xenograft mice model. Conclusions: CTOM-DHP, a new TKI identified in this study, enhances endogenous NIS expression and thereby is a promising compound for restoring RAI avidity in ATC.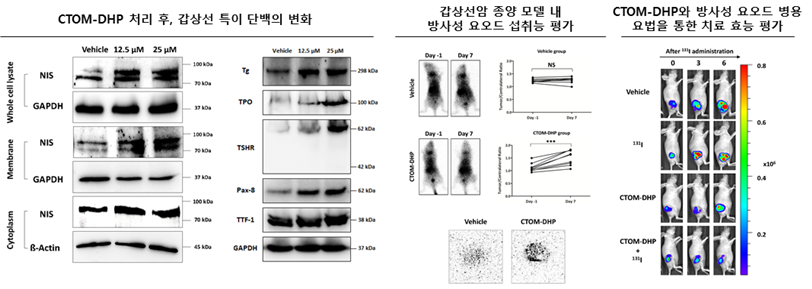
Author informationOh JM1,2, Baek SH1,2, Gangadaran P1,2,3, Hong CM1,2, Rajendran RL1,2,3, Lee HW1,2, Zhu L1,2, Gopal A1,2, Kalimuthu S1,2, Jeong SY1,2, Lee SW1,2, Lee J1,2, Ahn BC1,2,3.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
2
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
3
BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Department of Biomedical Science, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
- 키워드
- anaplastic thyroid cancer; cytotoxicity; radioactive iodine therapy; sodium iodide symporter; tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- 연구소개
- 방사성 요오드 치료에 저항성을 가진 갑상선암은 세포의 탈분화로 인해 요오드를 섭취하는 Sodium iodide symporter (NIS) 등 갑상선 특이 단백의 발현이 감소하여 방사성 요오드 섭취 능력을 소실하게 됩니다. 본 연구팀은 기존에 구축한 NIS 발현 강화 후보약물 스크리닝 시스템을 활용하여 새로운 티로신 키나아제인 CTOM-DHP를 발굴하였습니다. 본 후보 약물을 난치성 탈분화 갑상선암 세포주에 처리 후, NIS를 포함한 갑상선 특이 단백들의 상당히 증가와 이에 의해 세포의 재분화를 유도하여 방사성 요오드 섭취능 증진과 종양 성장 저해 및 사멸 효과를 확인하였습니다. 갑상선암에서 많이 관찰되는 유전자 이상 중 하나인BRAFV600E 돌연변이를 포함하여 KRAS, RET/PTC 재배열 세포주에서도 NIS 발현이 증가되는 유의미한 결과를 확인하였습니다. 현재까지 다양한 표적치료제의 개발이 활발히 진행되고 있지만, 치료 반응이 나타나더라도 내성 등의 부작용으로 인해 그 효과를 장기간 유지하지 어렵다는 단점이 있습니다. 따라서 여러 약물을 이용한 병합 치료 및 세포의 재분화를 통한 치료용 방사성 요오드의 종양 사멸 효과를 유도하는 것도 충분한 상승효과를 거둘 수 있습니다. 본 연구결과는 세포의 탈분화 특성으로 인해 방사성 요오드 치료에 저항성을 가진 갑상선암 내 세포의 재분화와 이를 통한 방사성 요오드 민감성 갑상선암으로 전환할 수 있는 CTOM-DHP 약물의 역할과 효과를 기대할 수 있습니다.
- 덧글달기










편집위원
방사성요오드 불응성 갑상선암은 예후가 불량하며, 이를 극복하기 위해 다양한 갑상선재분화 요법이 시도되고 있다. 해당 연구는 갑상선암의 재분화를 높이는 새로운 tyrosine kinase inhibitor를 선별하고 이를 이용한 갑상선암 재분화 및 방사성요오드 치료를 다시 적용하는 전임상연구이다. 검색된 CTOM-DHP는 MAPK 신호전달 체계를 억제하여 갑상선 특이 단백의 발현을 증가시키고 이차적으로 갑상선암세포내로 방사성요오드 축적을 증가시키는 것을 확인함. 갑상선암 관련 연구자, 방사성요오드 치료 핵의학의사에게 관심을 끌 논문으로 생각됨.
2020-05-28 14:04:34