글로벌 연구동향
핵의학
- 2020년 06월호
[Cells.] Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Promotes Hair Growth.경북의대 / Ramya Lakshmi Rajendran, Prakash Gangadaran, 안병철*
- 출처
- Cells.
- 등재일
- 2020 Apr 1
- 저널이슈번호
- 9(4). pii: E856. doi: 10.3390/cells9040856.
- 내용
Abstract
Hair loss is a common medical problem affecting both males and females. Dermal papilla (DP) cells are the ultimate reservoir of cells with the potential of hair regeneration in hair loss patients. Here, we analyzed the role of macrophage-derived Wnts (3a and 7b) and macrophage extracellular vesicles (MAC-EVs) in promoting hair growth. We studied the proliferation, migration, and expression of growth factors of human-DP cells in the presence or absence of MAC-EVs. Additionally, we tested the effect of MAC-EV treatment on hair growth in a mouse model and human hair follicles. Data from western blot and flow cytometry showed that MAC-EVs were enriched with Wnt3a and Wnt7b, and more than 95% were associated with their membrane. The results suggest that Wnt proteins in MAC-EVs activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways, which leads to activation of transcription factors (Axin2 and Lef1). The MAC-EVs significantly enhanced the proliferation, migration, and levels of hair-inductive markers of DP cells. Additionally, MAC-EVs phosphorylated AKT and increased the levels of the survival protein Bcl-2. The DP cells treated with MAC-EVs showed increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and keratinocyte growth factor (KGF). Treatment of Balb/c mice with MAC-EVs promoted hair follicle (HF) growth in vivo and also increased hair shaft size in a short period in human HFs. Our findings suggest that MAC-EV treatment could be clinically used as a promising novel anagen inducer in the treatment of hair loss.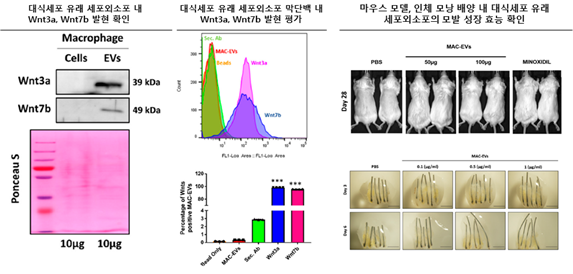
Author informationRajendran RL1,2, Gangadaran P1,2,3, Seo CH4, Kwack MH5, Oh JM1,2,3, Lee HW1,2, Gopal A1,2, Sung YK3,5, Jeong SY1,2, Lee SW1,2, Lee J1,2, Ahn BC1,2,3.
1
Department of Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu-41944, Korea.
2
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu-41944, Korea.
3
BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Department of Biomedical Science, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu-41944, Korea.
4
New Drug Development Center, Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation (DGMIF), Daegu-41061, Korea.
5
Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu-41944, Korea.
- 키워드
- Wnt; dermal papilla; extracellular vesicles; hair follicle; macrophage; β-catenin signaling
- 연구소개
- 탈모는 정상적으로 모발이 존재해야 할 부위에 모발이 없는 상태를 일컬으며, 남녀노소 불문하고 흔히 나타나는 질환입니다. 모유두 세포(Dermal papilla cell)는 모발의 발생과 성장에 있어 중요한 세포로, 이 세포가 기능을 잃으면 탈모가 시작되는 것으로 알려져 있습니다. 본 연구팀은 모발의 성장에 있어 대식세포 유래 세포외소포의 역할과 기능, 신호전달 체계를 증명하였습니다. 대식세포 유래 세포외소포에는 Wnt3a/Wnt7b의 단백질이 증가하였으며, 실험군에서는 대조군에 비해 Akt의 인산화, ß-catenin 및 Bcl-2 발현 증가로 인해 세포 증식, 이동, 모발 성장 유도 인자의 발현이 증가되었습니다. 마우스 모델에서 대식세포 유래 세포외소포는 모발 성장 촉진뿐만 아니라 모공의 수와 진피의 두께가 증가함을 확인하였습니다. 또한 인체 모낭 배양에서 대식세포 유래 세포외소포 처리를 통한 모발 성장 효과를 확인하였습니다. 본 연구결과를 통해 대식세포 유래 세포외소포가 모발 성장에 효과적이며, 탈모 환자 치료를 위한 새로운 치료 전략으로 임상적용 가능성을 시사합니다.
- 덧글달기








편집위원
세포외 소포는 세포에서 유래되는 나노크기의 물질로 유래되는 세포에따라 상이한 특성을 가진다. 해당 연구는 대식세포에서 유래한 세포외 소포가 모발 성장을 증진 시킨다는 것은 확인한 연구임. 대식세포 유래 세포외 소포가 모발 성장 증진에 Wnt/β-catenin 신호전달체계를 통한 것임을 밝힘. 이러한 연구결과는 모발관련 연구자 및 세포유래 물질의 임상적용에 관심이 있는 연구자에게 관심을 끌 논문으로 생각됨.
덧글달기닫기2020-05-28 14:05:06
등록